基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(52168069,52068037,51568028)
第一作者:张智吉(1997—),男,硕士生,主要研究结构工程抗震.E-mail: 1097467690@qq.com 通信作者:张品乐(1975—),男,博士,副教授,主要研究结构抗震和防灾减灾.E-mail: 554689591@qq.com
(昆明理工大学 建筑工程学院,云南 昆明 650500)
(School of Civil Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650500, China)
high-strength steel bar; high-strength concrete; short-leg shear wall; seismic performance; seismic damage model
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2022.01.006
短肢剪力墙结构体系作为近十多年来的新兴结构体系,因其具有结构布置灵活、建筑结构经济等优点,在我国许多地区得到广泛的推广及应用.受限于短肢剪力墙的构造特点,其抗震性能表现差强人意[1-4],《高层建筑混凝土结构技术规程》[5]中对其适用条件有严格的要求,如何提高短肢剪力墙的抗震性能有待继续研究.近年来国内外学者开展了一系列的探究[6],曹万林等[7]、苏益声等[8]、张敏等[9]试验研究表明,对短肢剪力墙进行带暗支撑、带型钢、局部设缝等构造措施能有效提高短肢剪力墙的抗震性能,并已形成较为全面的理论.但以上研究也存在施工难度不低,工程造价成本偏高等问题.
结构的抗震性能实质就是结构的损伤性能[10],结构地震损伤是一个随着地震作用不断累积的过程,各项力学性能随之逐渐退化,最终结构破坏、倒塌,掌握结构地震损伤性能和破坏规律,明确其损伤程度是十分重要的.损伤指数便是能定量描述结构地震性能的重要参数,建立适合的损伤模型可以较为确切的反应损伤指数,采用地震损伤指标对目标性能进行量化也已成为研究的趋势.依据结构震后破坏模式可将其分为首次超越破坏和累积损伤破坏两种形式,与之相对应形成首次超越破坏准则和能量、变形双控准则[11],国内外学者针对此提出了多类损伤模型,基于变形[12]、刚度[13]、能量[14]等基于单参数损伤模型都具有一定的局限性,考虑位移与滞回耗能的Park-Ang双参数损伤模型[15]被广泛认可,但其仍然存在不足,王东升[16]、Kunnath[17]、陈宗平[18]、jiang[19]等在Park-Ang损伤模型基础上提出了各类修正的损伤模型.
高强材料作为现代化施工工艺与新理论结合的产物被广泛推广及运用,高强钢筋及高强混凝土具有强度高、经济效益明显等优点,将两者结合而成的短肢剪力墙抗震性能还有待考究.研究高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙的抗震性能及损伤特性的需求应运而生.本文设计6个一字形高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙构件进行低周水平往复荷载试验,分析其试验过程中累积损伤及破坏现象,研究其抗震性能,结合相关剪力墙地震损伤模型[21-24],建立了适用于高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙的累积损伤模型,为其结构震后有效评估和修复加固提供依据.
试验试件为6个缩尺比例为1:2的一字形高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙,试件竖向高度为1 400 mm,截面厚度为100 mm并按高厚比为5:1、6.5:1和8:1以此确定试件截面高度,试件参数见表1.试件SPW500-1、SPW650-1和SPW800-1端部箍筋间距为100 mm,其余试件端部箍筋间距加密为50 mm,具体配置见图1.
试件钢筋均为HRB500E型高强钢筋,纵筋、箍筋直径分别为12 mm、6 mm,钢筋材性见表2.试件混凝土设计强度为C60,普通施工方式浇筑,室内自然养护.每个试件预留三组混凝土立方体标准试块进行材性试验,混凝土材性指标见表3.
通过图2所示加载装置对6个试件按位移控制法进行低周往复荷载试验.首先由油压千斤顶一次性对加载梁按设计轴压比加载到预设值,为保证作用力一直保持竖直方向,使用了半球形铰.之后再由水平作动头对墙体施加水平往复荷载,工况荷载位移增量2 mm,往复3次.当发现试件破坏失去承载力或水平荷载减小至极限荷载的85%时,停止试验.
各试件最终破坏形态如图3所示,依据其破坏过程及结果可将其分为弯曲破坏和弯剪破坏两类进行损伤说明.
(1)弯曲破坏
试验加载初期,混凝土未开裂前试件处于弹性阶段.伴随着第一条水平裂缝在腹板端部出现,试件进入开裂阶段.随着荷载的增加,受拉纵筋开始屈服,试件进入屈服阶段.之后原有腹板端部的水平裂缝向腹板内部延伸,同时在周围发现更多的细小水平裂缝及竖向裂缝,墙身也渐渐出现斜裂缝并不断发展,混凝土端部受压区开始鼓起、剥落.最终多条水平裂缝汇集成一条主水平裂缝,纵筋断裂,端部混凝土压碎失效.
