基金项目:陕西省教育厅专项科学研究计划(17JK0070); 陕西省自然科学青年基金(2017JQ5013)
第一作者:段瑞芳(1980-),女,硕士,副教授,主要从事桥梁结构理论教学与研究.E-mail: 65491968@qq.com 通信作者:白云腾(1995-),男,硕士生,主要研究桥梁结构理论.E-mail: 1071153073@qq.com
(1. 陕西交通职业技术学院 公路与铁道工程学院,陕西 西安 710018;2. 山东省交通规划设计院,山东 济南 250031; 3. 长安大学 公路学院,陕西 西安 710064)
(1. Highway and Railway Engineering College, Shaanxi Communications Vocational and Technical College,Xi'an 710018, China;2. Shandong Institute of Transportation Planning and Design, Jinan 250031, China;3. College of Highway, Chang'an University, Xi'an 710
reliability; response surface; BPANN; non-linear optimization; cable-stayed bridge
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2019.01.010
为了有效解决在斜拉桥施工中各种不确定因素的影响,合理制定索力张拉方案.本文提出了一种基于统计回归和非线性优化的结构可靠度优化方法.利用统计回归拟合得到结构可靠度指标与设计变量之间的拟合函数关系,形成约束函数和目标函数,建立优化模型.为提高计算效率,在拟合之前对影响结果的随机变量进行了可靠度分析和灵敏度分析,筛选出拟合所需的最小样本容量和最小随机随机变量个数.通过对一个刚架模型的可靠度分析,比较了BP神经网络响应面法和多项式响应面法两种拟合方法的优劣性,并确定使用BP神经网络响应面法进行函数拟合,同时验证本文所述方法的可行性.并将该优化方法应用于一座带有水平索的双斜塔斜拉桥,通过优化张拉方案使边墩支座的脱空概率减小至可接受的范围.
In order to effectively solve the influence of various uncertainties in the construction of cable-stayed bridge, the cable tension plan is reasonably developed. A reliability optimization method based on statistical regression and nonlinear optimization is proposed in this paper. The fitting function relationship between structural reliability index and design variables is obtained by statistical regression fitting, forming constraint function and objective function, and establishing optimization model. In order to improve the computation efficiency, reliability analysis and sensitivity analysis were carried out before the fitting of random variables, and the minimum sample size and minimum random variables needed for fitting were screened out. Based on a frame model of reliability analysis, the advantages and disadvantages of two kinds of surface fitting method and polynomial response surface method BP neural network response were compared and identified using BP neural network response surface fitting. Meanwhile, the feasibility of the method described in this paper is proved. The method presented in this paper is applied to a double tower cable-stayed bridge with horizontal cables. By optimizing the cable tension plan, the probability of unseating of the side pier is reduced to acceptable range.
斜拉桥在跨径上具有很强的竞争力,而且在经济上,美观上与其它桥型相比具有优势.然而,由于其主要承载构件是柔性索,结构非线性很强,因此斜拉桥的索力优化一度成为研究的热点.但是大多数的研究都是基于结构参数完全确定性的假设,也被称为确定性分析[1].
影响矩阵法[2,3]是目前常用斜拉桥索力优化方法,我们可以采用这种方法确定斜拉桥的成桥索力以及施工过程的张拉方案.然而斜拉桥在施工过程中,由于结构整体刚度较小,对张拉误差,构件加工误差及施工误差等不确定因素的影响非常敏感,各种不确定因素的影响常导致结构偏离理想状态,而影响矩阵法在斜拉桥索力优化中没有考虑这些不确定因素产生的影响.因此,为对斜拉桥进行一个完整的评估,应对其进行可靠度与灵敏度分析,在保证设计要求可靠度的前提下,对斜拉桥索力进行优化就变得尤为重要.
本文采用基于可靠度的结构优化方法去优化斜拉桥的张拉方案,这种方法将结构受力合理性或成本经济性作为优化目标,将设计要求可靠度作为约束对结构设计变量进行优化.既考虑了不确定因素的影响,又能使结构处于合理受力状态,更能保证施工的安全与效率.
本文介绍的基于可靠度的结构优化方法分为两个模块,第一个部分是结构可靠度分析和灵敏度分析模块; 第二部分是基于拟合函数的非线性优化模块.在结构可靠度和灵敏度分析模块,本文首先采用拉丁超立方体抽样法抽取样本点,之后利用一次二阶矩法分析结构在优化设计前的可靠度指标,并通过灵敏度分析筛选出对结构可靠性影响显著的随机变量,这样可以减少优化过程中分析结构可靠度所需的随机变量的数量,减少拟合响应面所需样本容量,从而提高计算效率.基于拟合函数的非线性优化部分包含两个步骤:拟合目标函数和约束函数; 单目标有约束非线性优化.
