基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(51708532)
第一作者:贾纪康(1994-),男,工学硕士,工程师,主要从事建筑节能与可再生能源应用. E-mail: 18890356952@163.com 通信作者:司鹏飞(1984-),男,工学博士/博士后,高级工程师,主要从事建筑节能与可再生能源应用. E-mail: 175987342@qq.com
(China Southwest Architectural Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd., Chengdu 610041, China)
passive solar energy; building heating; solar window; solar heat gain coefficient
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2021.06.015
被动太阳能建筑被认为是高原建筑最适宜的供暖方式[1].江亿等[2]针对拉萨市的资源条件提出了在提升建筑围护结构性能的基础上,被动太阳能技术优先的技术路线; 刘艳峰、杨婧等[3-4]针对我国气候条件提出三级指标,分析了不同地区各类被动太阳能采暖技术适宜性; 王登甲等[5]针对大量被动太阳能示范建筑实测得出在采暖期过渡时段室温可达到12 ℃以上,与传统建筑相比,被动太阳能示范建筑节能率可达到86%.
直接受益窗作为被动太阳能得热最有效的构件,可利用进入室内太阳能的65%~70%[6].Levinson R,Oliveti G,Offiong等[7-9]分别研究了太阳能高度角、窗户位置和玻璃吸收率等对直接受益窗集热部件的影响.刘艳峰等[10]对直接受益式太阳能建筑测试发现,直接受益窗可提升室内平均温度和最高温度3 ℃和7 ℃,但室温温度波动较大,这是由于传统窗户的热工参数固定不变(传热系数U、太阳得热系数SHGC),无法解决白天太阳得热要求的太阳总透射比大和夜间防止失热希望的传热系数小的矛盾.基于此问题,冯雅、王登甲等[11-12]均提出了采用外窗加设内置保温板或保温窗帘的方式; 余庄等[13]针对亚热带地区夏季需要隔热、冬季需要保暖的气候特点提出了气候适应性窗.
本研究团队提出了一种具有阶跃传热特性的透明围护结构[14],该技术在“若尔盖县暖巢一号”项目中得到验证,具有良好的实际应用效果[15].通过对该工程评估后发现,由于外侧玻璃与墙体结合不严密,围护结构气密性难以保障,由此导致透明围护结构耗热量大,同时存在施工难度大,造价高等问题.介于上述问题,研究团队开发了一种热工参数可变的被动太阳能窗,其通过创新围护结构型材,将内窗扇、外窗扇一体化集成.本文将介绍该技术的原理与具体构造,并通过实测和模拟的方式对窗户的性能进行优化分析,对于工程应用具有一定的指导意义.
热工参数可变的被动太阳能窗构造如图1所示,其由内窗扇与外窗扇通过型材构造一体化组合而成.外窗扇分为固定窗扇和可外开窗扇,外窗扇采用6 mm单层透明玻璃,其特点是SHGC高,可有效增加进入室内的太阳辐射能; 内窗扇采用内开式中空玻璃窗,构造为6 mmLow-E+12 mm空气+6 mm透明玻璃,其特点是保温性能好,可有效降低通过窗户散失的热量; 整窗长度、宽度均为1.5 m,厚度为110 mm.
冬季,白天太阳辐射较强时,开启内窗扇,大部分太阳辐射透过外侧单层玻璃进入室内,太阳得热系数高; 夜晚关闭内窗扇,窗户热阻增大,与Low-E玻璃对中远红外辐射高反射特性同时作用,减少夜间通过窗户的失热量.夏季,炎热地区室内空调运行,关闭内、外窗扇,增加窗户热阻,防止室内冷量损失,同时可降低白天太阳得热系数,减少空调负荷; 室外气候凉爽的地区同时开启内、外开窗扇,通过自然通风方式降低室内温度并保证室内空气质量.
本文主要采用劳伦斯伯克利实验室开发的WINDOW和THERM软件对产品性能进行模拟研究.窗户模型的建立需要WINDOW和THERM软件联合完成,具体流程如图2所示.WINDOW软件用于计算窗户U值、SHGC、遮阳和采光等参数,THERM软件采用二维有限元方法计算窗框等复杂建筑构件传热模拟[16].同时,通过实验测试对计算模型进行了验证,实验由具有工程检测资质的第三方检测机构进行.
WINDOW软件计算整窗的传热系数Ut时,将窗户分为窗框、玻璃中心和玻璃边缘三部分,分别计算各自的传热系数U,再以面积加权的方法计算Ut值,Ut计算公式见式(1).
