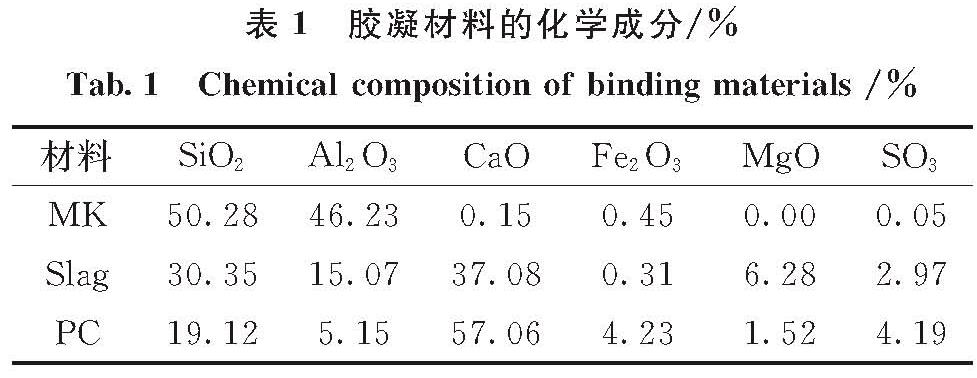
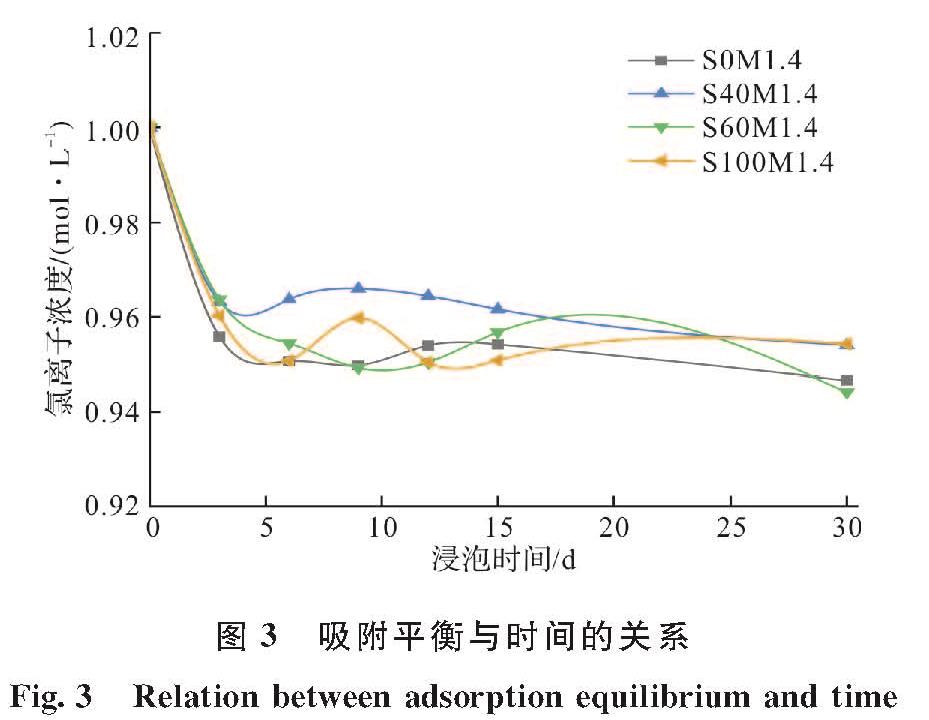
氯离子固化会影响氯离子的传输规律,进而影响碱激发偏高岭土/矿渣的耐久性能.本节采用等温吸附平衡法和XRD表征方法研究矿渣掺量、激发剂模数和激发剂浓度对AAMS固化氯离子性能的影响,并与水灰比(w/c)为0.4和0.6的水泥净浆的氯离子固化性能对比.
