基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(11447133,11602187); 陕西省教育厅重点实验室基金资助项目(15JS045)
第一作者:崔海航(1975-),男,副教授,主要从事水处理技术数值模拟研究,cuihaihang@xauat.edu.cn
(School of Environmental and Municipal Engineering, Xi'an Univ. of Arch. and Tech., Xi'an 710055, China)
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2018.02.019
渗透现象是一种广泛应用于污水处理、海水淡化、渗透马达和微泵等领域的自然现象.而Kedem-Katchalsky(K-K)模型作为描述渗透现象的经典热力学模型,存在诸多不足之处,如对压强分布描述不够清晰、无法揭示壁面位移情况等.为更加深入的理解渗透现象,建立了边界滑移条件下基于CFD模拟单孔道数学模型.通过对K-K模型中溶质反射系数和纯水渗透系数的模拟,验证了模型的可靠性.在此基础上,模拟并研究了孔道内流场分布、压强分布及边界应力分布.同时合理地解释了溶质反向渗透及溶胀现象.
Osmosis phenomenon is a natural phenomenon, widely encountered in the fields of sewage treatment, seawater desalination, osmotic motor and micropump. The Kedem-Katchalsky(K-K)model, as the classical thermodynamic model for describing the osmotic phenomenon, has many shortcomings: the description of the pressure distribution is not clear and it can't reveal the wall displacement and so on. In order to understand the phenomenon of osmosis deeply, the mathematical model of a single channel, based on CFD simulation, was established under the condition of boundary slip. The reliability of the model was verified by the simulation of solute reflection coefficient and pure water permeability coefficient in the K-K model. On this basis, the flow field distribution, pressure distribution and boundary stress distribution were simulated and studied. At the same time, solute reverse osmosis and swelling were explained reasonably.
渗透现象指两种不同浓度的溶液隔以理想半透膜(允许溶剂分子通过,不允许溶质分子通过的膜),水分子或其它溶剂分子从低浓度的溶液通过半透膜进入高浓度溶液中的现象.渗透现象[1]于1748年由法国人Abble Nollot首次发现.1885年,Van't Hoff根据Preffer的实验数据发现稀蔗糖溶液渗透压与溶液浓度的关系,并由此提出Van't Hoff方程[2]:π=RTCS,式中CS表示溶质的摩尔浓度.现有文献不断尝试引入动力学模型来解释这一现象,主要有:优先吸附-毛细管流动模型[3]、溶解-扩散模型[4]、溶剂张力理论[5]等.由于微观状态下水分子的复杂运动,其在微纳孔道中的传递机理仍存在诸多争议,从而使得渗透现象的应用受到诸多制约.
从溶液中溶质和溶剂的角度来说,渗透现象中溶质和溶剂(通常情况是指水)的跨膜运输模型主要包括单参数模型(溶质渗透性)、经典两参数模型(溶质和溶剂的渗透性)以及三参数模型(溶质、溶剂的渗透性和反射系数,即K -K模型)[6].其中K-K模型引入了溶质与溶剂的相互作用参数,即反射系数,适用于溶质与溶剂共用输运通道的情况,使得该模型成为广泛应用的唯象学模型,能够很好地反映通量的变化规律.
对于描述自然界中普遍存在的管流而言,K-K模型的不足之处在于反射系数的物理意义不明确,同时包含了溶质组分、溶质分子量、溶剂分子量、系统熵等多个因素的综合影响[7],反射系数的引入使得对模型的理解更加困难,且易误解[8].此外,K-K模型对渗透现象不能给出清晰地描述,最突出一点就是不能体现出压强分布,而理解与压强相关的问题是渗透现象不可或缺的一部分.如Leraand和Kiil通过超声技术测得水力压差与渗透压作用下孔壁的位移情况,表明水力压差对孔壁位移影响明显,而渗透压作用则无明显偏移[9]; Soodak等认为孔道中大部分轴向长度内压力梯度为一定值,只在靠近孔道开口处压力梯度存在突变[10]; 材料溶胀的力学性能也与孔内压强分布有关.
