基金项目:西安市城乡建设科技计划项目(SJW2019-10)
第一作者:黄 莺(1979—),女,博士,副教授,主要研究方向为建筑施工安全与应急管理,E-mail: cch-by@163.com
(1.西安建筑科技大学 土木工程学院,陕西 西安 710055; 2.上海建科工程咨询有限公司,上海 200032)
(1.School of Civil Engineering, Xi'an Univ. of Arch. & Tech., Xi'an 710055, China; 2.Shanghai Jianke Project Management Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200032, China)
prefabricated building; falling accident; risk assessment; DS evidence theory
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2022.01.002
建筑业是我国安全事故的高发行业,而高处坠落事故在所有建筑安全事故中占比最高.中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部2018年的安全事故情况通报[1]显示,高处坠落事故占比高达52.2%,是造成人员伤亡和经济损失的主要事故类型.装配式建筑作为目前建筑行业发展的热点,其施工方式不同于传统建筑,由于不便于搭设内外脚手架,安装预制外墙板时,工人需在高空临边处作业,极易导致高处坠落事故的发生.因此,研究装配式建筑施工发生高处坠落事故的风险因素并建立有效的风险水平评价方法,对于提高安全管理效率、促进装配式建筑在我国的持续健康发展尤为重要.
目前,装配式建筑施工安全问题的研究主要从风险因素和风险评价的角度开展,如李皓燃等[2]采用SEM确定了装配式建筑施工5个阶段的关键风险因素,并分析了各阶段风险因素间的关联性; Fard等[3]通过对125个装配式建筑施工安全事故的调查研究,分析了事故的伤害类型及发生的原因; Tao Wang等[4]依据建筑工业化建设过程,构建了包括风险识别、风险分析和评估以及风险处理和控制的风险管理网络模型; 赵向东[5]采用系统动力学建立了建筑工业化全过程安全风险识别反馈模型,并基于可拓优度评估方法,构建了安全风险评估模型.关于施工安全风险评价的研究,还有很多学者在分析装配式建筑施工风险因素的基础上,采用灰色聚类[6]、测度理论[7]、集对分析[8]、神经网络[9]、突变理论[10]等方法构建了装配式建筑施工安全风险综合评估模型,以测评装配式建筑施工过程中的安全状态.
现有研究对装配式建筑施工中频发的高处坠落事故涉及较少,而装配式建筑施工中存在大量的吊装、拼接等高处作业,极易发生高处坠落事故.此外,在风险评价过程中,大多定量研究的初始数据常采用专家打分得到,其结果具有较强的主观性,而DS证据理论能有效融合不确定信息,现已广泛应用于风险分析与决策等邻域[11-13].因此,本文通过实地调研及专家咨询,在充分识别装配式建筑施工高处坠落风险因素的基础上,采用结构熵权法确定指标权重; 针对DS证据理论高冲突证据融合结果不合理的缺点,引入权值分配与矩阵算法改进DS证据理论的合成法则,以有效融合各位专家的评价意见,定量评估装配式建筑施工过程中发生高处坠落事故的风险,为后续施工采取何种防范措施提供辅助决策支持.
装配式建筑施工高处坠落风险评价的首要任务是识别风险因素,建立风险评价指标体系.与传统建筑工程相比,装配式建筑施工机械化程度高,在吊装拼接过程中存在大量的临边高空作业.在装配式建筑施工过程中,脚手架和塔吊的安装、拆卸与使用、临边与洞口处、吊篮或施工机具作业等部位都存在着发生高处坠落事故的风险.通过分析56起高处坠落事故案例发生原因,发现高处坠落事故的发生的原因具有很强的综合性,并且人、物、环境及管理是事故发生原因的基础构成因素.通过对实际项目调研与专家咨询,并查阅《建筑施工安全检查标准》(JGJ 59-2011)等标准规范,分析确定了装配式建筑施工中引发高处坠落事故的风险因素.用SPSS软件分析风险因素的重要度与离散度,最终构建出如图1所示的风险评价指标体系.
DS证据理论也称为Dempster-Shafer证据理论,1967年Dempster首次提出,后由Shafer[14]在此基础上进一步发展.DS证据理论作为一种不确定推理方法,具有直接表达“不确定”和“不知道”的能力.它通过信任函数度量未知因素引起的不确定性大小,从而有效表示和处理不确定信息,使评估结果更加准确可靠.目前已被广泛应用于决策与风险分析、人工智能、目标识别等领域.传统DS证据理论的相关基本概念奚婷婷[15]对其进行了详尽的论述,基于这一法则,多个独立证据的融合结果为
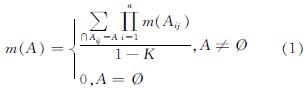
式中: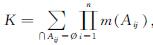 ,表示n个独立证据m1,m2,…,mn的冲突系数.