2.1 PC净浆的氯离子固化能力
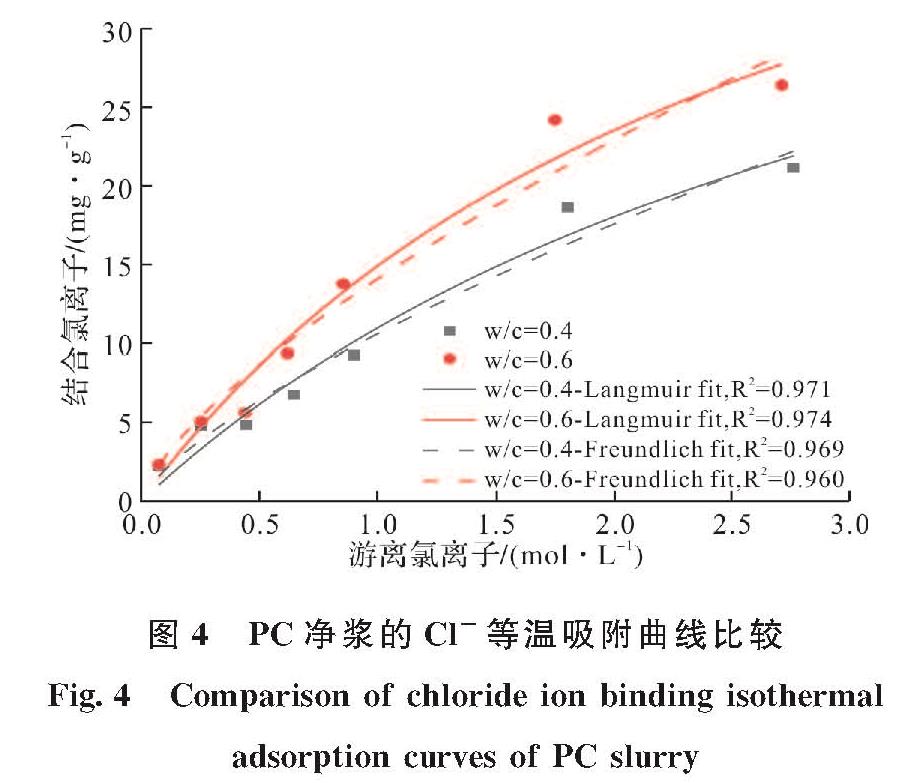
图4描绘了不同水灰比的硬化PC净浆在氯盐溶液中浸泡30 d后游离氯离子(Free chloride, Ce)与结合氯离子(bound chloride, Cb)之间的关系.由图4可看出,随着总氯离子浓度增大,PC净浆固化氯离子的能力和游离氯离子浓度都有所增大,这是因为随着外部氯离子浓度的增大,使得水泥水化产物C-S-H凝胶和AFm相接触氯离子的可能性增加,这两种水化产物分别可对氯离子进行物理吸附和化学结合.另一方面,PC净浆固化氯离子能力随着水灰比的增大而提高,这是由于水灰比可以提高水泥的水化程度,并导致微孔尺寸增大,从而提高对氯离子的吸附能力[2,28].水泥产物C-S-H凝胶对氯离子的物理吸附能力可由Langmuir等温线拟合,而AFm相对氯离子的化学结合(生成Friedel's盐)能力可由Freundlich等温线拟合[2].由图4可看出,与Freundlich等温线相比,Langmuir等温线的拟合优度更大,这表明本文试验中水泥净浆的氯离子固化能力以C-S-H凝胶对氯离子的物理吸附为主,与北欧标准试验方法NT BUILD 492中的结论相同[22].
图4 PC净浆的Cl-等温吸附曲线比较
Fig.4 Comparison of chloride ion binding isothermal adsorption curves of PC slurry
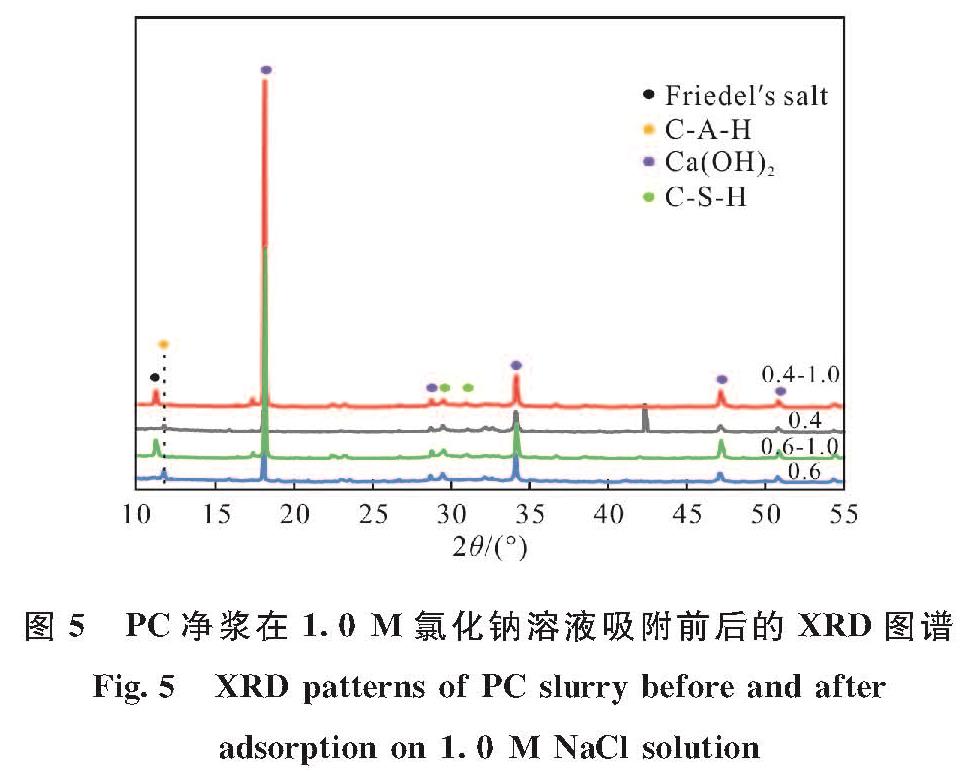
图5给出了不同水灰比的PC净浆和其在1.0 M NaCl溶液中达到吸附平衡后的XRD图谱.由图5可看出,吸附平衡后出现了新的物相Friedel's盐(Ca2Al(OH)6Cl·2H2O, PDF#42-0558).Pa-padakis等[29]认为Friedel's盐可通过吸附沉淀(氯离子与铝酸三钙相结合)或离子交换(具有很高电负性的氯离子置换出AFm相中的OH-)机制形成.因此,这里Friedel's盐的形成表明了水泥净浆对氯离子的化学结合能力的存在.
