基金项目:山西省应用基础研究基金项目(201701D221213); 杨凌职业技术学院科学研究基金项目(A2017036)
第一作者:田园(1986-),女,讲师,硕士研究生,主要从事岩土工程领域的教学与科研工作.E-Mail:1309462032@qq.com
(1.杨凌职业技术学院 水利工程分院,陕西 杨凌 712100; 2.山西省交通科学研究院,山西 太原 030000)
(1. Water Resources Engineering Branch,Yangling Vocational and Technical College, Shaanxi Yangling 712100, China; 2. Shanxi Transportation Research Institute, Taiyuan 030000, China)
tailings sand; consolidation coefficient; time square root method; void ratio; experimental research
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2020.01.013
为了探究尾矿砂固结系数随干密度及压力的变化规律,本文分别对不同粗细颗粒、不同干密度的尾矿砂进行标准固结试验,以时间平方根法求取固结系数,并进行相关分析.试验表明,尾矿砂在固结压缩起始阶段变形最大,有显著的瞬时压缩变形,稍后变形逐渐趋缓; 尾矿砂的固结系数皆随着压力的增加而下降,压力小于200 kPa时,固结系数下降较快,当压力达到200 kPa以后,固结系数下降趋缓.固结系数随着尾矿砂干密度的增大而减小,且粗粒尾矿砂比细粒尾矿砂的固结系数更大.
In order to explore the variation law of tailings sand consolidation coefficient with dry density and pressure, this paper conducts standard consolidation tests on different coarse and fine particles and different dry density tailings sand, and calculates the consolidation coefficient by time square root method. analysis. The test shows that the tailings sand has the largest deformation at the initial stage of consolidation and compression, and there is significant transient compression deformation, and the deformation gradually slows down later; the consolidation coefficient of the tailings sand decreases with the increase of pressure, and the pressure is less than 200 kPa. The knot coefficient decreases rapidly. When the pressure reaches 200 kPa, the consolidation coefficient decreases. The consolidation coefficient decreases with the increase of dry density of tailings sand, and the consolidation coefficient of coarse tailings sand is larger than that of fine tailings.
土的压缩是一个时间的函数,通常把土在外荷载作用下,压缩量随着时间增长的过程称为固结.由Terzaghi一维固结理论可知,固结度与时间因素Tv有关.固结系数Cv在工程中意义重大,它反映整个土层的平均固结度以及整个土层的沉降过程,Cv越大,土层的固结速度越快[1].对于尾矿坝而言,由于筑坝时间较长,各填筑材料的沉积时间相差较大,不同部位的密实度、固结度、应力场等变化较大,其固结程度也不同,因此研究尾矿坝的固结特性十分有必要.张慧颖[2]等通过对不同干密度、不同饱和度的非饱和磷矿尾矿砂试样进行压缩试验和分层固结试验,获得了磷矿尾矿砂的压缩系数和分层固结特性.保华富[3]等通过对铅锌矿尾矿砂的试验得出了尾矿砂在不同固结压力、不同孔隙比下的渗透系数及破坏比降.刘庭发[4]等通对西北某在建铜矿进行一系列试验,得到了尾矿砂的比重、固结系数、强度、渗透系数等物理力学指标.袁明月[5]等通过对淤泥制土进行一维固结试验,得到孔隙比与固结压力、固结时间的变化曲线.张引科[6]等通过数值计算,研究出饱和土在三维固结过程中孔隙水压力在空间的分布情况以及随时间的变化规律.在以往的尾矿坝稳定性分析中,一般假定固结系数为常数,而实际工程中,由于尾矿坝的固结系数随着渗透系数、孔隙比的变化而发生着变化,而固结系数随时间的改变影响着坝体的压缩沉降值,因此,研究尾矿砂固结系数的变化特性显得尤为重要,也更符合实际工程的需求.
为了分析尾矿坝的安全稳定性,必须合理的测出尾矿砂的固结系数.根据前人的研究,确定固结系数的方法主要分四大类:第一类为室内固结试验法; 第二类是间接推算法; 第三类采用反演分析计算法; 第四类是现场试验法[1].室内试验确定固结系数的方法以时间平方根法[7]、时间对数法[8]、反弯点法[9]、t60法[10]、速率法[11]、三点法[12]、两点法[13]等为代表.这些方法都是基于Terzaghi固结理论得出的,而通过室内试验确定固结系数还是目前应用最多的方法.
试验所采用的尾矿砂采自陕西省柞水县某铁矿尾矿坝,在出灰口取尾矿砂试样并运回实验室.为了研究尾矿砂固结系数随干密度的变化规律,分别将初始含水量为8.5%尾粉砂配制成干密度为1.55 g/cm3、1.65 g/cm3、1.75 g/cm3的粗粒样,初始含水量为13%尾粉土配制成干密度为1.55 g/cm3、1.65 g/cm3、1.75 g/cm3的细粒样作为试样进行试验.
为了精确地测出尾矿砂的固结系数,我们采用标准固结压缩试验方案并采用时间平方根法图解求出固结系数.试验在GJZ-3中压固结仪上进行,将试样置于单向固结仪内,按照荷载等级50 kPa、100 kPa、200 kPa、400 kPa、800 kPa分级施加竖向压力,在完全侧限条件下用百分表测定试样的压缩变形.试样在每级压力荷载下的固结稳定时间为24 h.根据每级荷载作用下的试样的压缩变形,得出尾矿砂的压缩特性相关参数.