,表示n个独立证据m1,m2,…,mn的冲突系数.
采用传统证据理论的合成法则融合高冲突证据,其结果难以客观反应评价意见,并且运算时间会随着证据数量的增加呈指数增长.本文在已有研究基础上,采用权值分配方式改进证据理论合成法则,以增加高冲突证据融合结果的可靠性,再通过矩阵算法缩短运算时间[16],具体过程见3.2小节.
结构熵权法是程启月[17]基于熵理论,提出的一种主客观相结合确定权重的方法.其基本思想是:采用德尔菲法采集专家意见,形成典型排序矩阵,再根据熵理论计算熵值,通过认识盲度减少典型排序的不确定性.最后对总体认识度归一化处理,即可得到指标的权重向量.采用该方法确定指标权重,不仅能降低采用主观赋值专家认知不确定性的影响,同时能避免客观赋值收集大量数据的困难.因此,本文采用结构熵权法确定指标权重,具体步骤参见文献[17].
(1)构造隶属度矩阵
模糊集理论可有效减少专家评价意见不确定性影响,因此,采用高斯型隶属度函数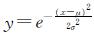 来表示正态分布的特征,式中μ表示不同风险等级的函数中心,σ表示专家对评价意见的不确定度,σ越大,表示不确信度越高.通过该隶属度函数,可求出指标评价意见属于不同风险等级的隶属度,进而构造出各指标的隶属度矩阵.
来表示正态分布的特征,式中μ表示不同风险等级的函数中心,σ表示专家对评价意见的不确定度,σ越大,表示不确信度越高.通过该隶属度函数,可求出指标评价意见属于不同风险等级的隶属度,进而构造出各指标的隶属度矩阵.
本文将专家评价等级划分为很低、低、中、高、很高五个等级,并定义相应的函数中心μ分别为0、0.25、0.5、0.75、1.
(2)数据融合
首先,通过权值分配方式将证据冲突系数K依据平均支持度q(A)进行分配.改进后的合成法则如下:
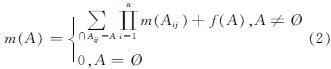
式中:f(A)=K·q(A)表示证据冲突的概率分配函数,且f(A)满足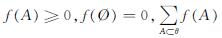
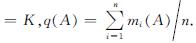
其次,引入矩阵算法对经权值分配改进后的合成法则进行改进.
设邀请n位专家评价高处坠落风险,评价等级如前所述分为五个等级,通过对隶属度矩阵归一化处理,可得mass函数:

其中:mij为专家i对某指标评价意见属于j级风险的置信度,并且满足行和为1,即:mi1+mi2+mi3+mi4+mi5=1,i=1,2,…,n.
首先对证据1和证据2合成,将M1的转置和行向量M2相乘,得矩阵:

其中:对主对角线元素求和为式(1)中的分子,对非主对角线元素求和为系数K.
取矩阵R1中主对角线元素构成列向量,与向量M3相乘,得新矩阵R2.此时,对矩阵R2主对角线元素求和仍为式(1)中的分子,但K应为矩阵R1和R2中所有非主对角线元素求和.
依次类推,将n条证据逐一融合,最终得到的矩阵Rn-1.对矩阵Rn-1中主对角线元素求和仍为式(1)中的分子,冲突系数K为矩阵R1,R2,…,Rn-1的所有非主对角线元素之和.
以上即为通过权值分配与矩阵算法改进后的证据合成步骤,其法流程如图2所示.
图2 基于权值分配与矩阵算法改进的证据合成流程图
Fig.2 Improved evidence synthesis flow chart based on weight assignment and matrix algorithm
(3)指标mass函数合成
结合所确定的权重,对所有二级指标的基本概率分配进行合成,得一级指标的基本概率分配:
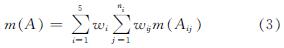
式中:m(Aij)表示指标Aij对A的支持度,ni为各一级指标所含二级指标个数.
(4)风险综合评价
为定量评价装配式建筑施工高处坠落风险水平,本文将高处坠落的五个风险等级取值限定于[0,1],通过对[0,1]进行等同划分,如表1所示,以界定风险等级,并定义各风险等级对应的评价量化值分别为0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9.
通过将一级指标的基本概率分配与对应的评价量化值相乘,并对其单值化处理,即可得到风险综合评价值与潜在主要风险因素.