在新的研究领域中,出现大量利用渗透现象的微纳器件,但其流动形式完全不同于管流,使得K-K模型对于这类流动形式难以描述.如K-K模型对于植物体内水分的输运[11]、基于化学势驱动的微泵技术[12]、自驱动马达/颗粒[13,14]等,渗透现象很难进行宏观现象和微观机理的解释.本文通过建立微纳尺寸的单孔道,结合层流流动控制方程和物质传递控制方程,采用边界滑移条件来模拟纳米孔道中的渗流.旨在表明在微观渗流中考虑边界滑移条件的必要性,同时分析孔道中溶质沿孔道轴向分布引起孔道内流场的变化以及孔壁受力情况.
基于Comsol Multiphysics多物理场耦合软件,对于渗透现象开展微纳孔道数值模拟,通过孔道中流体流动的通量、流速及压强分布等物理量来探索边界滑移条件对微纳孔道传输性能的影响.其结果不但能够反映K-K模型结论,而且给出了更多微观细节,如流场、压力场分布.这一方法不仅有利于与现有宏观尺度下膜组件中渗透现象的CFD模拟进行跨尺度耦合,并且有助于对渗透现象,特别是与压强相关现象的理解.此外,还能够通过此方法对材料所受应力进行分析,从而理解材料的溶胀机理,为渗透现象在相关领域应用提供借鉴.
对于渗透现象而言,采用基于多孔介质条件下非平衡热力学的半经验K-K模型,是非常有效的唯象模型.渗透过程中,溶质摩尔通量JS、溶剂体积通量JW、溶质反射系数σ可用以下方程表示:
JW=A(-ΔP+σΔπ)(1)
JS=-wRTΔc+(1-σ)JWc0(2)
式中:R指普适气体常量,8.314 J/(K·mol); T指溶液温度,K; ΔP和Δπ分别指进出口两侧水力压差和溶质摩尔浓度差; A表示渗透系统的纯水渗透系数; σ指高浓度侧溶质分子数占溶液分子总数的比例,即渗透系统对溶质的反射系数,σ=[ΔP∞/Δπ∞]JW=0=[JW/AΔπ∞]ΔP∞=0; w指溶质渗透系数; 是指初始时高浓度侧溶液摩尔浓度.
在渗透现象的CFD模拟中考虑物质传递作用.对于宏观现象而言,渗透和对流在“形式”上基本无差别,但在微观领域,并不能将渗透简单地与对流等同.在单孔道模型中,研究孔径在纳米级范围内.此时,流体微团在孔道内流动所受的粘性力远大于其所受的惯性力,则表征流体粘性影响的无量纲数——雷诺数Re1,因此在Comsol Multiphysics多物理场耦合软件中仅需要考虑层流作用且可忽略惯性力作用,孔道内流体流动呈不可压缩流.其控制方程如下:
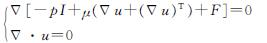 (3)
(3)
Δ·(-DΔc)+u·Δc=R(4)
式(3)为稳态条件下低Re流体流动方程,包括N-S方程、连续性方程.
式中:μ为流体动力粘滞系数; u为流体流动速度; Δ(-pI)为压力作用项,p为压力值,I为位置矢量; Δ[μ(Δu+(Δu)T)]为粘性力作用项; F为体积力作用项,本研究中不考虑体积力作用.式(4)为稳态条件下稀物质传递的对流扩散方程,式中:Δc为物质浓度梯度; D为扩散系数; R为反应源项,本研究仅考虑对流和扩散过程,无源项作用.
从宏观尺度到微观尺度,随着尺寸的减小,水力阻力急剧增大,流体系统极大的表面积与体积比,使得表面现象成为影响流动的主导因素.目前就渗透现象研究而言,都是基于无滑移边界条件假设进行的.而研究表明,宏观尺度下边界滑移通常不易发生,即边界滑移对宏观尺度现象影响微不足道.但对于微、纳米尺度下,边界滑移对流动性能将产生重要影响[15-17].当前已有的部分分子动力学模拟[18-19]表明,随着固液界面性质的改变,固液界面上的液体分子可以在无滑移、部分边界滑移以及在固体表面直接发生边界滑移等几种状态之间变化.因此,宏观尺度流动中普遍认可并应用的速度无滑移假设在微纳系统中不再适用[20],液体在固体表面纳米量级的滑移将会对流体输运产生重要影响[21].对于微尺度下渗透现象的研究,应当考虑边界滑移对渗透体系的影响.