拉丁超立方抽样法[4]简单来说就是将随机自变量按照其分布函数等概率分为k个区间(k是样本点数量),然后在每个区间内等概率抽出一点共得到k个点,即为随机自变量的样本点.当对n个相互独立的随机变量进行抽样,以两个自变量为例进行说明:
假设Z=G(x,y)是某结构的功能函数,其中x和y分别为该结构的两个相互独立的随机自变量,k为需要的样本数.将x和y按照各自的概率分布函数等概率分为k个区间,分别为Dx=(dx1,dx2,…,dxi,…dxk)和Dy=(dy1,dy2,…,dyi,…dyk).将向量Dx和Dy组成的二维向量空间看做是一个二维矩阵,在该矩阵中随机抽取k个元素,同时保证抽到的每个元素不同行,不同列.(dxi,dyj)为抽取的区间元素,共抽取k个区间元素,在抽取的每个区间等概率的抽取样本点.
可靠度分析采用传统的一次二阶矩法,对于功能函数较难得到,或者为非显示函数时的情况,需进行功能函数的拟合.响应面法则应用统计抽样技术和回归拟合技术,将原本难以表达的功能函数转化为简单的拟合函数.常用的响应面法有多项式拟合响应面法和BP神经网络拟合响应面法.
本文采用LHS抽样法得到的样本直接拟合多项式响应面[5].多项式响应面函数可以表达为
Z-=G-(X)=a+∑ni=1bixi+∑ni=1∑nj≤idijxixj(1)
式中:∑ni=1bixi代表拟合函数的一次项; ∑ni=1∑nj≤idijxixj代表拟合函数的交叉项和二次项.
假设随机变量服从相互独立的正态分布,按照一次二阶矩法,求得Z的均值和标准差,再通过可靠度指标的基本概念,最后得到下式.
ET*K*E-2ET*K*(A·D)β+(A·D)T*K*(A·D)β2=0(2)
式(2)是一个关于β的二次方程,求解该方程理论上可以得到两个可靠度指标β1和β2这时就需要和MC法得到的可靠度指标βmc做对比,选择于βmc较接近的解作为可靠度指标βFOSM.
BP神经网络(BPANN)[6,7]是一种单向传播的多层前馈网络结构,也是目前应用最广泛的一种网络结构.一个完整的BP神经网络结构包含:输入层、输出层、隐含层共三部分[8],如图1.隐含层可以为单层或多层,同层的神经元之间没有联系.信号由输入层输入,经过隐含层,最后由输入层输出结果,只有相邻的两个层由信号传递,且信号只能单向的传递给下一层,这也称之为多层前馈网络.
本文采用一个具有Tan-Sigmoid型传递函数的3层BP神经网络进行响应面的拟合[9].BP神经网络拟合的响应面函数可以表达为:Z-=G-(X)=
N-1G-(f2(∑pj=1vhf1(∑ni=1whiNxi(xi)-θh)-θ'))(3)
式中f1(·)表示一个Tan-Sigmoid函数,f2(·)表示一个线性函数,N(·)表示归一化函数.
一次二阶矩法[10,11],利用统计信息中数据的一阶矩(均值)和二阶矩(方差)去计算结构可靠度的方法.采用Taylor级数将复 杂的功能函数展开为一次多项式是这个方法的主要内容,然后通过数理统计直接计算结构可靠度[12].
可靠度指标为

其中,αi称作灵敏系数,可以反映第i个随机变量的标准差对整体标准差的影响.
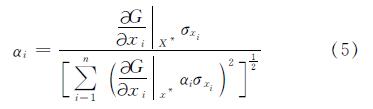
结构的灵敏度需要考虑自变量均值和标准差两方面对结构可靠度的影响,采用大连理工大学杨杰提出的一种计算随机变量灵敏度的方法[13].

式中:Pf表示结构的失效概率; G表示结构的功能函数; x*i表示可靠度分析的设计验算点; μi和σi表示随机变量xi的均值和方差.
随机变量的灵敏度可以表示为
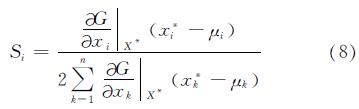
该方法包含了随机自变量均值和方差共同对结构失效概率的影响,不仅能够表征失效概率对各个随机变量灵敏度之间的相对大小,而且所得数值还具有实际含义,可为结构可靠性分析与设计提供参考信息.