相比DS证据合成法则,该方法能克服高冲突证据融合不合理与大数据导致的工作效率低下问题,使评价结果更为可靠.
本文选取某装配式建筑项目29#住宅楼进行实证分析,该住宅楼地下1层,地上32层,建筑高度91.55 m,总建筑面积15 665.16 m2,主体结构形式为剪力墙结构,墙体与楼梯均为预制墙板与楼梯,楼板采用叠合楼板,预制构件节点处通过现场浇筑混凝土连接.
依据图1建立的装配式建筑施工高处坠落风险评价指标体系,邀请20位相关专家对风险指标进行重要性排序.为简化计算,并有效减少极端评价值的影响,基于派生德尔菲法,将这20位专家按照5人一组,分成4组,各组专家相互独立的进行若干轮讨论后,给出各级指标的重要性排序表,形成各级指标的典型排序矩阵,具体见表2.根据结构熵权法计算公式,得出各级指标权重:w=(0.328,0.262,0.182,0.228),w1=(0.244,0.271,0.210,0.134,0.141),w2=(0.366,0.217,0.174,0.243),w3=(0.345,0.263,0.163,0.229),w4=(0.443,0.557).可见,人的因素中“三违行为”、自身缺乏安全意识是较大风险因素; 支撑设施搭设不合格,安全防护不到位是物的主要风险因素; 管理因素中制度不健全、安全技术措施不全面是主要风险因素; 现场吊装作业环境为主要环境风险因素.
编制指标定量评定表,邀请10位专家根据图1的评价指标体系与五个风险等级,评定各指标的风险等级及相应的不确定度.将收集到的数据代入隶属度函数中,求出隶属度矩阵.通过对隶属度矩阵进行归一化处理,即可得到各二级指标的基本概率分配.由于篇幅有限,本文只列举专家1的评价意见及数据处理结果,如表3、4所示.
根据所改进的合成法则,运用MATLAB进行编程,融合10位专家的评价意见,数据融合结果见表5.最后通过指标权重及公式(3)对表5中的数据逐层融合,得一级指标基本概率分配,结果见表6.
通过对一级指标的基本概率分配与各等级风险量化值相乘,计算出风险综合评价值R为0.443 7,即发生高处坠落的风险等级为中,将一级指标C1~C4分别做单值化处理,得风险值R1=0.511 0、R2=0.377 0、R3=0.448 0、R4= 0.419 9,由R1>R3>R4>R2可知,人的因素是较大风险因素,其次是管理因素,环境和物的因素对引发高处坠落事故的风险相对较小.这与实际情况相符,表明所提出的风险评价模型对高处坠落风险评价的有效性与实用性.
在施工过程中,对施工人员应做好系统、持续化的安全培训教育,针对不同高空作业类型设立特定的培训内容,以提升施工人员的安全意识,从根源上预防高处坠落事故的发生; 同时,应不断完善安全管理制度,确保管理人员履行好监督管理职责.
在风险评价过程中,当专家意见差异较大时,采用DS证据合成法则进行融合,其结果难以反映实际评价情况.以自身缺乏安全意识(C12)为例,有7位专家给出的意见为中风险等级,其余3位专家所给评价意见为高风险等级,计算其冲突系数K为0.887 5,采用传统合成法则进行数据融合,结果为“中”的概率为0.987 6,近乎为1,而“高”的概率是0.012 4,而实际上10位专家中有3位专家的意见是“高”,由此可见传统方法合成的结果并不能完全客观反应评价意见.采用本文改进的合成算法进行融合,结果为“中”的概率为0.693 9,“高”的概率为0.279 0,显然,采用该方法有效地反应了3位专家意见为“高”的事实.因此,采用本文改进的合成法则融合数据,能有效地解决高冲突证据融合结果不合理问题,两者融合结果对比见表7.
(1)通过研究高处坠落事故的风险因素,结合装配式建筑施工的特点,从人、物、管理、环境四个方面构建了装配式建筑施工发生高处坠落事故风险评价指标体系.这将有利于管理人员对这些风险因素加强监管,从而减少高处坠落事故的发生.
(2)采用结构熵权法确定指标权重,可利用典型排序的信息熵,减少专家认知模糊性的影响.结合模糊理论,采用高斯函数确定评价意见隶属于不同风险等级的程度,能有效降低评价意见的主观性.
(3)运用本文所改进的合成法则对评估数据进行融合,能综合考虑每个证据,减少因人的判断偏差而引起的随机误差,保证高冲突下证据融合结果的可靠性,并提高运算效率.通过实例分析,验证了该模型评价结果的有效性与实用性,从而为制定预防方案提供辅助决策支持.