流体流动中边界滑移是对固液界面处流体同固体间运动速度的数学近似处理,其可理解为:(1)沿固液界面轴向方向上物理梯度作用的存在(如浓度梯度)使得流体在微观界面处产生滑移长度;(2)界面处流体的滑移进而驱动流体运动,该情况下通常采用滑移长度b定量刻画[22].界面驱动现象对流体流动的增大作用受因数[1+(b/d)]控制.其示意图见图1.
文献[22]中给出滑移产生的微观机理,并运用Navier平衡条件推导出边界滑移速度表达式:
υs=-((RT)/(μ0))Γd(1+b/a)·(dc0)/(dx)(5)
式中:Γ=∫∞0dy[e-(U(y))/(RT)-1],表征界面附近溶质的厚度; d=Γ-1∫∞0dy[e-(U(y))/(kBT)-1],表征短程势能相互作用范围; μ0表示不可压缩流体主流粘度; c0表示主流浓度.但为便于理解和计算,本文通过引入滑移系数cslip,综合表征界面附近溶质厚度、短程相互作用范围等各因素对界面层流体流速的影响.则公式(5)简化为
υs=cslip·(dc)/(dx)(6)
式中,c表示壁面处溶质浓度,认为界面滑移速度正比于当地浓度梯度.由此在Comsol Multiphysics多物理场耦合软件层流模块下壁面边界条件选用滑动壁,其壁面滑移速度定义为:υs=cslip(cztz+crtr),(cztz+crtr)表征浓度梯度在壁面方向上的投影,式中,cz、cr分别表示沿壁面处溶质浓度梯度在膜孔径向和轴向方向上的分量,tz、tr分别表示沿壁面处溶质浓度梯度在膜孔径向和轴向方向上的单位矢量.
研究表明,在液体特征尺度大于10 nm情况时,连续介质方程依然有效,而特征尺度小于10 nm时,其流动控制方程将以离散化的方程为主[23].但在实验方面,Isrelachvili[24]曾测量了2 nm的水膜,发现仍具有连续介质的扩散性质.同样,Bocquet等[25]在其综述中对已有结果进行了分析,认为在大于1 nm的尺度(即5倍的水分子直径)下,连续介质假设的结论仍能适用.因此,本研究所建立几何模型为二维轴对称模型,模型中孔道半径R=1~10 nm、孔道长度L=10~100 nm,选用水作为工作介质.本研究仅考虑化学势和水力压强差对水通量的影响,暂不考虑溶质类型等因素.几何模型中入口、出口处分别设置压强Pinlet、Poutlet和物质浓度cinlet、coutlet.对所建几何模型,采用自由剖分三角形网格,同时对局部物理量变化剧烈的区域进行加密处理,其网格平均单元质量为0.992 6,通过对网格进行无关性验证,确保网格剖分合理.几何示意图见图2.
对于公式(1),当进出口两侧溶液只有水力压强差而无浓度差(ΔP≠ 0,Δc=0)时,其宏观物理现象为进出口两侧溶液水头不同、但溶液浓度相同,此时水分输运的推动力来自于ΔP,可根据此时水通量计算纯水渗透系数A; 当进出口两侧溶液Δc≠0,而ΔP=0时,其宏观物理现象为进出口两侧溶液水头相同、但溶液浓度不同,此时水分运输的推动力来自于渗透压差Δπ,根据此时水通量和纯水渗透系数A可求得渗透系统对溶质的反射系数σ.对于公式(2),若σ=1,表明渗透系统完全截留溶质分子,此时溶质渗透系数为零[26].在JW=0,即水通量为零时,由于溶质运输速率远小于水分的运输速率,使得宏观上进出口两侧溶液达到准静态,但实际上此时存在JS≠0,即溶质的输运仍在进行,将随着时间的推移,在进出口两侧达到浓度平衡,但这一时间尺度通常很长而被忽略.上述基本现象将被用于检验所建立CFD模型的正确性.
