基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(51578330)
第一作者:杜晓庆(1973-),男,博士,副教授,博士生导师,主要从事结构风工程研究.E-mail: dxq@shu.edu.cn
(1. 上海大学 土木工程系,上海 200444; 2. 上海大学 风工程和气动控制研究中心,上海 200444;3. 上海大学 上海市应用数学和力学研究所,上海 200444)
(1. Department of Civil Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China;2. Wind Engineering and Aerodynamic Flow Control Research Center, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China;3. Shanghai Institute of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, Shan
flow around rectangular cylinder; numerical simulation; aerodynamics; flow structure; separation bubble; secondary vortex
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2019.01.009
矩形截面结构在土木工程中有广泛的应用,其气动性能的流场机理有待进一步澄清.采用k-ω SST湍流模型,对宽厚比B/D=1~4的矩形柱绕流进行了数值模拟研究,得到了矩形柱气动性能随宽厚比的变化情况,给出了不同宽厚比矩形柱的流场结构,探究了流场结构、表面风压和气动力之间的内在关系.研究表明:宽厚比B/D=1和2矩形柱的分离剪切层不会发生再附现象,但在B/D=2矩形柱的近尾流中会形成独特的二次涡,二次涡的出现会延缓旋涡脱落速度,造成Strouhal数降低; B/D=3和4矩形柱的分离剪切层会发生再附,在侧面形成分离泡,并导致尾流宽度变窄和平均阻力系数下降,在矩形柱侧面后角附近会出现负压逐渐减弱的压力恢复区.
Structures with rectangular-section are widely used in the field of civil engineering, whose aerodynamic mechanism needs to be clarified further. The flow field around the rectangular cylinders with aspect ratios of B/D=1~4 is simulated using k-ω SST turbulent models. The effects of the aspect ratio on the aerodynamic characteristics and flow fields are investigated. Three categories of flow structure are proposed for various aspect ratios. The relationship between flow structures, pressure fields and aerodynamic forces are discussed as well. Results show that there is no reattachment of separated shear layers for the cylinders of B/D=1 and 2. However, for B/D=2, the special secondary vortices generated in the near wake of the cylinder, which causes a delay of vortex shedding and a noticeable decrease of Strouhal number. As for B/D=3 and 4, the reattachments of the separated shear layers promote the occurrence of separation bubbles on the side surface of the cylinder, which results in a narrower wake width, a reduction of drag force and a recovery of pressure at the side surface near the trailing edge.
超高层建筑的抗风设计是结构设计中需要重点考虑的因素.由于矩形截面在超高层建筑中经常被采用,二维矩形柱的气动性能和绕流场特性受到广泛关注[1-16].研究表明,在一定的雷诺数下,矩形柱的气动性能和流场结构受截面宽厚比B/D(其中B为顺风向宽度、D为横风向厚度)的控制[1-4].矩形柱的平均阻力系数会在B/D=0.6附近达到峰值[1],Strouhal数(St数)则会在B/D=2.8和B/D=6附近会发生不连续的跳跃现象[1-3].
研究者主要通过风洞试验对矩形柱的气动性能进行研究,对矩形柱绕流场的研究较少.随着计算机性能的提高和计算方法的改进,CFD方法逐渐被用于研究矩形柱绕流问题.YU和KAREEM较早开展了对矩形柱的研究[5-6],现有研究中对B/D=1的方柱[7-8]和B/D=5的矩形柱[9-10]的数值模拟研究相对较多.最近SOHANKAR[11]和YU等[12]采用大涡模拟方法分别对宽厚比为B/D=0.4~4.0和B/D=0.3~7.0的矩形柱进行了较为系统的研究.与雷诺平均法相比,大涡模拟虽然计算精度较高,但其计算量大.SHIMADA和ISHIHARA[13]采用雷诺平均法和修正的k-ε湍流模型研究了宽厚比B/D=0.6~8的矩形柱,其数值模拟结果与试验结果吻合较好.不少研究发现[11-13],矩形柱的St数在B/D=2附近达到最小值,并且B/D=2矩形柱的流场特性也与其他宽厚比矩形柱有明显差异,其确切的机理尚未得到澄清.
本文采用综合了标准k-ε模型和k-ω湍流模型优点的k-ω SST湍流模型,在雷诺数Re=2.2*104时,研究了宽厚比B/D=1~4矩形柱的气动性能和流场特性,探究了流场结构、表面风压和气动力之间的内在关系,基于表面摩擦力系数估算了B/D=3和4的分离泡长度,并重点分析了宽厚比B/D=2矩形柱的瞬态流场特性,澄清其St数较其他宽厚比矩形柱体小的流场机理.