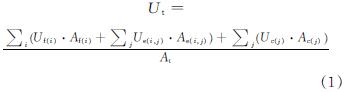
式中:U为传热系数,W/(m2·k); A为传热面积,m2; 下角标t表示窗户整体; 下角标f(i)表示第i部分窗框; 下角标e(i,j)表示第i部分窗框与第j部分玻璃对应玻璃边缘; 下角标c(j)表示第j部分玻璃.
玻璃系统中心传热系数Uc计算由WINDOW软件完成,玻璃参数如表1所示.
玻璃系统边缘和窗框的传热系数计算需要在THERM软件中计算,其窗户边框的二维截面模型如图3所示.玻璃系统由WINDOW软件经过计算后导入THERM软件,为降低窗户的传热系数,采用多腔隔热金属型材窗框,各材质的热物性参数如表2所示.模拟边界条件均依据《建筑门窗玻璃幕墙热工计算规程》(JGJT151-2008)[17]选择,并与实验边界条件保持一致,传热系数计算边界条件如表3所示.
经过模拟计算玻璃中心Uc值为1.24 W/(m2·K),不同节点处窗框传热系数Uf及玻璃系统边缘传热系数Ue值各不相同,图4采用等温线的形式展示了典型窗框节点的模拟结果,图4(a)窗框Uf(a)为2.29 W/(m2·K),玻璃边缘Ue(a)为1.74 W/(m2·K),图4(b)窗框Uf(b)值为2.32 W/(m2·K),玻璃边缘Ue(b)为1.75 W/(m2·K).由窗户不同部位模拟结果经过面积加权后整窗Ut为1.66 W/(m2·K),整窗温度分布如图5所示.第三方检测机构对产品Ut值的实验结果为1.6 W/(m2·K)[18],如图6所示,模拟误差为4%.
利用上述经过验证的模型,对窗户开闭状态、玻璃系统组合、窗框材料、窗框比等影响因素进行了优化分析.
窗户分为内窗扇和外窗扇的优势在于冬季白天太阳辐射较强时开启内窗,外侧为6 mm透明玻璃,可使更多的太阳辐射进入室内,夜间关闭内窗,增加热阻,减少室内热量流失.故有必要对内窗开、关状态下窗户的性能进行模拟分析.
模型尺寸1.5 m×1.5 m,计算边界条件依据《建筑门窗玻璃幕墙热工计算规程》(JGJT151-2008)选择,传热系数计算边界条件同表3,SHGC计算边界条件如表4所示.
模拟结果如表5所示,内窗扇开启时,SHGC增至0.69,进入室内的太阳辐射得热增加82%,同时,窗框比由0.31降低至0.16,降低了窗框对太阳辐射的遮挡作用,最大程度提升了冬季太阳能利用.可见光透射比Tvis由0.47增加至0.74,可减少部分室内的照明能耗.内窗扇关闭时,窗户Ut降低至1.66,与Low-E玻璃对中远红外辐射高反射特性同时作用,夜晚及夏季白天关闭内窗扇运行,可大幅降低室内冷/热量流失,同时Low-E玻璃对可见光的高透过性,使得Tvis保持在0.47,夏季白天即使关闭内窗扇也能保证一定自然采光.
由于窗户是围护结构节能薄弱部位,所以针对窗户不断有新的节能技术出现,如中空玻璃充惰性气体、Low-E玻璃、真空玻璃等,本文选择常用的5种玻璃系统进行对比模拟分析,典型玻璃系统形式如表6所示,其中G1为普通中空玻璃窗,其余为热工参数可变组合形式.
窗户传热系数模拟结果如图7所示,G5采用真空玻璃技术,Ut值为1.35 W/(m2·k),保温性能等级达到8级,相比于G1普通中空玻璃窗Ut值降低了50.3%.不同玻璃系统形式下整窗Ut值差别较大,对比普通三玻两腔玻璃系统G2,使用Low-E玻璃,玻璃系统Uc值降低29.7%,Ut值降低16.5%; 中空玻璃充氩气技术玻璃Uc降低14.9%,整窗Ut降低6.9%.可见真空玻璃技术对窗户传热系数降低效果最明显,随着玻璃系统Uc值逐渐降低,整窗Ut降低幅度逐渐减小,这是由于窗框Uf值较大,随着玻璃系统Uc值逐渐降低,窗框成为整窗的传热的主要部位,如果不能提升其性能,整窗Ut很难有明显降低.