损伤特性:大剪跨比试件SPW500-1和SPW500-2(>2.15)弯曲破坏特征明显,受压区混凝土被压溃,纵筋受拉屈服.试件破坏时墙体受压侧混凝土先被压碎,并逐渐向内部发展,该侧纵筋也随之被压缩,箍筋为约束混凝土受力较大而变形; 受拉侧混凝土较早开裂并退出工作,拉力主要由纵筋承担,纵筋按从最外排开始向内发展规律被拉断破坏,该侧箍筋应变小,说明受剪作用很小.
(2)弯剪破坏
加载初期与弯曲破坏试件损伤相同,但在构件进入屈服阶段,竖向裂缝产生后,端部会较早出现贯通的水平裂缝和极少混凝土剥落,随着继续加载,端部竖向裂缝延墙高发展明显,多条新的贯通水平裂缝在端部出现,原有水平裂缝向墙体内部延伸,端部混凝土出现明显剥落且呈块状,墙身出现多条斜裂缝并交叉形成了X形的交叉斜裂缝,最终主裂缝附近混凝土压溃剥落,形成靠近墙体底部的水平破坏带,纵向钢筋压曲,主筋未断裂,只有端部边缘箍筋约束区残留少量混凝土,墙体非约束区混凝土几乎全部剥落.
损伤特性:较小剪跨比试件SPW650-1、SPW650-2、SPW800-1和SPW800-2(≤2.15)弯剪破坏特征明显,拉压破坏特性模糊,强度丧失快.试件破坏从两端混凝土压溃开始,破坏区域迅速向内部延伸,形成一条明显的主水平破坏带,表现为混凝土压溃; 纵筋没有表现出拉断或颈缩的明显破坏现象,主要表现为水平错动,应变小,受弯成分少; 箍筋产生明显变形且大于受压时的变形,受剪作用大.
试验所测数据经后期处理可得如图4所示试件滞回曲线,通过观察分析可得:
(1)试件在位移循环下,正负向初始刚度相同,因无翼缘作用,正负向刚度退化程度、承载力及变形能力无较大差异,虽然试件会因制作、加载产生误差,但其误差在可容许范围内,因此可得出较为规律且关于原点对称的滞回曲线,相较于T形和L形可将正负向材料性能充分发挥,避免翼缘材性的浪费;
(2)试件在开裂前处于弹性工作阶段,存在极少残余应变; 开裂至屈服阶段残余应变略微增加,滞回曲线所包的面积小,刚度退化不明显,耗能能力弱; 试件进入屈服阶段后,残余应变显著增大,滞回曲线愈发饱满,刚度退化明显; 在达到极限荷载之后的加载过程中,承载力不断下降,刚度逐渐丧失;
(3)试件破坏整体趋势与普通一字形短肢剪力墙[4]相似,通过使用高强钢筋其滞回曲线在屈服阶段后的加载过程中都更为饱满,残余变形也更小,同时试件屈服后的承载力因高强材料整体协同发挥作用相较普通短肢剪力墙拥有更大的承载余力,因此高强材料短肢剪力墙的抗震性能比普通短肢剪力墙更好;
(4)对比试件SPW650-1和试件SPW650-2滞回曲线图4(c)和图4(d),在相同轴压比及高厚比条件下,采用对墙体端部箍筋适当加密的构造措施,滞回曲线包络面积明显增大,滞回环更为饱满,耗能能力和延性等抗震性能都有显著提高;
(5)对比试件SPW500-1和试件SPW800-1滞回曲线图4(a)和图4(e),在相同轴压比及配箍率条件下,随着剪跨比的减小,试件承载力有显著提高,但滞回曲线总体更靠近Y轴,展现出趋于脆性破坏的特征,延性变差,滞回环捏缩效应更为明显,此时要特别注意墙体两端约束边缘构件的抗震设计.
各试件的屈服荷载、峰值荷载、极限荷载及与荷载对应的位移实测值见表4.表中屈服点采用能量等值法确定,即理想弹塑性体系所对应的屈服位移为所求的屈服位移,如图5所示; 峰值荷载及位移取试件承受最大荷载时所对应的荷载和位移; 极限荷载及位移取试件达到最大荷载后随位移增大而荷载下降至最大荷载85%左右时相对应的荷载和位移.延性为极限位移与屈服位移之比.