本文主要针对以下角度进行模拟:(1)假设溶质初始反射系数为1,在层流情况下,模拟确定出不同几何尺寸对壁面滑移系数cslip值的影响.根据模拟得出的cslip值,加入稀物质传递模块,模拟计算溶质反射系数.(2)在一定孔径和孔长条件下,研究壁面滑移边界对渗透系统水通量QW的影响,并对比通过K-K模型计算的QW.由于仅研究系统边界对QW的影响,所以其他参数都设为定值.(3)研究溶质摩尔通量随ΔP /Δπ变化情况.(4)在确定d的单孔道中,进出口两侧ΔP=0时,模拟纯化学渗透作用对系统边界产生的作用力,并比较相当于化学渗透压的水力压强差对系统边界产生的作用力,同时揭示膜孔中压强分布.
壁面滑移系数cslip值受诸多因素影响,如材料、孔径、孔度等.本文在层流情况下,设定无壁面滑移和进出口压强差ΔP=105 Pa,在上述几何模型中求解出孔道内溶剂流量QW,并转化为溶剂体积通量JW,然后通过公式(1)计算得到纯水渗透通量A的值.
考虑孔径、孔长以及反射系数的作用,并结合Van't Hoff方程,通过量纲分析得到以下关系式:在ΔP=0,Δc= 10 mol/m3条件下,加入稀物质传递模块,引入对流与扩散作用,假设不同尺寸的孔道溶质初始反射系数σ=1(即系统对所有溶质均完全反射),不予溶质反向运输,排除溶质对cslip值的影响,根据公式(6)计算出cslip值.由图3可知,cslip值主要受孔径大小的影响,而孔长对其影响可以忽略不计.
图3 滑移系数cslip随孔尺寸变化规律
Fig.3 Variation of slip coefficient with pore size
由上述计算所得cslip值,设定ΔP=0,Δc=10 mol/m3以及壁面滑移条件,模拟计算孔道内溶剂体积通量Jw,再通过公式(1)确定不同孔道尺寸时的值σ.σ值属于一种唯象系数,其主要受孔道尺寸的影响,孔径越小、孔长越长,σ值越大且逐渐接近于1,但不可能大于1.该结论同王晓琳[27]实验结果相一致,且符合物理事实,表明本文所建模型的有效性.
层流和稀物质传递模块耦合条件下,对R=1 nm、L=100 nm的孔道进行模拟,研究压强梯度和浓度梯度对QW的影响; 并与K-K模型计算的QW进行比较,其结果如图4所示,为便于观察对比,对QW进行绝对值处理,其中(ΔP/Δπ)<1时,溶液主流方向朝向浓度梯度方向;(ΔP/ Δπ)>1时,溶液主流方向朝向压强梯度方向.从图4(a)中可知,ΔP=105 Pa,( ΔP /Δπ )=0~40时,QW的模拟值和K-K模型计算值与Δπ-1呈非线性关系; 当压强差与渗透压差比值(即ΔP/Δπ)接近于1时,QW出现最小值,而ΔP/Δπ在0.6~1.5时,模拟值与K-K模型计算值之间存在一定的偏差,认为由于系统误差使得偏差出现,且该偏差可忽略不计.分析认为溶质浓度较小时,渗透压随之较小,此时较大,ΔP/Δπ导致膜孔中主流方向朝向压力梯度方向,最大流速出现在膜孔中心区域,在近壁面处由于滑动边界作用,随着溶质浓度的增加而逐渐出现与主流方向相反的流动,从而使得模拟值与K-K模型计算值之间偏差逐渐变大.溶液在管道中流动如图5所示,其中箭头方向即溶液流动方向、箭头长度表示相邻观测点处速度值的相对大小、横轴表示截选孔径、竖轴表示截选长度.由图5可知,溶液在管道中的速度分布
图4 水通量QW模拟值与K-K模型计算值随ΔP/Δπ的变化规律:(a)ΔP恒定、Δc变化; (b)Δc恒定、ΔP变化
Fig.4 Simulation of water flux value and calculation of K-K model value changes with ΔP / Δπ:ΔP is constant、Δc is changed; Δc is constant、ΔP is changed.
由柱塞状分布和抛物线分布叠加而成,叠加后的速度分布取决于不同条件下二者对流动的贡献.溶质浓度较大时,ΔP/Δπ较小,使得孔道内主流方向朝向浓度梯度方向,最大流速出现在壁面表面处.由于动力粘性作用使得孔道中心的流速最小,此时孔道内流动主要受浓度梯度作用.因此ΔP/Δπ越小,模拟值与计算值偏差越小.
