基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(52078408); 陕西省杰出青年基金项目(2020JC-43)
第一作者:韩娅(1996-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:可再生能源利用与建筑节能技术. E-mail:1028868444@qq.com
通信作者:王登甲(1984-),男,博士,教授,主要从事建筑节能与太阳能供暖空调技术研究. E-mail:wangdengjia@xauat.edu.cn
(1.西安建筑科技大学 建筑设备科学与工程学院,陕西 西安 710055; 2.西安建筑科技大学 西部绿色建筑国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710055; 3.西安建筑科技大学 管理学院,陕西 西安 710055; 4.中国建筑科学研究院有限公司,北京 100013)
(1.School of Building Services Science and Engineering,Xi'an Univ. of Arch. & Tech.,Xi'an 710055,China; 2.State Key Laboratory of Green Building in Western China,Xi'an Univ. of Arch. & Tech.,Xi'an 710055,China; 3.School of Management,Xi'an Univ. of Arch. & Tech.,Xi'an 710055,China; 4.China Academy of Building Research,Beijing 100013,China)
altitude; solar energy; flat plate collector; heat loss; correction
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2021.05.021
为减少常规能源消耗,越来越多的建筑使用可再生能源进行供热采暖[1-2].而我国西部高原地区太阳能资源丰富,为利用太阳能进行供热采暖提供了充足的条件.平板集热器是使用较为广泛的太阳能集热装置,在太阳能供热采暖工程设计中,平板集热器全年平均集热效率根据经验值取0.25~0.50[3].而在实际情况下,不同海拔地区气压不同,空气物性参数、大气透明度等发生改变,进而影响平板集热器的对流和辐射热损失,导致不同地区集热效率差异较大,经验取值难以较好指导工程设计,而集热效率究竟如何变化则需根据不同海拔地区的环境条件具体确定.
现有关于平板集热器的研究多集中在结构优化和热性能研究方面.针对结构参数,Wang等人[4]对平板集热器的排管间距和翅片厚度进行了优化分析; Maatouk等人[5]通过模拟计算,分析了盖板厚度对平板集热器集热效率的影响.针对运行参数,Cristofari等人[6]通过有限差分模型法对一种使用共聚物性材料的平板集热器进行分析,研究了其在低流量条件下,工质流速、水槽层数等对于热性能的影响; 王岳人等[7]以沈阳一栋采用太阳能和化石能源进行联合供暖的住宅建筑中供暖系统使用的平板集热器为研究对象,建立了热性能分析的理论计算模型,改变集热工质的入口流量和温度,分析了其对集热效率的影响.
除了结构参数和运行参数等自身因素外,平板集热器的热性能还受到外界环境因素的影响[8].平板集热器的热损失包括对流和辐射热损失两部分,已有学者研究了气压对对流换热的影响,如胡松涛等[9]采用高原模拟舱模拟低气压环境,对比电加热器在常压和低压下的对流换热系数,得出表面对流换热系数随气压降低而减小的结论; 刘叶弟等[10]由理论推导发现唐古拉山垭口处竖平壁的自然对流换热系数约为海平面的73%; 海拔高度的变化也对长波辐射换热产生影响,周允华等[11]指出高原地区空气稀薄,大气逆辐射比平原低很多,在计算长波辐射热量时,常用的天空有效温度经验公式不适用于高原,其估算值偏高.
大量研究表明,不同海拔高度下环境因素通过影响对流和辐射换热过程进而影响平板集热器热性能.尽管目前已有分别针对海拔对对流换热及辐射换热的影响机理而进行的研究,但海拔对平板集热器热性能产生的综合影响尚未明确.鉴于此,该研究将海拔对对流及辐射换热的影响规律与平板集热器传热过程相结合,对现有平板集热器的热损失进行修正,得到实际情况下平板集热器热损失随海拔变化的规律,以便于为太阳能供热采暖系统的精准设计提供参考.
平板集热器主要由盖板、夹层空气、吸热板、侧板和背板构成,图1为平板集热器主要构成及传热过程示意图.平板集热器接受的太阳辐射,一部分被盖板吸收,另一部分透过盖板到达吸热板,吸热板将吸收的太阳能转化为热能,其中大部分热能通过集热管传递给集热工质,被集热工质带走的热量称为有用能.在热量传递的过程中,一部分热量以对流和辐射换热方式由吸热板传递给盖板,一部分热量通过侧面和背面保温层的导热分别传递给侧板及背板,最终,盖板、侧板及背板以对流和辐射方式向环境散失热量,通过位于侧板上的呼吸孔进出的空气也以对流方式带走一部分热量.