试验时,将量表读数分别按以下时间点读取:0 s、15 s、60 s、90 s、135 s、180 s、240 s、375 s、540 s、735 s、960 s、1 215 s、1 500 s、1 815 s、2 160 s、2 535 s、1 h、23 h、24h.且每组试验同时进行2组平行试验,并按相关规定进行数据处理.按照GB/T 50123-1999 《土工试验方法标准》[14]的要求,以量表读数为纵轴,时间平方根t1/2为横轴,分别画出不同干密度的粗粒尾矿砂及细粒尾矿砂在压力为50 kPa、100 kPa、200 kPa、400 kPa、800 kPa下的测微表读数与时间平方根t1/2的关系曲线[1],如图1所示.
图1 不同干密度尾矿砂的d~t1/2曲线
Fig.1 Different dry density tailings ofd~t1/2curve
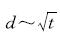
曲线整体随着压力的增大而下降.曲线的压缩变形过程可划分为三个阶段:起始阶段曲线的斜率较大,试样的压缩变形增长迅速,中间阶段压缩变形增长趋势逐渐放缓,末尾阶段压缩变形增长缓慢且趋于线性,这说明尾矿砂在固结变形的初始阶段有显著的瞬时压缩变形.对比图1(a)~图1(f)可知,对于相同干密度不同粗细程度的尾矿砂,粗粒样的测微表读数比细粒样的测微表读数更大,这是因为细粒样更为密实的缘故,且表现出随着干密度的逐渐增大,两者之间的差值越不明显.这是因为随着干密度的增大,尾矿砂更为密实,其可变形的空间更小,其颗粒粗细程度对变形的影响越小.对比相同粗细程度不同干密度的图1(a)、图1(c)、图1(b)、以及图1(e)、图1(d)、图1(f)可知,干密度大的尾矿砂比干密度小的尾矿砂测微表读数d值更小,这是因为干密度大的尾矿砂更加密实,其颗粒位移空间更小.
根据GB/T 50123-1999《土工试验方法标准》[14]要求,按照时间平方根法图解求出各尾矿砂的固结系数值如表1所示.
由以上分析可以看出:
(1)尾矿砂的固结系数皆随着压力的增大而减小.这是由于随着压力的不断增加,尾矿砂受压而变得越来越密实,尾矿砂中原有的排泄流体通道被淤塞填充,导致尾矿砂中排水排气不顺畅,因此固结系数随着压力的增加而下降.当压力达到200 kPa以后,固结系数趋于稳定.如干密度为1.75 g/cm3的粗粒样,当p从50 kPa增加至100 kPa时,Cv从1.50×10-4 cm2/s减小至1.17×10-4 cm2/s,下降较多; 当p从100 kPa增加至200 kPa时,Cv从1.17×10-4 cm2/s减小至6.90×10-5 cm2/s,下降了一个数量级; 当p >200 kPa之后,Cv略有下降.
图2 粗粒尾矿各干密度Cv 变化曲线
Fig.2 Curve of dry densityCv of coarse tailings
图3 细粒尾矿各干密度Cv 变化曲线
Fig.3 Curve of dry densityCv of fine tailings
(2)对于承受同样压力的尾矿砂,固结系数随着干密度的增大而减小.这主要是因为,当尾矿砂干密度较小时,试样中孔隙较多,联通孔隙的通道大多被气体所填充.尾矿砂受压时,由于气体的压缩性大,因而固结系数较大; 尾矿砂干密度大时,尾矿砂更加密实,因而固结系数较小.
(3)由图4 ~图6可知,对于同一干密度不同粗细程度的尾矿砂, 粗粒尾矿砂的Cv曲线均位于图像上方,细粒尾矿砂的Cv 曲线均位于图像下方,这说粗粒尾矿砂比细粒尾矿砂的固结系数更大.这主要是因为,粗粒尾矿砂的变形模量较大,在压力作用下应力重分布的时间短; 而细粒尾矿砂在压力作用下应力重分布的时间长.
图4 γd=1.55时粗、细尾矿砂Cv曲线
Fig.4 Cvcurve of coarse and fine tailings sand when γd=1.55
图5 γd=1.65时粗、细尾矿砂Cv 曲线
Fig.5 Cv curve of coarse and fine tailingssand whenγd=1.65
图6 γd=1.75时粗、细尾矿砂Cv 曲线
Fig.6 Cvcurve of coarse and fine tailings sand when γd=1.75
对不同尾矿砂固结压力作用下Cv-e的关系曲线进行分析,如图7所示:
图7 固结压力作用下不同尾矿砂Cv-e关系曲线
Fig.7 Cv-e relationship curve of different tailings sand under consolidation pressure
(1)尾矿砂在固结变形的初始阶段有显著的瞬时压缩变形,随后变化缓慢.
(2)尾矿砂的固结系数变化的分界点出现在200 kPa左右,当压力小于200 kPa时,固结系数下降较快,当压力达到200 kPa以后,固结系数下降趋缓.
(3)固结系数随着尾矿砂干密度的增大而减小,且粗粒尾矿砂比细粒尾矿砂的固结系数更大.由此可知,以往分析中将固结系数设定为常数与实际情况差别较大,按照经验拟合公式计算的固结系数更准确,也更符合实际工程的需求.