本文采用基于k-ω SST湍流模型的雷诺平均法N-S方程进行模拟.
连续性方程:

其中:ρ, μ为空气的密度和分子的粘性; p为压力; ui, uj(i, j=1, 2, 3)表示速度矢量u在x、y、z方向的分量; u'i,u'j(i, j=1, 2, 3)表示速度矢量u在x、y、z方向的脉动分量; xi, xj(i, j=1, 2, 3)表示x、y、z三个方向的坐标分量.-ρu'iu'j^-为关于湍流脉动值的雷诺应力项,称之为雷诺应力.为了处理雷诺应力项,引入湍动粘度或称涡粘系数,然后把雷诺应力表示成涡粘系数的函数:
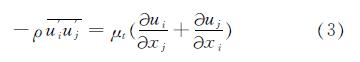
式中:ut=ρCμk2/εμt=ρCμk2/ε为湍流黏性; Cμ为经验常数; k和ε分别为湍动能及耗散率,需要通过求解湍流模型方程来确定.
本文采用综合了标准k-ε模型和k-ω湍流模型的k-ω SST湍流模型.因为标准k-ε模型适合剪切层模拟而k-ω模型适合近壁区模拟,所以k-ω SST湍流模型通过设定一个混合函数,使得 k-ω模型能在边界层内靠近壁面使用,而边界层外则利用k-ε模型求解.
本文采用四种宽厚比的矩形柱体,分别为B/D=1, 2, 3和4.来流为均匀来流,风速为Uo,风攻角为0°,雷诺数为Re=2.2*104(根据矩形柱厚度D和来流风速Uo计算得到).
图1为本文采用的计算域及边界条件.本文计算采用结构化网格,以矩形柱的中心做为半圆域的圆心,半圆域的直径为40D,顺风向计算域的总长为45D,展向长度为B,阻塞率为2.5%.网格在靠近矩形柱体处加密,第一层网格高度为0.001D,近壁面网格增长率为1.08.计算模型局部网格如图2所示.
计算域采用速度入口边界条件,自由出口边界条件,展向采用周期性边界条件,矩形柱表面采用无滑移壁面边界条件.本文采用SIMPLEC算法来求解压力-速度场耦合方程; 速度和压强的离散采用二阶迎风格式; 时间离散方法采用二阶隐式格式.定义矩形柱体的升力系数、阻力系数为
CL=(FL)/(0.5ρU20B); CD=(FD)/(0.5ρU20D).(4)
式中:FL和FD分别为单位长矩形柱的气动升力和气动阻力,ρ为空气密度.
矩形柱表面的风压系数和摩擦力系数分别为
Cp=(p-po)/(0.5ρU20); Cf=(τw)/(0.5ρU02)(5)
式中:p-po为当地风压和远前方上游压力之差,τw为表面粘性切应力.
图3为各种宽厚比矩形柱表面的平均风压系数分布图,图中也列出了文献值[6][13]进行对比,由图可见,本文结果与文献结果的总体变化趋势是相同的,结果吻合较好.
各宽厚比矩形柱的迎风面(a-b)风压相近,但其侧面(b-c)和背风面(c-d)风压有明显差异.宽厚比B/D=1和2时,矩形柱侧面的风压分布比较平稳,侧面负压绝对值随着宽厚比的增大有减小趋势; 而宽厚比B/D=3和4时,侧面的风压分布有较大的变化,靠近前角(b点)的侧面负压较强,而靠近后角(c点)的侧面负压有逐渐减弱的趋势,出现压力恢复区.而矩形柱背风面的负压绝对值则随着宽厚比的增大逐渐减小,风压系数从B/D=1的-1.3逐渐变为B/D=4的-0.5左右.
图4和图5分别为不同宽厚比矩形柱体的平均阻力系数和脉动升力系数,图中也列出了文献中的风洞试验值[1,3,17-18]和数值模拟值[5-6,13,19]进行比较.