外窗作为自然采光主要围护结构,保证其可见光透射比是基本要求,同时夏季外窗的太阳得热系数对节能的影响不亚于传热系数的影响,Tvis和SHGC模拟结果如图8所示,相比普通双层中空玻璃窗G1,采用G2产品Tvis降低10.4%,SHGC降低11.7%,这是由于增加一层透明玻璃,对可见光波段及其他波段降低基本一致; G3使用Low-E玻璃相比G2,Tvis降低3.1%,SHGC降低12.9%,可见Low-E玻璃在保证采光的条件下可有效降低太阳得热; G4和G5选用玻璃与G3相同,但改变了中空玻璃的气体间层,相比于G3,Tvis完全相同,SHGC略有下降.
通过以上分析可知,随着玻璃系统Uc不断降低,整窗Ut主要受窗框Uf影响,降低窗框Uf是提升整窗传热性能的有效措施.由于玻璃纤维增强聚氨酯(GRPU)材料导热系数为0.36 W/(m·K),结合了塑料材料的优越保温性能和金属的高强度,作为窗框型材具有很高适宜性.因此,本文通过对G3玻璃系统分别选择多腔断热铝合金窗框和GRPU窗框进行了对比模拟分析,结果如图9所示.采用GRPU型材之后窗框Uf值降低52.3%,达到1.09 W/(m2·K),玻璃边缘Ue值降低6.9%,主要是窗框传热的变化减小了窗户线传热系数,整窗Ut值降低23.3%,可见GRPU窗框对窗户整体传热性能有较大提升作用.
影响窗户性能的另一个重要参数是窗框比,窗户尺寸越小,窗框占比越大,本文选择尺寸分别为2.1 m×2.1 m、1.8 m×1.8 m、1.5 m×1.5 m的三种窗框比的窗户对Ut值、SHGC、Tvis分别对比分析,窗户玻璃系统均采用G3玻璃系统.结果如图 10所示.
随着窗框比由22.3%增大到30.5%,Tvis由0.53线性降至0.47,SHGC由0.42线性降至0.38,SHGC与Tvis基本与玻璃面积占比呈正比例关系; 随着窗框比增加Ut值由1.55 W/(m2·K)增加至1.66 W/(m2·K),这是由于窗框Uf值通常低于玻璃系统Uc值,整窗Ut值通过窗户各部分U值面积加权求得,故随着窗框比增加,整窗Ut值不断增加,且窗框Uf值与玻璃系统Uc值差距越大,窗框比对整窗Ut值影响越大.
热工参数可变的被动太阳能窗,解决了室外环境变化与室内热环境需求不统一的矛盾.不仅适用于高寒地区,也适用于其他严寒、寒冷气候区,白天能尽可能多的利用太阳辐射,夜晚防止热量流失; 同时也可应用于夏热冬冷地区,夏季可隔绝大部分室外得热,冬季可增加太阳辐射.该窗户成本增加较少,相对普通三玻两腔窗户,增量成本约5%以内,且功能多样的窗户结构可降低建筑空调季、供暖季负荷,过渡季通过通风调节室内环境,通过配合不同的玻璃系统形式以及窗框材料可满足大部分建筑节能设计标准以及建筑采光标准.
开发了热工参数可变的被动太阳能窗,通过对该太阳能窗进行模拟优化与第三方检测,得出如下结论:
(1)样窗(G3玻璃系统)内窗扇开启时,Ut值虽增加至5.30,但进入室内的太阳辐射得热增加82%,远高于传热损失; 内窗扇关闭时,Ut值降低至1.66 W/(m2·K),与Low-E玻璃对中远红外辐射高反射特性同时作用,可有效降低室内热量流失;
(2)铝合金窗框采用不同玻璃系统形式时,Ut值差别较大,但随着玻璃系统Uc值逐渐降低,Ut值降低幅度逐渐减小,可见,当Uc降低至一定程度后,玻璃系统Uc值对窗户传热性能提升效果有限;
(3)采用GRPU型材之后窗框Uf值降低52.3%,Ut值降低23.3%,可见,窗框型材的传热性能对窗户整体Ut值较大提升作用;
(4)窗户SHGC与Tvis基本与玻璃面积占比呈正比例关系,当窗框Uf值与玻璃系统Uc值差别越大时窗框比对整窗Ut值影响越大,高窗框比时,降低窗框的Uf值对降低窗户Ut值有显著的效果.