图5 孔道流体流动随ΔP/Δπ变化示意图,ΔP/Δπ为:(a)0(b)0.2(c)1(d)2(e)∞
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of changes fluid flow in pore with ΔP/Δπ, ΔP /Δπ equal:(a)0(b)0.2(c)1(d)2(e)∞
从图3(b)中可知,Δ c=10 mol/m3,(ΔP/Δπ)= 0~40时,模拟值和K-K模型计算值均与ΔP呈非线性关系.ΔP/Δπ接近于1时,模拟值与K-K模型计算值同样存在偏差并且达到最大,偏差分析类似图4(a).
渗透过程中不仅存在溶剂由浓度较低侧向浓度较高侧的渗透过程,同时存在着溶质从浓度较高侧向浓度较低侧的反向输运过程.研究表明[28],溶质的反向跨膜过程与溶剂的渗透过程相互制约.
在上述模型中,对Δc=10 mol/m3、(ΔP/Δπ)=0.02 ~ 2时进行模拟并计算溶质摩尔通量.经拟合计算发现溶质通量大小满足以下方程:
JS_Diffusion/JS_Convective=1.8×10-4(7)
JS_Total=-2.764 2(ΔP/Δπ)×10-8(8)
式中JS_Diffusion表示溶质扩散通量; JS_Convective表示溶质对流通量; JS_Total表示溶质总通量.结果表明,当ΔP/Δπ=1(即水通量最小,接近为零)时,溶质通量Jw不等于零且对流作用表现更显著,其中负号表明溶质由浓度较高侧向浓度较低侧流动.其结果与K-K模型中(2)式理论分析一致,即水通量QW为零时,依旧存在溶质的反向渗透.
对于进出口两侧Δc≠0,ΔP=0时,即膜孔两侧仅存在浓度差,不存在水力学压差,此时膜孔轴线处压强分布如图6(a)所示.结果表明,远离孔道进出口处,溶质浓度基本维持恒定,压强梯度几乎为零.但在溶液进入或流出膜孔时均产生阶跃现象即压强存在急剧变化,主要原因是在进出口附近由于孔道内外尺寸的剧烈变化而在孔道轴线方向上出现溶质浓度梯度,从而表现出渗透压.此外,溶质浓度在进口侧高于出口侧,因此表现出高于远离孔道进口处的压强; 在出口侧,由于孔道内溶质浓度高于孔道外部溶质浓度,从而在孔道内靠近出口侧表现出负压现象.而在孔道内部,由于溶质浓度梯度恒定,根据Van't Hoff方程可知其压强梯度也同样恒定,即孔道内压强呈线性分布.随着Δc的减小,溶质浓度梯度也在减小,因此出现压强梯度减小.该模拟结果同Soodak等[10]的理论分析相一致.
当进出口两侧仅存在水力压强差且大小等于上述渗透压差时,孔道轴线处压强分布如图6(b)所示.远离进出口处,压强梯度恒定为零,原因是在该区域内不发生溶质浓度和边界变化,使得压强值恒定.在孔道出入口处,由于溶质浓度梯度为零,因此不表现出如图6(a)中的阶跃现象.而在孔道内,由于进口处压强较大、出口处压强较小,且其流动属于层流,因此压强呈线性分布.此外,ΔP的作用主要体现在孔道内部,因此ΔP越大,沿孔长方向的压强梯度也越大.
从上述两模拟结果可知,无论是渗透压作用还是水力压强差作用,其都会使得孔道内部压强呈现线性分布,但呈现这种线性分布的来源有所不同.而孔道外部区域边界条件和溶质浓度都不发生变化而呈现出压强梯度为零的分布.
渗透过程中,系统本身受到诸多作用力,包括:水力压强差作用、化学渗透作用、温度梯度作用、电势作用等[29].考察进出口两侧Δc≠ 0,ΔP=0时,边界受力情况,并与仅水力压强差存在、无渗透作用时比较.结果表明,当进出口两侧ΔP=0时,由于Δc≠0,使得低浓度侧溶剂在渗透压作用下向高浓度侧发生运动.此时两侧边界受力相同,但在入口处附近小范围存在较大梯度,其表观现象为在渗透压作用下边界位移不明显,同引言中Leraand和Kiil关于渗透压作用下孔壁发生位移的结论相一致.