(1)为比较不同高厚比对试件的影响,选择试件SPW500-1、SPW500-2分别对比试件SPW800-1、SPW650-2,峰值承载力分别提高了84%和56%,但延性降低了18%和1%.不难看出增大高厚比可提高试件承载力,但对其延性有不利影响,因此在构件设计时需综合考虑经济性及试件延性,不能一味追求承载力的提升;(2)对比试件SPW500-1和SPW500-2,轴压比从0.1变为0.3,其峰值承载力提高了10%; 试件SPW800-1和SPW800-2,轴压比从0.1变为0.2,其峰值承载力提高了23%,因箍筋加密对承载力提高并不明显,可见在轴压比限制内适当增大轴压比,可有效提高短肢剪力墙的承载能力;
(3)6个试件平均峰值承载力为266.7 kN,远高于普通一字形短肢剪力墙(175.7 kN[4]),承载力可提升52%,因此采用高强材料对其承载力提升明显; 但采用高强材料对其延性有不利影响,试件延性系数平均值为3,相较普通一字形短肢剪力墙(5.1[4])下降41%,因此需严格限制高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙轴压比;
(4)试件SPW650-2相较SPW650-1采用端部箍筋加密的方法,使峰值承载力提高了4%,延性提高了22%,这是因为箍筋加密后,对混凝土有更好的约束力,在大变形下也能保证混凝土参与工作,优化了整个试件的变形能力,使延性有较大提高,但只在墙体端部范围进行加密,墙身面积占比较小,因此对承载力的提高较小,故可采用约束边缘构件的措施与高强材料互补提高墙体性能.
通过研究高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙在低周往复荷载作用下的试验结果,结合构件的滞回耗能进行分析,以图6试件SPW650-1为例可将构件损伤过程分为以下几个阶段:
(1)无损阶段:高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙在开裂之前主要处于弹性阶段,构件损伤主要集中在短肢剪力墙内部,刚度和强度无明显退化,此阶段损伤较小,可忽略不计;
(2)轻度损伤阶段:伴随着构件腹板端部产生第一条水平裂缝,标志着墙体进入此阶段.随着荷载增加,陆续产生新裂缝,构件损伤逐渐增大,同时主筋应力缓慢增加,但仍处于弹性阶段.此阶段损伤主要是因腹板端部混凝土开裂及裂缝发展造成,刚度衰减不明显,不影响结构安全使用;
(3)中度损伤阶段:此阶段腹板受拉纵筋开始屈服,原有腹板端部的水平裂缝继续向腹板内部延伸,同时在周围新增多条细小裂缝,伴随循环位移的加载,腹板端部受压区混凝土出现竖向裂缝,墙身出现斜裂缝.此阶段损伤主要是因新老裂缝不断发展,部分混凝土失效,试件刚度下降较快;
(4)重度损伤阶段:墙体纵筋已经屈服,端部竖向裂缝延墙高发展明显,水平裂缝增多,端部混凝土出现明显剥落且呈块状,墙身出现多条斜裂缝并交叉形成了X形交叉裂缝.此阶段损伤主要是因大量斜裂缝发展和贯通,受压区混凝土逐渐失效;
(5)破坏阶段:端部受压区混凝土出现外鼓开始大量剥落,端部箍筋暴露,原有水平裂缝汇集成一条主水平裂缝并向腹板内部发展,X裂缝向下延伸约占墙高三分之二,纵筋压曲,此阶段试件承载力快速丧失,无法继续加载,墙体失去承载力.
损伤指标的选择和性能目标的量化是结构抗震设计的主要内容之一,结构损伤的量化应较为合理的反应震后损伤程度,现有的单参数或者双参数损伤模型采用强度、刚度、变形、延性等来作为损伤参数反映结构或者构件非线性变形引起的破坏,也有学者将滞回曲线累积耗能,累积塑性变形作为参数来反映非线性循环引起的累积破坏.在此结合试验研究得到的大量数据,研究可真实反映构件损伤状态的损伤模型,其损伤模型与试验结果的吻合程度可以较好的反映该损伤模型的正确性.基于高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙破坏特征,结合试件的加载破坏过程,以美国ATC[25]给出的损伤状态划分以及相应的损伤指数范围为基础,结合高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙的试验结果,表5给出了适合高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙的损伤状态与相应指数的量化值.
损伤模型一般由位移、能量等参数组合而成,下文对几种经典损伤模型进行介绍.
(1)Powell-Allahahadi损伤模型
Powell-Allahahadi所提出的是只考虑结构塑性变形的损伤模型,未考虑滞回耗能的影响,评估表达式为
D=(δm-δy)/(δu-δy)=(δm/δy-1)/(δu/δy-1)=(u-1)/(uu-1)(1)
式中:D为试件损伤指数; δm为地震作用下构件的最大变形; δu为单向荷载下构件的极限变形; δy为构件屈服位移; u为构件位移延性系数; uu为构件极限延性位移系数.