图5 PC净浆在1.0 M氯化钠溶液吸附前后的XRD图谱
Fig.5 XRD patterns of PC slurry before and after adsorption on 1.0 M NaCl solution
2.2 碱激发偏高岭土/矿渣硬化浆体(AAMS)的氯离子固化能力
2.2.1 AAMS对氯离子固化的拟合曲线
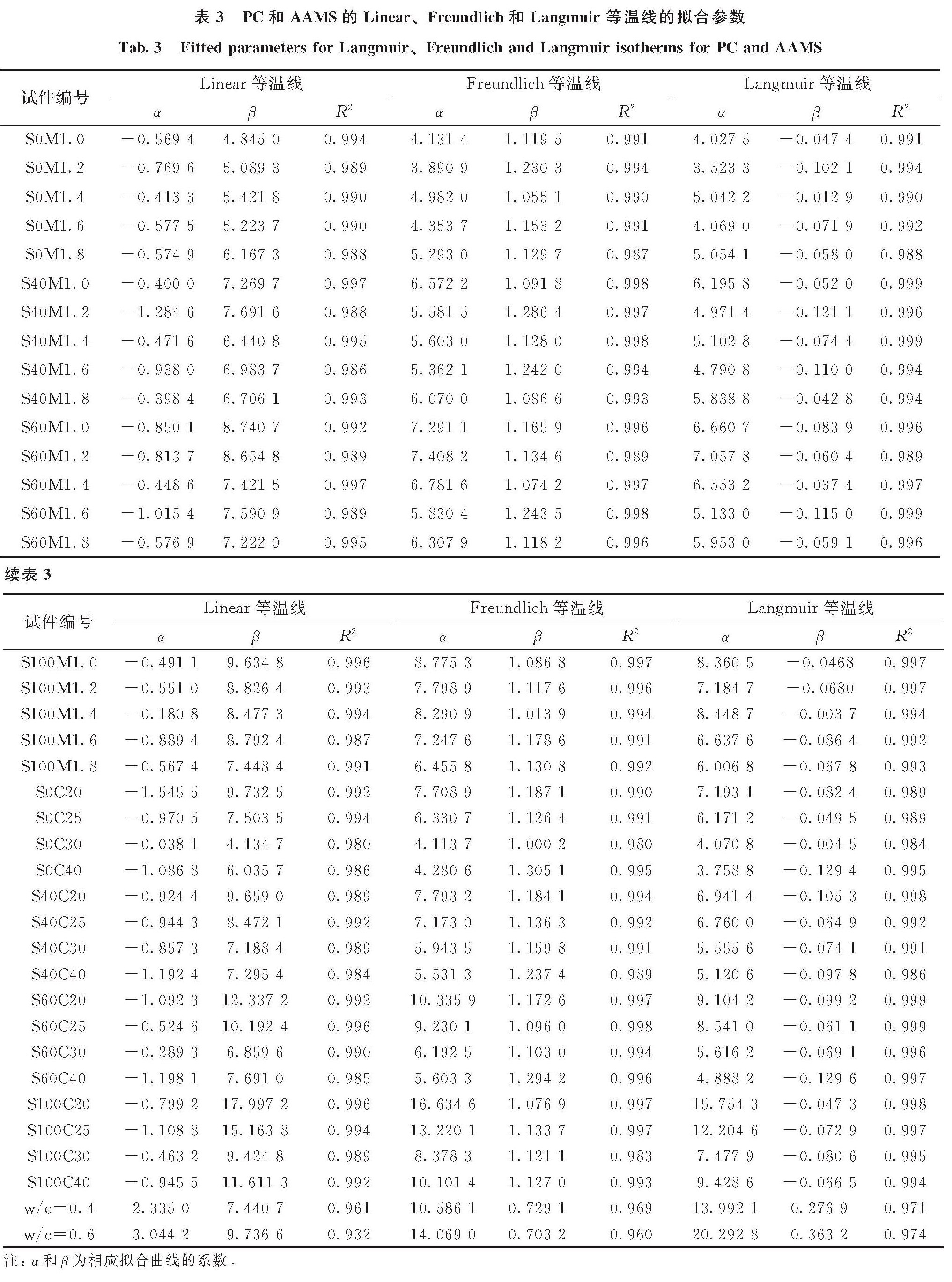
表3列出了Linear、Freundlich和Langmuir等温线的拟合参数.由表3中的拟合优度(R2)可看出,在本文所考察的Cl-浓度范围(0.1~3.0 mol/L)中,游离氯离子和结合氯离子之间的关系使用 Langmuir等温线可以更好地拟合,这可能归因于AAMS对氯离子的固化作用是以物理吸附为主,而化学结合具有相对较小的作用[7].