本文建立的单目标有约束非线性优化模型如下:
find X=[x1 x2 … xn]T
min fobj(X)
s.t. fcon(X)≥β-1
fcon(X)≥β-2
[X0-0.2|X0|
其中X=[x1 x2 … xn]T表示设计变量组成的向量; fobj(X)表示目标函数(结构的总花费、总质量、构件截面积、弯矩或弯矩能等力学指标); fcon(X)表示约束函数,为结构的某个可靠度指标; β-表示设计要求的可靠度.
本文采用外点罚函数法[9]进行非线性优化,设D={x|βi(x)-β-i≥0,i∈I}为约束集,也称作可行域,首先构造一般形式的外点罚函数:
P(X,rk)=
C(X)+Mk∑nβi=1{min[0,βi(X)-β-i]}2(10)
其中,Mk∑nβi=1{min[0,βi(Xo)-β*i]}2表示罚函数项.当罚函数项为零,表示设计变量满足所有约束条件,反之罚函数项必定大于0,开始影响优化方向使其回到可行域内.Mk称作惩罚因子,为一递增数列,要求Mk>0,一般取M1=1,若不满足-(βi(X(k))-β*i)≤ε,则Mk+1=cMk(c=5或者10),进入下一步迭代.
为了保证设计变量对目标函数和优化函数的拟合精度和优化效率,每次的拟合区间确定为[X0-0.2|X0|
可靠度分析及灵敏度分析计算步骤:
(1)初步拟定影响结构的随机变量X和一组样本数量N1,N2,…,Nm,并确定各个自变量的概率分布函数.(2)建立结构有限元模型,样本数量为Ni,采用基于LHS抽样法的MC法粗略分析结构可靠度.(3)利用(2)中的随机变量样本和有限元模型响应样本拟合分析可靠度的响应面函数.(4)将MC法的分析结果作为初值,带入基于JC法的FOSM法迭代求解结构的精确可靠度β0.(5)利用(4)最终拟合的响应面函数,对设计变量进行灵敏度分析,筛选影响结构可靠度的随机变量.
基于拟合函数的非线性优化方法步骤,如图2.
(1)确定需要优化的设计变量,以及目标函数所选用的指标和约束函数所选用的可靠度指标.(2)初定设计变量的优化区间,一般选择以当前设计方案X0为中心,优化区间[X0-0.3|X0|,X0+0.3|X0|].(3)采用LHS抽样技术,在设计变量优化区间均匀抽取个设计变量样本点.(4)结合有限元模型,计算每个样本点的优化指标,依照可靠度和灵敏度分析模块确定的随机变量数量和样本数量进行可靠度分析,得到相应的优化指标样本数据和可靠度指标样本数据.(5)利用拟合函数拟合设计变量与目标变量、可靠度之间的函数关系式.(6)将(5)中得到的函数关系式分别作为目标函数和约束函数,同时考虑设计变量的优化区间,进行非线性优化求解.(7)分析(6)的优化结果,若结果落在优化区间的中心区域,则停止优化输出优化结果,反之,将结果作为新的优化中心重新执行(2)~(7).
用本文所述的可靠度分析方法和结构优化方法分析优化一个刚架模型[14],如图3所示是一个12层的刚架结构,它包括84个构件和104个自由度.图3中选取A点的水平位移作为要研究的可靠度指标,图中的序号1~5表示相应杆件的规格,同一个序号表示这类杆件采用同一个大小的截面积.
选取了6个随机影响因素以及它们的分布函数,其中Ai表示第i种规格的杆件的横截面积如表1所示,P表示作用在结构上的一个静风荷载,将荷载等效在刚架的节点处,P的均值为30 kN,标准差为7.5 kN,服从Gumbel分布I型分布,假设上述随机变量相互之间没有相关性.假设所有构件的杨氏模量都是一个定值,大小为2.0*107 kN/m2.所有杆件的横截面积和抗弯惯性矩之间的关系表达为Ii=γiA2i(11)为了比较蒙特卡洛法(MC)[15]和基于不同响应面拟合法下的FOSM法的分析结果,本文对该刚架结构同时采用多种方法分析其结构可靠度,在使用FOSM方法时,本文采用两种响应面拟合法拟合响应面:(1)多项式拟合响应面,(2)BP神经网络拟合响应面.图4显示了不同分析方法下,可靠度分析结果随着样本容量的增加的变化趋势.