当进出口两侧物质浓度相同即不存在浓度梯度时,ΔP由Van't Hoff方程设置为相当于仅存在物质浓度差Δc时对应的压强差时,从图6(b)可看出孔道进出口处存在压强差,表明进出口两侧受力不等使得系统综合受力不为零,且主要取决于压强较大处边界的受力情况,其表观现象为在水力压强差作用下系统位移较明显.同引言中Leraand和Kiil关于水力压强差作用下孔壁发生位移的结论相一致.上述结论在边界总应力分布中同样得到验证,如图7所示.
图6 轴线处压强分布:(a)Δc≠0、ΔP=0;(b)Δc=0、ΔP≠0及Δc=9、ΔP= 0时浓度分布
Fig.6 The distribution of pressure at the axes:(a)Δc≠0、ΔP=0;(b)Δc=0、ΔP≠0 The distribution of concentration:Δc=9、ΔP=0
图7 孔道边界总应力示意图(a)Δc≠0、ΔP=0;(b)Δc=0、ΔP≠0
Fig.7 Schematic diagram of total stress at the hole boundary (a)Δc≠0、ΔP=0;(b)Δc=0、ΔP≠ 0
此外,还可同无滑移边界条件下的壁面位移变化情况进行对比.无滑移边界情况下,孔道中壁面不存在正应力,即壁面上的总应力仅包括切应力,且沿壁面方向.无论在水力压强差还是渗透压差作用下,孔道中壁面均不会发生变化.而存在滑移边界条件时,由于壁面所受的总应力由正应力和切应力两部分组成,使得孔道随着渗透作用的进行,进口侧在向孔道外侧的正应力作用下逐渐向两侧拓宽,而出口侧在向孔道中心的正应力作用下逐渐中心轴线处收缩.该结论对于管流状态下渗透现象在工业应用中具有重要的借鉴作用.
基于Comsol Multiphysics多物理场耦合软件建立了修正的渗透模型.
(1)通过对K-K模型中溶质反射系数σ、纯水通量及溶质通量的模拟验证了模型的可靠性.所建模型较K-K模型的优势在于物理意义明确,如通过模拟发现溶质的反向渗透并不是一个独立因素,其本质是对流和扩散综合作用的结果.
(2)滑移系数cslip的引入,一方面在于凸显化学势驱动过程属于非平衡热力学问题,另一方面在于理解孔道变形问题.在水力学压差作用下,孔道外壁面将被压缩,而内壁面将向两侧扩张,其结果在于孔道变宽,但渗透压作用并不引起外壁面的变形,且内壁面进出口两侧发生反向变形.本文研究所得cslip值同郑旭等人[30]研究Janus颗粒自驱动机理所采用的cslip值数量级相当,从而证明本研究所建模型的合理性,同时有助于理解渗透压概念,渗透压并不等同于水力压差,且渗透压是渗透现象发生的结果,而不是渗透现象发生的原因.
(3)该模型对压强分布的预测还可以解释一些宏观物理现象.尽管对边界滑移条件的形成机理以及滑移系数的确定还值得商榷,但该模型在一定程度上得到符合直观物理现象的解,为渗透现象与其他基础学科交叉的研究提供工具,而这种交叉更有利于对渗透现象物理本质的理解.
尽管采用CFD方法建模,但仍为三参数模型,分别采用溶液动力粘度μ、溶质扩散系数D、壁面滑移系数cslip.尽管采用基于连续介质假设,但仍有必要采用分子动力学方法,从分子间相互作用角度进一步解释壁面滑移系数对系统传输性能的影响.渗透压与水力压强对边界作用力情况完全不一样,可以从该角度探索材料的溶胀现象.此外,尽管通过引入cslip值来研究渗透现象,但式(6)表征的是存在浓度梯度时的滑移速度,暂不能表征纯溶剂时的滑移速度,速度滑移方程还有待继续完善.因此,在后续研究中,还可针对恒定流和非恒定流进行研究,探索不同时间尺寸壁面滑移系数、溶质反射系数等参数变化对渗透作用的影响,为渗透系统优化提供理论依据,同时为其他新领域[11,12-14,31,32]的研究提供借鉴.