表3 PC和AAMS的Linear、Freundlich和Langmuir 等温线的拟合参数
Tab.3 Fitted parameters for Langmuir、Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms for PC and AAMS
2.2.2 矿渣掺量对氯离子固化能力的影响
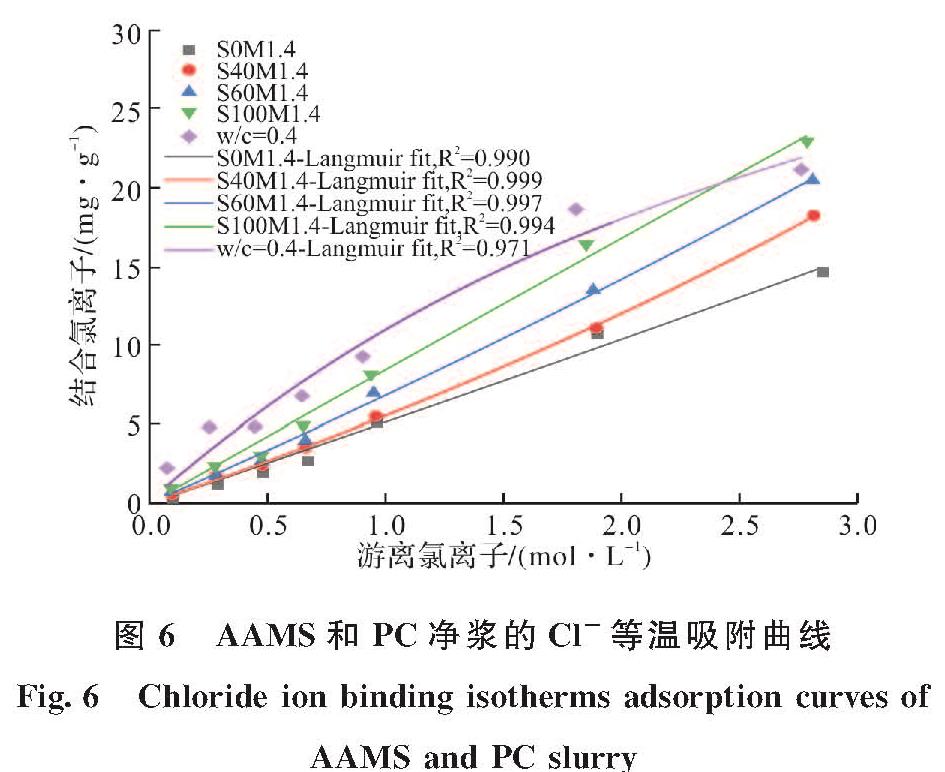
图6描绘了具有不同矿渣掺量的AAMS和水灰比为0.4的PC净浆在氯化钠溶液中吸附平衡后的氯离子固化等温线.
图6 AAMS和PC净浆的Cl-等温吸附曲线
Fig.6 Chloride ion binding isotherms adsorption curves of AAMS and PC slurry
由图6可看出,总体上AAMS,包括未掺矿渣的碱激发偏高岭土,对氯离子的固化量显著低于PC净浆.但矿渣掺入对碱激发偏高岭土的固化氯离子能力有较好的提升效果; 且随矿渣掺量的增大,固化氯离子的能力不断提高.这是因为矿渣掺入后生成的C-(A)-S-H凝胶在碱性溶液中呈带正电的表面,这意味着可对表面带负电的OH-和Cl-进行物理吸附[11],且C-(A)-S-H的氯离子结合能力随着Ca/Si比的增加而增加,这是由于Ca/Si比的增加提高了C-(A)-S-H凝胶表面的正电位[30]; 并随着矿渣掺量的增大,生成的C-(A)-S-H凝胶量不断提高,可进一步提高对氯离子的吸附[31].此外,矿渣的掺入可以提高偏高岭土原料的溶解,进而提高碱激发偏高岭土/矿渣复合凝胶体系的反应水平[32],生成更多的N-A-S-H凝胶,而N-A-S-H凝胶与氯离子的物理吸附量的提高有关[33].