从图4可以看出,采用基于多项式拟合响应面法(PRSM)分析结构可靠度时,相比于MC法其波动幅度显著减小,但是其分析结果仍然没有收敛,存在小幅度波动.采用BP神经网络拟合响应面法分析结构可靠度时,可靠度分析结果随样本容量的增加几乎没有波动,分析结构收敛性最佳.综上所述,本文选择BP神经网络响应面法对结构进行可靠度分析.从图中看一出,样本容量为50和500的情况下,采用BP神经网络法的可靠度分析结果基本一致,为了提高分析效率,本文可靠度分析所采用样本容量为50,BP神经网络模型为隐含层含有5个神经元的单隐含层神经网络模型. 根据拟合得到的响应面函数,对随机变量进行灵敏度分析,如图5.从中得出随机变量A1、A4、P的灵敏度相比于A2、A3、A5要高,其中随机变量P的灵敏度最高,说明随机变量A1、A4、P对A点水平位移的可靠度指标影响较为显著,其中水平荷载P是主要影响因素.A2、A3、A5灵敏度非常低,可以认为A2、A3、A5的随机性对A点的可靠度分析结果影响不大.选择随机变量A1、A4、P对结构进行可靠度分析.为了确定采用筛选后的随机变量对结构的可靠度分析结果与原分析结果一致,本文将具有3个随机变量模型分析得到的设计验算点和可靠度指标与具有6个随机变量模型分析得到的结果进行比较,如表2所示.
从表2可以看出,采用模型中采用6个随机变量与采用3个随机变量对结构的可靠度分析结果基本一致,表明结构在3个随机变量与6个随机变量的影响下具有相同的失效模式.综上所述,可以采用3个随机变量的BP神经网络模型对该结构在A点的水平位移进行可靠度分析.
根据上述分析,12层刚架模型的可靠度指标为1.47,相应的失效概率为7.09%.为了提高结构可靠度,本文对该刚架结构进行基于可靠度的杆件截面优化设计.根据上一节灵敏度分析的结果,对结构可靠度影响最为显著的随机变量为水平荷载,但是水平荷载属于不可控影响因素,不能人为的改变,因此只能通过优化杆件的横截面面积来提高结构可靠度.根据上文灵敏度分析结果,本文选择灵敏度较高的截面积A1,A4作为设计变量对结构进行可靠度优化设计.建立非线性优化模型如下:find X=[A1,A4]T;
min fobj(X);
s.t. fcon(X)≥β-;
[X0-0.2|X0|
其中,[X0-0.2|X0|
表3显示了优化前后结构的设计验算点和可靠度分析结果.从表中可以看出,经过优化增加了A1、A4的截面积大小,所以对应的设计验算点均有所增加.同时可以看出,P的设计验算点也有所增加,这是因为经过优化,结构失效的条件更加苛刻,需要更大的水平荷载才能导致A点水平位移超过允许值,因此P的设计验算点增大了.设计验算点的变化很好解释了经过优化设计结构可靠度提高的原因.从表中还可以看出,经过优化结构的可靠度从1.49提高到了2.42,失效概率也从6.82%降低到了0.79%,优化效果显著.
表3 优化前后设计验算点及可靠度分析对比表
Tab.3 Design check points and reliability analysis and contrast table before and after optimization
对上述算例采用本文所述的可靠度优化方法优化效果显著,同时采用与该优化方法配套的可靠度分析和灵敏度分析方法也显示优化前后结构各方面性能的改善,客观的对优化设计进行了评价,保证了优化设计的可信度.采用BP神经网络响应面法比多项式响应面法拟合得到的功能函数的拟合优度高.所以在非线性优化模型中也采用BP神经网络拟合优化函数.
本文以某斜拉桥为例进行索力优化.如图6所示,主桥采用钢拱塔斜拉桥,塔墩固结,塔梁分离,双索面半漂浮体系,钢箱梁跨径布置为80+80=160 m,单幅桥宽23.5 m.全桥钢结构重约7 109 t.主梁和桥塔均为钢结构,均采用Q345qD型钢材.采用顶推法借助临时墩的支撑完成主梁施工,之后通过张拉斜拉锁完成体系转换.
本桥主梁采用钢箱梁结构形式,梁高1.8 m,单箱多室结构.主塔与墩固结,钢拱塔外观横立面呈斜伸的双网球拍型,塔高约51.46 m,其中桥面标高以上部分高39.718 m.拉索采用密索体系,顺桥向及横桥向对称布置,拉索为空间索.钢箱梁横截面截面原张拉方案,在斜拉索初次张拉之后,已经没有临时墩支撑的情况下,边墩支座反力为2.763 t.但是在实际工程中,由于诸多不确定因素的影响,导致初次张拉后,钢箱梁的边墩支座脱空.因此,本文将考虑不确定因素影响,对该桥边墩支座反力进行可靠度分析,并通过优化初次张拉方案.
