基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51308218)
第一作者:林康强(1989-)男,博士,讲师,主要研究方向为数字建筑、参数化建筑等.E-mail:Linkangqiang577@163.com 通信作者:林育松(1990-)男,硕士,高级审计师,主要研究方向为金融统计学和数理统计学.E-mail:sendlys@126.com
(1.广州美术学院 建筑艺术设计学院,广东 广州 510006; 2.香港中文大学(深圳)深圳高等金融研究院,广东 深圳 518000)
(1.School of Architecture and Applied Art, Guangzhou Academy of Fine Arts, Guangzhou 510006, China; 2.Shenzhen Finance Institute,The Chinese University of Hong Kong(Shenzhen),Shenzhen 518000, China)
building energy saving; climate data; data cleaning; adaptive clustering; BP neural network
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2021.02.017
建筑节能是绿色建筑的三大要素之一,也是当前建筑领域的研究热点,在设计初期对建筑能耗进行动态模拟分析,是实现建筑节能的关键.研究表明采暖能耗和空调能耗在建筑能耗中占据很大比重,而气候变化是影响采暖和空调使用的主要因素[1],因此对建筑气候数据进行分析,对精确构建建筑能耗模型具有重要意义.然而由于历史原因,我国早期气象台站气候测量仪器较为老旧,同时采取人工纸记的方式获得的气候数据存在主观性强、误差大、精度低等问题,为使有限且宝贵的历史气候数据在能耗模拟和气候研究等领域发挥更大作用,首先需要对其进行清洗,以提升数据的正确性、完整性和实效性[2].
数据清洗是采用某种方法对数据进行分析,发现其中的错误、冗余、不确定或不一致等“脏数据”并对其进行解析、增强或归并[3].文献[4]针对数据集中存在的丢失值、错误值和冲突值等问题进行研究,提出一种基于网络模式的数据清洗方法,利用文本之间依赖关系挖掘数据中的隐含信息,从而达到数据清洗的目的,基于网络文本数据的实验验证了所提方法的有效性; 文献[5]针对数据集中的重复冗余问题,利用N-Grams算法对每个数据计算属性键值,并生成哈希表和哈希值,最后利用哈希值对数据之间的相似程度进行量化和判断; 文献[6]针对存在计算流体力学关系的堤防工程数据集的清洗问题,定义了一种数据之间的函数依赖关系指标,并以该指标为基础实现了对数据的清洗; 聚类算法作为一种无监督学习算法,能够自动将相似或相同的数据聚合到同一类中,由于原理简单、容易实现等优点被广泛应用于数据清洗领域:文献[7]在基于密度聚类算法基础上,提出一种空间成群聚类算法,通过对每个数据点的邻域进行区域查询将数据点划分至距离最近的簇中实现对数据的聚类清洗; 文献[8]针对建筑节能气候的数据清洗问题,利用最小二乘法对K-MEANS算法进行改进,提升K-MEANS算法的离群点处理能力,获得了93.6%的有效清洗率.
本文在上述研究的基础上,针对建筑节能气候数据存在的异常数据检测和修正,缺失数据填充等问题,提出一种基于模糊气候聚类和改进BP神经网络的数据清洗方法,首先利用K-MEANS算法对气候数据进行自适应聚类,根据相似性将数据集划分为不同模糊气候子类,针对K-MEANS算法初始聚类中心和类别数设置困难问题,利用主分量分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)方法自动获得K个正交主分量作为初始聚类中心; 然后对每种模糊气候子类数据分别构建BP神经网络模型,建立不同气候之间的关联关系,针对BP神经网络初值选取困难问题,利用遗传模拟退火(Genetic Simulated Annealing,GSA)算法进行优化,最后根据网络输出值与真实值之间的差异实现异常检测和数据校正,并利用网络输出值对缺失值进行填充,最终完成数据清洗.