在AAMS中,氯离子的固化量主要受到氯离子浓度的影响.较低的[Cl-]/[OH-]比将导致较低的表面电荷密度和较薄的扩散层,从而减少了留存在扩散层中的氯离子量[17],进而影响AAMS固化的氯离子量.另一方面,由图6可看出,虽然在NaCl溶液浓度较低时(<0.7 mol/l),AAMS对氯离子的固化量远低于PC净浆; 而在NaCl溶液浓度较高时(>1.0 mol/L),AAMS对氯离子的固化速率大于PC对氯离子的固化速率,且与PC的固化速率逐渐下降相比,AAMS的固化速率随着NaCl溶液浓度的增大而逐渐提高,并在NaCl溶液浓度为2.0~3.0 mol/L之间,AAMS对氯离子的固化量超过了PC净浆.这可能是因为在低NaCl溶液浓度的境况下,PC对氯离子的固化作用有物理吸附与化学结合两种,其中化学结合的氯离子量较大且不容忽视[34]; 而在高NaCl溶液浓度的境况下,PC对氯离子的物理吸附与化学结合量逐渐达到了饱和.由AAMS对氯离子的固化表现来看,在低NaCl溶液浓度(<0.7 mol/L)的境况下,AAMS对氯离子的固化能力远低于同浓度下PC的氯离子固化量; 当NaCl溶液浓度高达1.0 mol/L以上时,AAMS对氯离子的固化量表现出了极大的提升[30].表明AAMS固化氯离子的潜力在高浓度NaCl溶液的境况下得到了充分的体现,这与已有文献[17,35]中的研究结论一致.
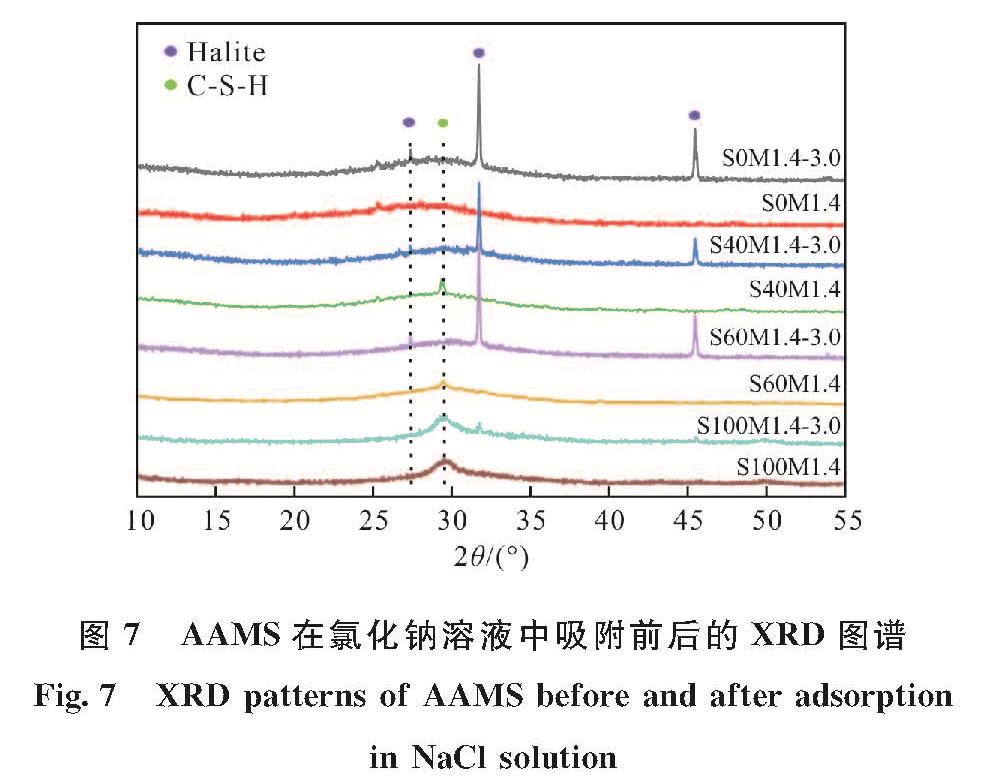
图7描绘了AAMS和其在氯化钠溶液中吸附平衡后的XRD衍射图谱.由图7可看出,矿渣掺入后在AAMS的XRD衍射图中检测到了C-S-H(PDF#15-0641)的存在,但峰强较弱.含矿渣的AAMS在氯化钠溶液中浸泡后,由于NaCl等晶体峰型较强C-S-H凝胶在XRD衍射图中难以体现.同时,C-S-H凝胶是碱激发偏高岭土试件中所不具有的,而C-S-H凝胶在水泥净浆中对氯离子的固化发挥了重要作用[20,34],这为矿渣掺入后AAMS固化氯离子能力获得显著提高提供了重要依据.此外,AAMS在氯化钠溶液中浸泡后的矿物相变化较小,未发现Friedel's盐和其他含氯物相的形成,仅多出了Halite(NaCl, PDF#70-2509)的晶型[35].这表明AAMS对氯离子的固化主要归因于C/N-A-S-H和C-S-H凝胶的物理吸附.多出的Halite晶型意味着C/N-A-S-H凝胶的外表面上可能物理吸附了大量的氯离子[24],这可能是C/N-A-S-H凝胶中的羟基(OH-)基团由Cl-取代所致[11].