采用BEAM44单元模拟主梁和索塔,采用LINK10单元模拟斜拉索和水平索,为了提高有限元计算速度,钢箱梁,索塔和拉索均采用数值截面.对于斜拉索不考虑垂度效应的影响,通过控制拉索的无应力索长来使模型达到设计状态.
将样本容量为400时的BP神经网络法拟合函数作为结构边墩支座支反力R0的功能函数,对结构进行可靠度和灵敏度分析.
图8是考虑27个变量,并对有限元模型进行400次抽样后的灵敏度分析结果,从上图可以看出,R0点可靠度指标对参数XL1、XL2、XL3、G、R1、R2灵敏度较高,说明它们是影响R0点受力的主要不确定因素.其中,参数XL1~XL8、XR1~XR8和SP1~SP8表示拉索张拉后对应的无应力索长.G表示钢箱梁由于加工制造的误差,造成梁体自重的不确定性,从图中可以看出,梁体自重对R0点可靠度指标影响最为显著.R1、R2表示由于测量误差和施工误差导致的塔梁支座的标高的不确定性,该误差对R0点可靠度的影响仅次于梁体自重的影响.依据结构灵敏度的分析结果,筛选出灵敏度大于0.01的6个变量对结构进行可靠度分析,结果见表4.
从表4可以看出,筛选变量并压缩样本容量后,可靠度指标和结构失效概率变化不大,筛选随机变量并没有改变结构的失效模式,筛选后随机变量可以完成对结构的可靠度分析.
对于工程而言,31%的失效概率显然不能保证结构的安全施工和正常使用,有必要采取一系列措施控制R0点的失效概率,通过上一节的可靠度分析和灵敏度分析可知,降低结构失效概率最有效的方法是提高钢箱梁的加工精度和降低塔梁支座的标高误差.然而,这些方案虽然有效但却难以实现,无论是钢箱梁的加工精度和梁塔支座的标高误差,都受到施工工艺水平限制和构件加工机床、测量仪器等器材的限制,都不能在短时间内有所改观,所以只能通过调整XL1、XL2、XL3对应的拉索的张拉程度来优化R0点的可靠度.
本文提出对R0点可靠度的优化方案:将X1、X2、X3对应拉索的张拉程度作为设计变量,采用无应力索长表示拉索的张拉程度,记为XS1~XS3.为了保证优化方案拉索张拉后的主梁线型的接近设计线型,考虑到桥梁结构的对称性,选择一侧主梁的8个下吊点位置的竖向位移作为控制主梁线型的变量,记为d1~d8.
建立非线性优化模型:

数,表示8个下吊点的竖向位移最小化; fcon(XSopt)为优化约束函数,表示R0处支反力要满足设计要求β-,本文中β-取值为2.5.[XS0opt-0.2|XS0opt|
从表5可以看出优化设计后,R0点的可靠度水平显著上升,从0.490提高至2.633,对应从31.14%的失效概率降低至0.42%的失效概率,优化效果明显.优化后的结构失效概率在1%以内,可以满足工程要求,保证了正常使用和施工的安全.
表6显示优化前后钢箱梁和索塔的最大正弯矩和最大负弯矩,以及R0点支座支反力的结构.从表中可以看出,优化后R0点的支座支反力从27.083 kN上升到了203.320 kN,支反力显著提高,这是因为通过对拉索伸长量的优化,将原本由斜拉索承担的荷载部分分配到了R0点的支座上,提高了支座的压力储存,从而降低了支座因脱空而失效的概率.通过优化,并没有改变原设计方案下的结构受力模式,钢箱梁弯矩和索塔弯矩均与原设计方案下的弯矩相近,表明结构其他力学指标仍然满足设计标准,并没有降低结构整体的受力合理性.
通过将基于可靠度的结构优化方法应用于本文所分析的斜拉桥,得到以下结论:(1)在斜拉桥的施工过程中,受到各种不确定因素的影响,可能会产生各种影响施工安全的风险问题.特别是体系转换的施工过程.(2)通过可靠度分析和优化设计切实解决了该桥在拉索完成初次张拉并已撤去临时墩的工况下边墩支反力的可靠度问题,并对优化前后的边墩支反力可靠度进行了评价和对比.(3)经过张拉方案优化设计,拉索初次张拉后,边墩支座支反力显著提高,其可靠度指标也显著提高,失效概率显著降低,被控制在1%之内,优化效果显著.