由图4可见,本文计算得到的平均阻力系数与文献结果的总体变化趋势是相同的.除了B/D=1的方柱的平均阻力系数稍小于文献结果,这可能是本文采用的湍流模型造成的; 其他宽厚比矩形柱体的平均阻力系数都处在之前文献值的区间范围内.从总体上看,随着宽厚比B/D的增大,矩形柱平均阻力系数有逐步减小的趋势.由于矩形柱的阻力主要是其迎风面和背风面的压差造成的,因而阻力系数的这种变化趋势也可以从图3的表面风压分布看出:随着宽厚比的增大,矩形柱迎风面的风压基本保持不变,而背风面的负压绝对值却逐渐减小.
由图5可见,本文计算得到的脉动升力系数与文献总体变化的趋势是相同的.随着宽厚比的增大,脉动升力系数会迅速下降,其均方根值会从宽厚比B/D=0.6的2.8减小至B/D=4的0.2左右.但从图中也可以看出:对于宽厚比为B/D=2~4的矩形柱,不同研究者得到的脉动升力系数偏差较大,这可能是因为这一宽厚比区间正好是两种不同流态发生突变的范围,因而对于试验和数值模拟的条件比较敏感,特别是来流湍流度和雷诺数.
图6为不同宽厚比矩形柱体的St数(St=fD/Uo,其中f为涡脱频率),图中也列出了文献中的风洞试验值[2-3]和数值模拟值[5-6,13,19].
由图可见,本文计算值随宽厚比的变化趋势与文献结果是一致的和接近的,但数值上总体有偏小的趋势,这可能是k-ω SST湍流模型的局限性造成的.随着宽厚比的增大,St数的变化比较复杂.总体来说,St数在B/D=2.5左右出现最小值,而在B/D=3附近达到最大值,即St数在B/D=2~3之间会发生突变.
图6 不同宽厚比矩形柱体的Strouhal数均风压系数
Fig.6 Strouhal numbers of the rectangular cylinders with different aspect ratios
图7为不同宽厚比矩形柱的时间平均流线图,并基于计算结果绘制了流场结构图.
由图7可见,不同宽厚比矩形柱的侧面和背风面均存在两个尺度较大的回流区,但这两个回流区随着宽厚比的增大会发生显著变化.当B/D=1和2时,分离的剪切层并没有再附到矩形柱的侧面上,侧面和背风面的两个回流区在矩形柱的后角处相互连接,并在侧面后角有一尺度很小、方向相反的回流; B/D=2的背风面回流区的长度和宽度均大于其他工况,这是其St数远低于其他宽厚比矩形柱的原因.当B/D=3和4时,侧面和背风面的两个回流区被后角分隔开,形成两个相互独立的回流区,并且侧面回流区的尺度很大,而背风面的回流区很小; 随着宽厚比从B/D=3增大到4,侧面回流中心会向上游移动,而尾流回流中心则有向下游移动的趋势.
为了进一步定量研究流场结构,图8给出了不同宽厚比矩形柱侧面的平均摩擦力系数分布.从图中可见,矩形柱侧面的摩擦力系数大部分为负值,在靠近后角处有一大小不一的正值区域,但摩擦力系数出现正负交替的原因不同.对于B/D=1和2的矩形柱,摩擦力系数正负交替是由于侧面后角处的小回流区造成的,回流区的长度分别为0.04D和0.05D.对于B/D=3和4的矩形柱,摩擦力系数的正负交替则是因为存在剪切层再附造成的,在侧面回流区的壁面摩擦力为负值,在再附点后侧的摩擦力则为正值; 根据TAFTI和VANKA的定义[20],平均摩擦力系数由负到正的位置即是时间平均的分离流再附点,从平均流线图中也可明显地看到存在分离泡和再附流; 当B/D=3时,再附点到前角分离点的长度(即为分离泡的长度)约为2.90D,而B/D=4时约为3.82D.
正是由于B/D=3和4的矩形柱的侧面存在分离泡,分离泡内的侧面风压强度较强,在后角分
离流再附区出现风压的恢复区; 分离泡的出现还会引起其旋涡脱落强度降低和尾流变窄,这也是其平均阻力系数和脉动升力系数较小、而St数较大的原因.图9为不同宽厚比矩形柱绕流场的典型时刻瞬时涡量图(升力系数达到最大的时刻).从图中可以看出,所有宽厚比的矩形柱都会有旋涡从两侧交替脱落,在下游形成一条交错排列的涡街,但涡街的特性会随着宽厚比发生剧烈变化.B/D=1的尾流宽度最大,这也说明其涡脱强度最强,B/D=3和4的由于存在分离再附现象因而其尾流最窄; B/D=2时尾流中相邻旋涡的间距最长,而B/D=3时的涡间距最短,这也反映出前者的St数最小而后者最大; 此外,B/D=2矩形柱尾流中的上下两侧剪切层的相互作用范围明显长于其他工况,呈现出独特的流场特性,目前尚未有明确的解释.