(2)Gulkin-Sozen损伤模型
Gulkin-Sozen提出的是通过刚度的降低定义损伤模型,评估表达式为
D=1-(km)/(k0)(2)
式中:k0为构件初始刚度; 一般为开裂点的刚度; km为构件最大位移时的刚度.
(3)Park-Ang双参数损伤模型
Park-Ang提出的是综合考虑变形及累积滞回耗能的损伤模型,评估表达式为
D=(δm)/(δu)+β(∫dE)/(Qyδu)(3)
式中:∫dE为构件的累积滞回耗能; Qy为构件的屈服强度; β为构件的耗能因子.
依据表4损伤指数及所对应损伤状态的划分,选用Powell-Allahahadi模型、Gulkin-Sozen模型和Park-Ang模型与试验损伤曲线进行对比分析,如图5所示.
从图7中可以看出,Powell-Allahahadi延性损伤模型、Gulkin-Sozen刚度退化模型与试验损伤曲线符合度不高,且分别在屈服及开裂后损伤指数开始大于0,Park-Ang双参数模型相较更为符合试验损伤值,但仍有一定的离散性.
在Park-Ang模型的基础上,结合高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙抗震性能试验过程,提出变形与耗能相结合的双参数地震损伤模型,其损伤变量表达式如下.
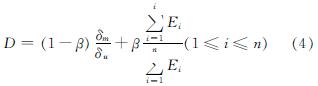
式中:Ei为第i个荷载循环下构件的耗能增量;(1-β)和β为线性组合系数,β的影响因素包括轴压比、体积配箍率等,文献[26]建议表达式为
β=(-0.357+0.73λ+0.24n0+0.314ρ)×0.7βw (5)
式中:λ为构件的剪跨比,当λ<1.7时取1.7; ρ为构件纵筋的配筋率,小于0.75%时取0.75%; ρw为构件的体积配箍率; β一般在0~0.85之间变化.依据式(5)计算方法β取值如表6即为所求.
所提出的双参数地震损伤模型与试验损伤曲线如图8所示.从图8(a)和图8(b)可以看出,构件SPW500-1损伤模型在试验加载初期与试验损伤值较为符合; 中度损伤阶段及破坏阶段虽然损伤模型和试验损伤值的符合度不高,但仍能体现出构件损伤积累、发展的过程.从图8(c)可以看出,构件SPW650-1在重度损伤之前,损伤模型和试验损伤值较为吻合,重度损伤阶段损伤模型和试验损伤值有一定的离散性.从图8(d)可以看出,虽然构件SPW650-2在中度损伤阶段损伤模型和试验损伤值吻合度不高,但两条曲线走势一致,仍能反应出构件损伤积累、发展至破坏的过程.从图8(e)可以看出,构件SPW800-1和SPW800-2从加载至重度损伤阶段,损伤模型和试验损伤值都较为吻合,在破坏阶段有一定偏差.从图8(f)可以看出,构件SPW800-2在加载至中度损伤阶段前损伤模型和试验损伤值吻合较好; 中度损伤阶段损伤模型和试验损伤值的离散性较大,但仍可较好体现构件试验损伤过程,破坏阶段损伤模型和试验损伤值也有离散性,但偏差不大.
通过图8对比可知,本文提出的高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙地震损伤模型,从加载初期直至构件破坏,试验损伤值和损伤模型都有较高的吻合度,虽然试验损伤值和损伤模型在有些阶段具有离散性,但偏差不大.结合构件试验损伤全过程仍然能被较好的体现,可为基于损伤的震后研究提供参考.
(1)试件的破坏形式可分为弯曲破坏与弯剪破坏两类,轴压比和剪跨比是影响其破坏特性的主要因素,随着轴压比的增大与剪跨比的减小试件承载力有明显提升,但受剪特性愈发明显,考虑延性影响应对轴压比限值严格控制.
(2)与普通短肢剪力墙相比,高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙承载力提升较大,虽然试件延性不足,但采用端部密配高强箍筋的构造措施可以有效提高试件的整体性能,满足抗震所需,对受剪占比大的试件作用更为明显.
(3)基于高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙抗震性能试验,提出了与之对应的双参数地震损伤模型.通过与试验结果对比,发现该模型能较好的体现试验构件的累积损伤程度,计算简易,可为高强钢筋高强混凝土短肢剪力墙震后损伤评估及修复提供参考和依据.