图7 AAMS在氯化钠溶液中吸附前后的XRD图谱
Fig.7 XRD patterns of AAMS before and after adsorption in NaCl solution
上述结果表明:AAMS对氯离子的固化能力总体弱于PC净浆,其固化机制主要为C/N-A-S-H和C-S-H凝胶的物理吸附; 矿渣的掺入对于AAMS固化氯离子的能力有显著的提升效果; NaCl(>1.0 mol/L)溶液浓度越高,AAMS的固化氯离子能力越强,在NaCl溶液浓度大于1.0 mol/L时,AAMS对氯离子的固化量超过PC净浆.
2.2.3 激发剂模数对氯离子固化能力的影响
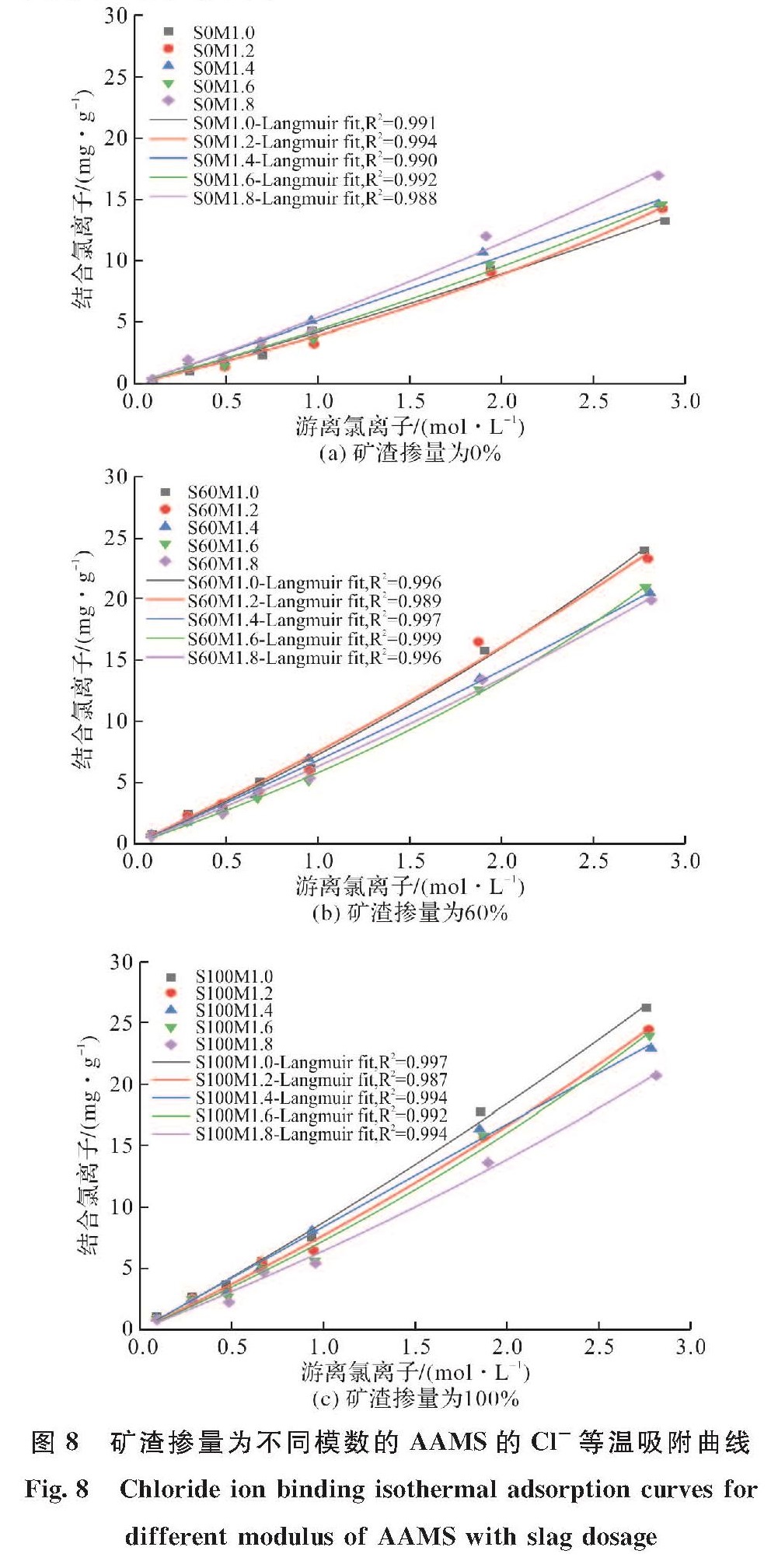
图8、9描绘了具有不同激发剂模数的AAMS在氯化钠溶液中吸附平衡后的氯离子固化等温线和XRD衍射图.由图8(a)可见,对于碱激发偏高岭土而言(S0组),激发剂模数较低时,其对氯离子的固化能力较差.这一方面是因为激发剂模数较低时(MS=1.0)会导致碱激发产物凝胶的沸石相转变,进而固化Cl-的凝胶量减少.在含偏高岭土且模数较低(MS=1.0)AAMS的XRD衍射图中检测到了沸石Zeolite X(Na2Al2Si2.5O9·6.2H2O, PDF#38-0237)和八面沸石Faujasite-Na((Na2Ca)0.075(Al0.3Si0.7)O2(H2O), PDF#76-0843)的存在,反映其结晶度较高,生成的这两种沸石相不太可能与氯离子发生化学键结合[36].Zhang and Shi等[37]也发现较低模数的激发剂会导致碱激发产物的沸石相转变.而高模数的AAMS的XRD衍射图中以无定形相为主,未看到明显的沸石晶型.另一方面,模数较低的激发剂碱性较强,碱激发反应后多余的OH-会与Cl-之间产生吸附竞争[11],进而降低对Cl-的固化.上述两方面可能是低模数的碱激发偏高岭土固化氯离子能力较弱的原因.
图8 矿渣掺量为不同模数的AAMS的Cl-等温吸附曲线