图1 平板集热器主要构成及传热过程示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of main components and heat transfer process of flat plate collector
同平原地区相比,高原地区的环境条件特殊,对平板集热器的影响体现出以下两个特点:
(1)高原地区的气压较低,根据已有研究[12],气压降低使得空气密度减小,进而导致对流换热系数减小,使得平板集热器的对流热损失受到影响.
(2)高原地区空气较为稀薄、大气透明度较高,相比于平原地区,大气逆辐射减弱,物体向天空以长波辐射散失的热量显著增多,将平板集热器应用于高原时,其长波辐射散热量所占比例变化.
因此,海拔变化造成的空气密度及大气透明度的改变将对平板集热器的对流及辐射热损失产生影响,其总热损失如何变化需通过理论分析进一步确定.
为了研究平板集热器热损失的影响因素,通过以下假设,对平板集热器的传热过程进行了简化:
(1)平板集热器的盖板、吸热板、侧板和背板可看作集总系统;
(2)平板集热器集管和排管的管壁温度与吸热板温度相同;
(3)在平板集热器的对流换热过程中,夹层内空气和环境空气均视为理想气体.
基于平板集热器的传热过程分析,建立了平板集热器传热过程热网络,如图2所示,图中各符号的含义见第1.2.1和1.2.2节计算过程.
(1)平板集热器热损失
图3为平板集热器热损失组成及其环境影响因素.由该图可知,平板集热器通过盖板、侧板和背板三部分以对流和辐射换热的方式与环境进行热交换,从而形成各部分热损失.
① 平板集热器对流热损失
平板集热器表面同环境间的对流换热量可由公式(1)~(2)计算得到
qci=hciAiΔti,(i=1,2,3) (1)
hci=Nuλ/L,(i=1,2,3) (2)
平板集热器外表面的对流换热为风引起的受迫对流,临界雷诺数取5×105,Nu数可由公式(3)~(6)计算得到[13].其中,气压仅通过改变流体密度对对流换热系数产生影响[12],而不同气压条件下的流体密度可通过理想气体状态方程计算得到.
层流: Nu=0.664Re1/2Pr1/3 (3)
湍流:Nu=0.037Re4/5Pr1/3 (4)
其中,Re=ρuL/μ, (5)
Pr=μcp/λ. (6)
式中:qci(i=1,2,3)为盖板、侧板及背板向环境的对流热损失,W; hci(i=1,2,3)为盖板、侧板及背板同环境的对流换热系数,W/(m2·K); Ai(i=1,2,3)为盖板、侧板和背板面积,m2; Δti(i=1,2,3)为盖板、侧板及背板与环境空气的温差,℃; λ为空气导热系数,W/(m·K); L为特征长度,m; ρ为空气密度,kg/m3; u为风速,m/s; μ为空气的动力粘度,Pa·s; cp为空气的定压比热容,J/(kg·K).
通过呼吸孔进出的空气带走的热量可由下式计算.
qc6=macp,a(tai-ta) (7)
式中:tai为夹层内空气温度,℃; ma为通过呼吸孔进入的空气的质量流量,kg/s; ta为环境温度,℃.
② 平板集热器辐射热损失
平板集热器的辐射热损失包括各表面以长波辐射形式向天空及地面散失的热量[14],可由公式(8)~(10)计算得到
qri=hriAiΔti,(i=1,2,3) (8)
对于任意倾斜表面,其同天空和地面的辐射换热系数可由公式(9)和(10)计算得到[15]

式中:qri(i=1,2,3)为盖板、侧板及背板向环境的辐射热损失,W; hrsi(i=1,2,3)、hrgi(i=1,2,3)为盖板、侧板及背板向天空、地面的辐射换热系数,W/(m2·K); εi(i=1,2,3)为盖板、侧板及背板发射率; σ为斯蒂芬-玻尔兹曼常数; Tc、Tg、Ts为分别为盖板、地表及天空温度,K; β为集热器倾角.
海拔变化时仅对公式(9)和(10)中的温度值产生影响,因此上述公式适用于不同海拔高度的长波辐射热损失计算.天空有效温度可由下式计算得到[11]
Ts=Ta[(0.649+0.313lgP/(P0)+0.127lge)×(1.24-0.24S)]1/4 (11)
式中:P、P0为分别为当地及海平面的气压,Pa; e为水汽压,mbar; S为日照百分率.
为了便于对不同海拔下的热损失进行对比分析,提出基于平板集热器的采光面积,以集热工质进口温度为基准的热损失系数:
h=(q)/(A(tfi-ta)) (12)
式中:A为平板集热器采光面积,m2; tfi为集热工质进口温度,℃; q为平板集热器的热损失,W; h为热损失系数,W/(m2·K).