K-MEANS算法是当前应用最广的一种基于划分的聚类方法,由于理论简单、计算效率高等优势被大量应用于数据挖掘和模式识别等领域[9].本文采用K-MEANS算法对建筑气候数据进行聚类,根据数据之间的相似程度将其划分为不同子类,对每个子类分别进行清洗,K-MEANS算法步骤可以总结为[10]:
Step 1:设置聚类个数K,并从数据集{xl}Nl=1中随机选取K个样本作为初始聚类中心u1,u2,…,uK;
Step 2:计算数据集中剩余样本与每个聚类中心的欧式距离,并将其划分至距离最近的类别中,欧式距离的定义如式(1)所示;
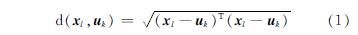
Step 3:根据式(2)计算得到新的K个聚类中心,其中nk为第k个子类中的样本数;
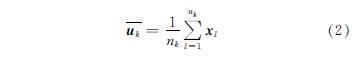
Step 4:按K个新聚类中心对样本集进行重新划分,若连续两次得到的划分结果一致,则算法收敛,否则重复Step 2~ Step 3.
K-MEANS算法聚类个数和初始聚类中心的选取对最终聚类结果影响较大,如果选取不当,会导致算法迭代复杂度增加,聚类性能下降等问题.PCA是一种经典的数据分析方法,通过对隐含在数据中的相关性进行分析,按相关性大小将数据划分为不同的簇,将每个簇内的信息合并成一个主分量的同时保证不同簇之间的信息尽量不相关,即PCA能够自动从数据提取K个主分量,这K个主分量相互正交并且包含了数据中的绝大部分有用信息[11].
对于给定数据集{xl}Nl=1,其协方差矩阵可以表示为
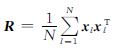
对其进行特征值分解可以得到
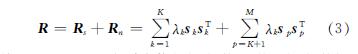
其中:Rs和Rn分别为信号协方差和噪声协方差矩阵; sk为信号对应的主分量; sp为噪声对应的次分量; λk为特征值且λ1≥λ2≥…≥λK>λK+1≈λK+2≈…λM.PCA通常选择占总能量90%的特征值个数为主分量个数K,即
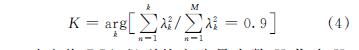
本文将PCA得到的主分量个数K作为K-MEANS算法聚类个数,同时将K个主分量sk作为K-MEANS的初始聚类中心.
典型的BP神经网络模型由输入层,隐含层和输出层构成,相邻两层神经元节点之间通过权值实现全连接,同一层内部的神经元节点之间不连接.网络的学习过程包含由输入层通过权值映射到隐含层并产生网络输出值的正向传播过程,以及输出层误差由隐含层向输入层映射的反向传播过程.通过正向传播和反向传播相对迭代的学习过程,不断对网络权值进行优化,使输出值最终逼近于预期值[12].
对于具有n个输入神经元的BP神经网络模型,设第i个输入样本为xi,i=1,…,n,则由输入层到隐含层的映射关系可以表示为

其中:wij为输入神经元和隐层神经元之间的连接权值; θ为阈值; f(·)为Sigmoid激活函数.
由隐含层到输出层的传播过程可以表示为
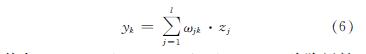
其中:ωjk,j=1,…,l,k=1,…; m为隐层神经元与输出神经元之间的连接权值.假设网络预期输出值为y*k,则其与输出值之间的误差可以表示为

BP神经网络的反向传播过程就是利用梯度下降法按照δ减小的方向对权值{wij,ωjk}和阈值θ进行优化的过程.
由于BP神经网络采用梯度下降法求解,因此权值和阈值初值的选取会对结果产生较大影响,初值选取不当会导致算法收敛于局部最优值[13],因此需要一种全局优化算法对BP神经网络权值和阀值的初值进行优化,以保证模型最终能够收敛于全局最优解.