为了进一步理解B/D=2时独特流场特性的发生机理,图 11给出了4个典型时刻B/D=2矩形柱局部流场的瞬时涡量图、瞬时风压场和瞬时流线图.这4个采样时刻在升力系数时程曲线上的位置见图 10.从图 11可见,在t1和t4时刻,B/D=2的矩形柱上侧面后角有一个逆时针旋转的旋涡; 在t7和 t8时刻,B/D=2的矩形柱下侧面后角有一个顺时针旋转的旋涡.这是因为矩形柱的一侧剪切层在角点分离后,会在背风面回流到矩形柱上,并在另一侧后角的角点处再次分离,随后又再附到另一侧后角,在另一侧后角形成一个小旋涡,旋涡旋转的方向如局部流线图所示,这也解释了图7中宽厚比B/D=2矩形柱的平均流线图侧面后角出现了一个小回流区的原因.从风压场中可以看出,模型的迎风面除了靠近角点处均为正压,模型的侧面和背风面为负压.在后角旋涡的位置,局部的负压会比其它地方明显增大,这是后角旋涡导致的.从图 11b的流线图(第三列)中可见,在t4时刻,矩形柱上侧尾流会形成一个二次涡(见箭头所指处); 同样,在t7时刻(见图 11(d)第三列),下侧尾流中也会形成一二次涡.这些二次涡并非是在矩形柱上脱落的涡形成的.为了研究二次涡的形成过程,图 12进一步在升力时程曲线上选取更多的瞬时时刻(t2~t6)流线来进一步分析,这些瞬时时刻的具体位置见图 10.在t2时刻,下侧尾流中已形成一个即将脱离矩形柱的旋涡,而矩形柱下侧剪切层会沿着背风面回流到上侧面,下侧剪切层回流的方向与上侧的剪切层方向相反(见图 12(a)).在t3时刻,在下侧尾流中的旋涡和上侧剪切层的相互作用下,在上侧尾流中会形成二次涡(见图 12(b)箭头所在处).在t4和t5时刻,二次涡有所发展,并有朝着来流方向运动的趋势.顺时针旋转的二次涡与下侧尾流中逆时针旋转的旋涡会发生相互作用,由于两者的运动方向相反,二次涡的出现会阻止矩形柱下侧尾流旋涡向下游的移动及其脱落过程(见图 12(c)(d)).二次涡在t6时刻消失(见图 12(e)).
从上述分析可知,二次涡的出现会延缓矩形柱尾流涡脱的速度,同时也会使矩形柱尾流中的旋涡被拉长,从而大大增大了旋涡脱落的周期,从而使得St数明显低于其他的矩形柱.
本文采用雷诺平均法和k-ω SST湍流模型,对四种宽厚比的矩形柱体绕流场进行了CFD计算,并对气动力、Strouhal数、压力分布以及流场特性进行了分析,得到下述结论:
(1)计算得到的不同宽厚比矩形柱的表面风压系数、气动力系数和Strouhal数和文献结果吻合较好,说明采用k-ω SST湍流模型可较准确地模拟矩形柱体的绕流问题.
(2)宽厚比B/D=1和2的矩形柱没有分离剪切层再附现象; B/D=3和4的矩形柱会发生分离剪切层的再附现象,并在侧面形成分离泡,分离泡的出现会引起尾流宽度变窄和涡脱强度减弱,并导致平均阻力系数和脉动升力系数的减小.
(3)根据矩形柱侧面的平均摩擦力系数,可以估算B/D=1和2矩形柱侧面后角回流区的宽度分别为0.04D和0.05D; 而B/D=3和4矩形柱的分离泡长度分别为2.90D和3.82D; 随着宽厚比从B/D=3增大到4,分离泡的中心位置会向上游移动.
(4)对于宽厚比B/D=2的矩形柱,其在一侧分离的剪切层会在背风面回流,并在另一侧的后缘角点再次分离,矩形柱一侧的尾流旋涡会与另一侧的剪切层相互作用,在矩形柱后侧形成二次涡,二次涡的出现会抑制脱落旋涡的速度,增大旋涡脱落的周期,从而使得B/D=2的矩形柱的St数明显低于其他宽厚比矩形柱.