Fig.8 Chloride ion binding isothermal adsorption curves for different modulus of AAMS with slag dosage
图9 矿渣掺量为不同模数的AAMS在氯化钠溶液中吸附前后的XRD图谱
Fig.9 XRD patterns before and after adsorption of different modulus of AAMS in NaCl solution with slag dosage
由图8(b)和(c)可见,对于AAMS而言,激发剂模数较高时,其对氯离子的固化能力较差,且随着矿渣掺量的增大,较低激发剂模数的AAMS固化的氯离子量在不断增大.彭晖等[19]的研究表明,在各矿渣掺量下,碱激发偏高岭土的反应水平均随激发剂模数的增大而降低,同时,矿渣的掺入对于碱激发偏高岭土的反应水平具有促进作用,且在其所用的碱激发条件下,不同矿渣掺量的碱激发偏高岭土/矿渣中的矿渣原料几乎完全参与反应.因此,矿渣掺入和较低的激发剂模数意味着较多的C/N-A-S-H和C-S-H凝胶的生成量,而凝胶量的增加为吸附Cl-提供了更多的接触位点,进而提高了对Cl-的固化量.
2.2.4 激发剂浓度对氯离子固化能力的影响
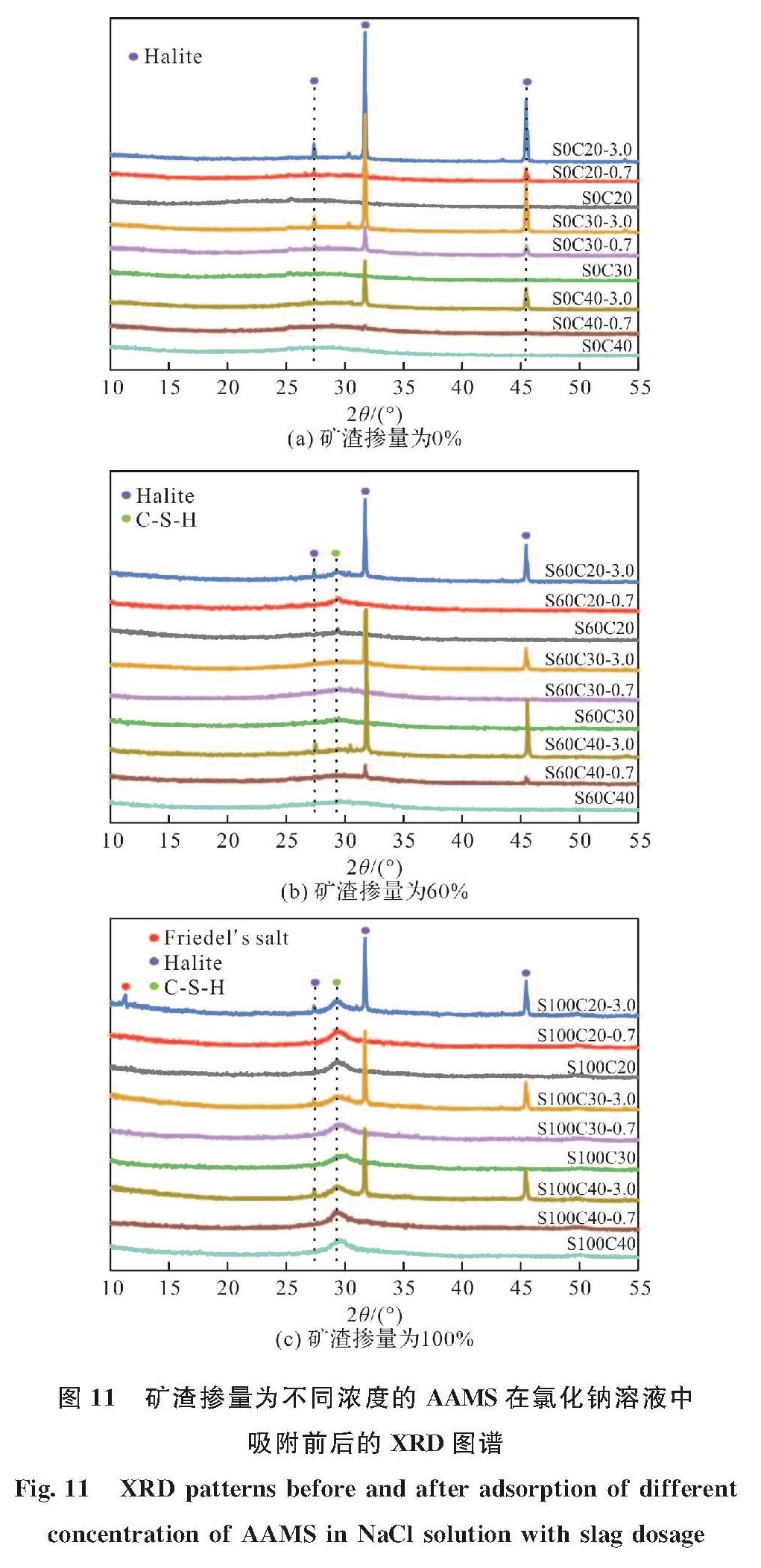
图 10、11描绘了具有不同激发剂浓度的AAMS在氯化钠溶液中吸附平衡后的氯离子固化等温线和XRD衍射图.由图 10(a)可看出,对于碱激发偏高岭土而言(S0组),激发剂浓度较低(C20和C25)时,其对氯离子的固化能力较好; 当激发剂浓度为30%时,碱激发偏高岭土对氯离子的固化效果最差.这可能是在低浓度的碱激发条件下,碱激发偏高岭土的反应水平较低,凝胶产物减少.同时,低浓度的碱激发条件下,孔溶液中的OH-浓度较小,而固化的氯离子量会随着OH-浓度的减少而增加[38].上述结果的出现可能是这二者耦合作用造成的结果.