本文将遗传模拟退火(Genetic Simulated Annealing,GSA)算法与BP神经网络结合,利用GSA的全局寻优能力优化BP神经网络.GSA算法包含遗传算法(Genetic-Algorithm,GA)[14]和模拟退火(Simulated-Annealing,SA)[15]算法2部分内容,综合了GA全局搜索能力强和SA局部搜索能力强的特点.GSA算法首先利用GA在全参数空间内对BP网络权值和阀值进行寻优,得到当前状态下的最优解后,将其作为SA的初值,利用SA在初值附近进行局部搜索,获得满足Metropolis要求的新解,再将该新解作为下一轮迭代中GA的初始种群,通过多次全局搜索和局部搜索的交替迭代,最终获得全局最优解,并将其作为BP网络的初值.所提GAS对BP神经网络进行优化的步骤如表1所示:
典型的气候数据包括气压,温度,湿度,风向,风速,总云量,地表辐射强度,直接辐射强度,红外辐射强度等多个维度,各个维度之间彼此相互关联,相互作用,呈现出复杂的非线性关系,因此数据清洗前,需要对数据之间各个维度的关联关系进行挖掘与表征.BP神经网络作为当前理论最为成熟,应用最为广泛的一种神经网络模型,具备任意非线性函数描述能力,因此适合于对气候数据进行建模与分析.但是建筑气候数据具有高维、大数据量的特点,若直接利用BP神经网络进行建模时会出现模型复杂度高、网络训练时间长、运算量大等问题,因此本文将K-MEANS聚类算法与BP神经网络结果,首先利用K-MEANS对数据进行分析,将高相似度的数据聚集到同一模糊气候子类中,并使不同子类之间的差异尽量大,然后利用利用BP神经网络模型对每一模糊气候子类建模,降低模型复杂度.
图1给出了所提数据清洗算法的流程图,可以看出整个算法包含训练和测试两个阶段,其中训练阶段的具体实现可以总结为:
Step1:提取建筑气候数据典型指标(如气压,温度,湿度等)构成特征数据矩阵;
Step2:利用PCA对其进行分析得到大特征值个数K;
Step3:将Step2得到的K作为K-MEANS算法的聚类个数,然后利用K-MEANS算法对特征数据进行自适应聚类,根据相似性将数据集划分为K个子类;
Step4:根据表1所示步骤,对每个了类分别构建GSA-BP神经网络模型,得到K个网络用于对测试样本进行分析.
在测试阶段,对于给定的待清洗测试数据,利用所提方法对其进行清洗的具体实现步骤可以总结为:
Step1:子类划分,计算待清洗数据到训练阶段获得的每个子类之间的欧式距离,并将其划分至距离最小的子类中;
Step2:利用对应子类已训练好的GSA-BP网络模型对数据进行分析预测;
Step3:根据预测结果,按以下准则完成数据清洗:
(1)异常数据检测和修正:当测试点与左右相邻点的均值差异超过30%,且与网络输出点的差异超过30%时,判定该样本为异常数据,利用网络输出值和左右相邻点的均值对其进行修正;
(2)缺失数据填充:利用网络输出值对缺失数据进行填充.
为了验证所提模糊气候聚类和GSA-BP神经网络方法的数据清洗效果,采用Sandia生成的国内某城市典型年14时的气候数据(含气压,温度,湿度,风向,风速,总云量,地表辐射强度,直接辐射强度,红外辐射强度共9个维度)作为训练数据集(共400组数据),从国家气象局网站读取该城市2000年真实年14时的气候数据作为测试数据(误差精度为2,共365组)开展试验.实验采用Matlab-R2016b软件平台,运行环境为Windows-10操作系统,Inter-Core-I7处理器,3.4 GHz主频,16 GHz内存的ThinkPad便携式计算机.
根据图1所示流程,首先利用PCA对训练数据集进行分析得到大特征值个数K,图2给出了计算得到的归一化特征值谱图,可以看出前4个特征值要远远大于剩余5个特征值,根据式(4)可以计算得到K=4.进而利用 K-MEANS算法对训练数据进行聚类得到的聚类结果如图3所示,由于聚类结果的高维分布(9维空间)情况难以直观观测,图3给出了将9维空间投影到温度和湿度,温度和气压,气压和湿度3种二维平面中,可以看出所提方法能够根据数据之间的相似程度对其进行合理分配,投影到二维平面后仍具有较好的聚类效果,能够自动将相似程度高的数据聚集为同1个子集中,子集内的数据聚集性较好,不同子集间区别性较为明显.
在完成聚类后,根据图1所示流程对4个子类数据分别构建如图4所示BP神经网络模型,输入层节点数为9个气候数据指标,隐层节点数根据文献[8]所提方法设置为5,输出层节点数可以设置1,即对每个气候指标分别清洗,也可以设置为多个,即对多个气候指标一起完成清洗,但会增加运算时间,并且精度出现一定程度下降,因此本文设置输出节点为1,对每个指标分别进行清洗,即本文所用网络结构为9-5-1.试验中GSA算法的初始种群设置为BP网络初始参数集合C=[ω,w,θ],试验中设置参数空间上下限分别为Cmax=[100,100,10]和Cmin=[0.1,0.1,0.01],利用GSA算法最终得到的最优参数完成BP神经网络的训练.