(2)太阳能集热量
盖板及吸热板吸收的太阳能可由下式计算.
qs1=αcA1qs (13)
qs2=(ατ)eApqs (14)
式中:qs1、qs2为分别为盖板和吸热板吸收的太阳能,W; αc为盖板吸收率; (ɑτ)e为有效透射率-吸收率乘积; Ap为吸热板面积,m2; qs为太阳辐照度,W/m2.
(3) 平板集热器内部传热量
① 吸热板与盖板间传热
吸热板同盖板间的辐射换热量为
qr4=hr4A1(tp-tc) (15)
式中:qr4为吸热板和盖板的辐射换热量,W; Tp为吸热板温度,K; εp为吸热板发射率.
其中,hr4可由下式计算得到[16]:

吸热板同盖板间的对流换热为平行平板间的对流换热,对流换热量可由公式(17)~(20)计算.
qci=hciApΔti,(t=4,5) (17)
其中,hci(i=4,5)可由下式计算得到[17]:
hci=Nuλ/L,(i=4,5); (18)
Nu=1+1.44×sgn(1-(1 708)/(Racosβ))×[1-(1 708(sin1.8β)1.6)/(Racosβ)]+sgn[((Racosβ)/(5 830))1/3-1]; (19)
Ra=(gβ'ΔtL3)/(va) (20)
式中:g为重力加速度,m/s2; β'为体积膨胀系数,1/K; v为空气运动粘度,m2/s; α为热扩散系数,m2/s.
② 吸热板向侧板、背板的传热
qd1=hd1A2(tp-tw) (21)
qd2=hd2A3(tp-tb) (22)
hdi=λ/δi,(i=1,2) (23)
式中:qd1、qd2分别为侧面、背面保温层导热量,W; hdi(i=1,2)为保温层传热系数,W/(m2·K); tw、tb为侧板、背板温度,℃; δi(i=1,2)为保温层厚度,m.
(4)平板集热器有效集热量
qu=hfAf(tp-tf)(24)
hf=Nuλ/Dt(25)
平板集热器集管和排管内的换热为圆管内的对流换热,临界雷诺数为2 300,Nu可通过下式计算[13].
层流
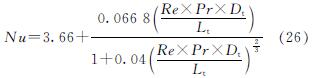
湍流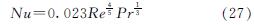
式中:tf为集热工质温度,℃; hf为集热器管壁与集热工质间的对流换热系数,W/(m2·K); Dt为集热管内径,m; Lt为集热管管长,m.
根据各传热节点的热量平衡关系可得到如下热量平衡方程

式中:mc、mp、mw、mb分别为盖板、吸热板、侧板和背板的质量,kg; cp,c、cp,p、cp,w、cp,b为盖板、吸热板、侧板和背板的比热容,J/(kg·K); τ为时间,s.
在Matlab/Simulink中建立平板集热器传热仿真模型,采用P-G/0.6-T/L/PT-1.86型号的平板集热器,其规格参数见文献[18],参照GB/T 4271-2007《平板型太阳集热器热性能试验方法》[19],集热器倾角取40°,集热工质进口温度设置为35℃,集热工质流量为0.02 kg/(m2·s).采用变步长常微分方程求解器进行求解,初始步长为0.01 s.
平板集热器对流热损失及热损失系数随海拔高度的变化规律如图4所示,随着海拔升高,平板集热器顶部的对流热损失大幅降低.由西安至拉萨,平板集热器的顶部对流热损失由40.5 W/m2减小到4.9 W/m2,降低了87.9%.由于顶部热损失降低导致平板集热器温度较高,侧面及底部的对流热损失有所增加.而由于平板集热器顶部对流热损失降低的幅度远大于侧面和底部对流热损失增加的幅度,平板集热器的对流热损失整体随海拔升高而降低.
图4 平板集热器对流热损失及热损失系数随海拔的变化
Fig.4 Convective heat loss and heat loss coefficient of flat plate collector with altitude
随着海拔升高,平板集热器的对流热损失系数逐渐降低.当海拔由近400 m升高至近3 600 m,对流热损失系数由2.8 W/(m2·K)减小至1.1 W/(m2·K).这主要是由于随着海拔升高,空气密度降低,空气物性参数变化对对流换热系数产生影响,进而导致平板集热器的对流热损失系数降低.