由图 10(b)和(c)可看出,随着矿渣掺量的增大,低浓度的激发剂对AAMS固化氯离子的能力也越好,尤其是S100C20对氯离子的固化能力最好.由图 11可看出,浓度为20%的AAMS的XRD图谱中检测到了C-S-H凝胶相的存在,而C-S-H凝胶相未在其他更大浓度的AAMS中检测出来,如前所述,C-S-H凝胶可以提高对氯离子的固化能力.此外,在S100C20-3.0的XRD图谱中检测出了Friedel's盐(PDF # 42-0558)的存在,表明S100C20对氯离子的固化主要归因于C-S-H凝胶的物理吸附以及Friedel's盐的化学结合,这可能是S100C20对氯离子固化效果最好的原因之一.在未浸泡氯化钠溶液的S100C20中未能检测出Friedel's盐的前驱体AFm相,可能是因为碱激发矿渣中的AFm相衍射峰被C-(A)-S-H凝胶衍射峰掩盖所致; Wang和Scrivener[39]以及Bernal等[40]均在研究硅酸钠激发矿渣时通过SEM、EDS、DTA等表征技术确定了AFm相的存在,但是在XRD图谱中AFm相的峰因被无定形的C-S-H凝胶叠加掩盖而难以观察到.当激发剂浓度增大时,未能检测到Friedel's盐结晶相,这可能是较大的激发剂浓度促使矿渣溶出的Al元素参与C-(A)-S-H凝胶相的形成而不是AFm相的形成,相关机制还需进一步研究.故而,较低浓度(C20和C25)的AAMS对氯离子的固化能力强于较高浓度(C30、C35和C40)的AAMS对氯离子的固化能力.
图 10 矿渣掺量为不同浓度的AAMS的Cl-等温吸附曲线
Fig.10 Chloride ion binding isothermal adsorption curves for different concentrations of AAMS with slag dosage
图 11 矿渣掺量为不同浓度的AAMS在氯化钠溶液中吸附前后的XRD图谱
Fig.11 XRD patterns before and after adsorption of different concentration of AAMS in NaCl solution with slag dosage