图5中虚线给出了随机选取初值构建BP神经网络在算法迭代过程中反馈误差随迭代次数变化曲线,实线为将GSA获得的最优初值赋予BP神经网络进行迭代时反馈误差随迭代次数的变化曲线,可以看出,GSA-BP模型收敛时的反馈误差更小,收敛速度更快.图5所示结果验证了算法改进的有效性.
图5 不同初值选取方法反馈误差变化曲线
Fig.5 Feedback error variation curve of different initial value selection methods
图6(a)~(i)分别给出了针对测试数据气压,温度,湿度,风向,风速,总云量,地表辐射强度,直接辐射强度,红外辐射强度9个维度进行清洗得到的结果与真实值之间的残差变化曲线,为了对比,图6中给出了采用文献[8]所示方法在相同条件下对测试数据进行清洗得到的结果.从图6可以看出,对于上述9个维度的数据清洗结果,所提方法相对于文献[8]方法的网络输出值与真实值较为接近,残差较小,表明所提方法数据清洗性能更优.同时温度,湿度和总云量3个维度预测结果出现了少数误差较大点,对其进行分析可知其与左右两侧值之间的差距较大,且明显与实际气候情况不符,采用所提方法修正后数据曲线更加平滑,与实际情况接近.表2给出了所提方法和文献[8]方法数据清洗结果的均方误差和有效清洗效率指标,可以看出,对于本文所用试验数据,所提方法可以获得更高的清洗效率和更小的均方误差,即数据清洗性能更优.
在实际工程应用中,受限于训练数据集的获取手段匮乏,有时难以获得足够的训练数据以保证模型得到充足的学习,因此小样本情况下的数据清洗能力也是评估一种方法性能的重要考量指标.在本节内容中,我们分别将训练数据容量减少为总量的20%,40%,60%和80%,分别对所提方法和文献[8]方法的数据清洗性能进行评估,图7给出了2种方法的有效清洗率随着训练样本数的变化曲线,可以看出,随着训练样本数的减少,2种方法的数据清洗性能都出现了不同程度的下降,但是所提方法的性能均优于文献[8]方法,在训练样本数减少至40%时,所提方法仍能获得优于90%的有效清洗率.
在实际工程实践中,数据清洗模型对不同测试数据的泛化能力是评估算法性能的一项重要指标.如果一种数据清洗模型在完成训练后,对不同的测试数据均能取得较好的清洗效果,则认为该模型具有较强的泛化能力.
在前述试验的基础上,采取每次从国家气象局网站随机读取该城市2000年~2008年真实年14时的气候数据构建测试数据集的方式对所提方法的数据清洗性能进行验证,每组测试数据集包含256组数据,重复进行10次随机抽取试验,并对结果求平均.表3给出了所提方法和文献[8]方法数据清洗结果的均方误差和有效清洗效率指标,可以看出在测试数据集发生变化时,所提方法的性能依然优于文献[8]方法.同时将结果与表2进行对比可知,在面对不同测试集时,所提方法的数据清洗性能与单一数据集的数据清洗性能非常接近,验证了所提方法的泛化能力.
(1)提出一种基于PCA联合K-MEANS的模糊聚类算法,利用PCA获得的主分量作为K-MEANS的初始聚类中心,提升算法的噪声稳健性以及小样本情况下的适应能力;
(2)提出一种GSA优化BP神经网络模型,利用GSA的全局寻优能力对BP神经网络进行优化,确保其收敛于全局最优解,提升模型性能;
(3)提出一种基于模糊聚类和GSA-BP模型的数据清洗算法,利用GSA-BP神经网络的任意非线性函数逼近能力对复杂气候数据之间关系进行建模,同时针对神经网络网络训练时间长和运算量大的问题,利用模糊聚类算法将数据集划分为不同子类,降低模型复杂度;
(4)基于实际数据开展试验,结果表明所提方法能够获得优于94%的有效清洗率,并且在小样本情况下仍然具备较高的稳健性,以及对不同测试数据集的泛化能力,适合实际工程应用.