平板集热器辐射热损失及热损失系数随海拔高度变化的规律如图5所示.随着海拔升高,平板集热器的顶部辐射热损失大幅增加,在拉萨,顶部辐射热损失高达62.2 W/m2,其值比西安增加5.3倍; 由于保温层的存在,使得侧面边框和背板温度较低,侧面和底部辐射热损失也较小.海拔升高时,平板集热器侧面和底部辐射热损失的变化值远小于顶部辐射热损失的变化值,最终辐射热损失整体随海拔升高而增大.此外,平板集热器的底部辐射热损失会出现小于0的情况,即背板辐射得热,这是由于地表温度高于背板平均温度,使集热器背板受到的地面的长波辐射大于其向环境散失的辐射热量.
图5 平板集热器辐射热损失及热损失系数随海拔的变化
Fig.5 Radiant heat loss and heat loss coefficient of flat plate collector with altitude
与平板集热器对流热损失系数的变化趋势相反,辐射热损失系数随海拔升高而增大.从西安至拉萨,海拔升高,空气变得稀薄,天空有效温度降低,大气逆辐射减弱,导致平板集热器的辐射热损失系数由0.5 W/(m2·K)增大至2.3 W/(m2·K).
平板集热器总热损失系数随海拔高度的变化规律如图6所示,随着海拔升高,平板集热器的总热损失系数先降低后升高.在西安、西宁和拉萨,平板集热器的总热损失系数分别为3.3 W/(m2·K)、3.2 W/(m2·K)和3.5 W/(m2·K),由西安到西宁,平板集热器总热损失系数减小3.0%,由西宁到拉萨,总热损失系数增大9.4%.这主要受对流和辐射热损失系数的综合影响,随着海拔升高,对流热损失系数减小,辐射热损失系数增大,由低海拔到中海拔地区,辐射热损失系数增幅小于对流热损失系数降幅,而从中海拔到高海拔地区,辐射热损失系数的增幅大于对流热损失系数的降幅.
平板集热器总热损失随海拔高度的变化如图7所示,在各地区平板集热器顶部的总热损失均较大,其值分别为50.2 W/m2,69.2 W/m2和67.2 W/m2,由于西安的太阳辐射较弱,平板集热器集热量较小,使得集热器表面与环境的换热温差也较小,其值为20.9 ℃,而在西宁,平板集热器与环境间的换热温差较大,其值高达29.0 ℃,最终使得由西安到西宁,集热器总热损失增加较多.从西宁到拉萨,虽然在拉萨的总热损失系数比西宁大0.3 W/(m2·K),但受换热温差的影响,使得拉萨总热损失略低于西宁.在拉萨,平板集热器整体的总热损失为92.2 W/m2,为西安的1.3倍,仅比西宁低1.8%.
根据图8所示平板集热器总热损失各组分比例随海拔高度的变化可知,当海拔高度增加,平板集热器对流热损失所占的比例逐渐减小,而辐射热损失所占比例大幅增加.在海拔约为400 m的西安,平板集热器对流热损失占比高达85.7%,为辐射热损失占比的6.0倍; 而在海拔约3 600 m的拉萨,对流热损失占比仅为32.2%,约为辐射热损失占比的1/2.
采用与前述相同的数值计算方法,对不同海拔高度下、不同规格参数平板集热器的传热模型进行求解,以平板集热器实验室稳态标准工况下的总热损失系数为基准,得到了表2所示的不同海拔地区平板集热器总热损失系数的修正系数.
对于平板集热器在采暖期内或全年运行的地区,可根据表中数值分别对采暖期和全年的总热损失系数进行修正.
在该研究中,基于平板集热器的传热过程分析,建立了该传热过程数学模型,并通过实验对其进行了验证; 采用数值求解方法,得到了不同海拔地区平板集热器对流、辐射和总热损失的变化规律,主要结论如下:
(1)海拔高度增加,大气压力降低,平板集热器对流热损失系数减小; 随着海拔升高,大气透明度增加,大气逆辐射减弱,平板集热器辐射热损失系数增大.由海拔近400 m至海拔近3 600 m,对流热损失系数减小了1.7 W/(m2·K),辐射热损失系数增大了1.8 W/(m2·K);
(2)平板集热器对流和辐射热损失系数随海拔升高变化幅度不同,受二者综合影响,平板集热器的总热损失系数呈现先减小后增大的趋势.从海拔近400 m至海拔近2 300 m,总热损失系数减小0.1W/(m2·K),从海拔近2 300 m至海拔近3 600 m,总热损失系数增大0.3 W/(m2·K);
(3)为了对实际工程中平板集热器的热损失进行较为准确的计算,得到了不同海拔地区平板集热器标准工况下总热损失系数的修正系数.无论是在采暖期内还是全年使用时,总热损失系数先减小后增大,减小和增大的幅度均超过10%.