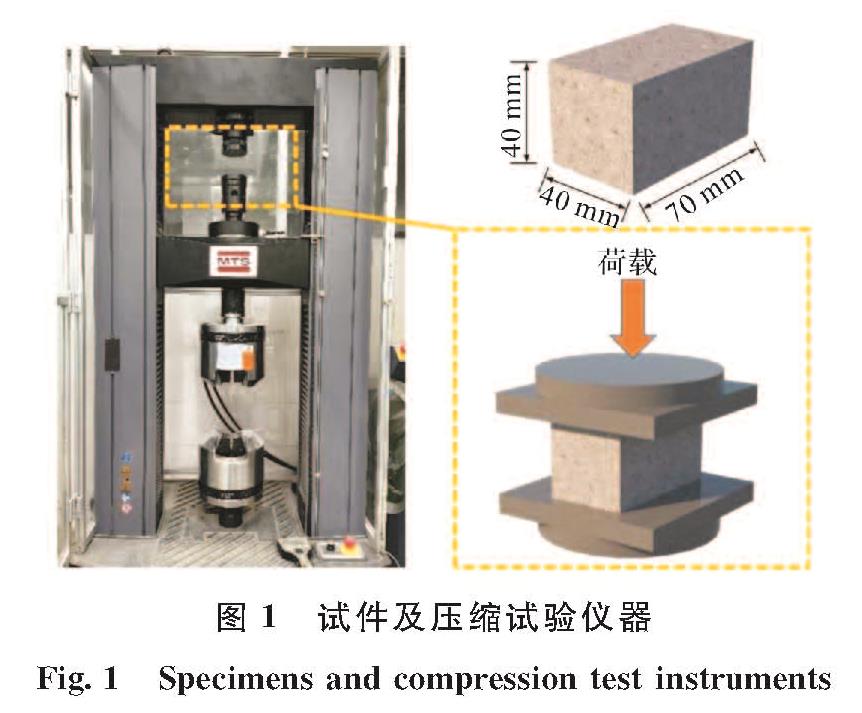
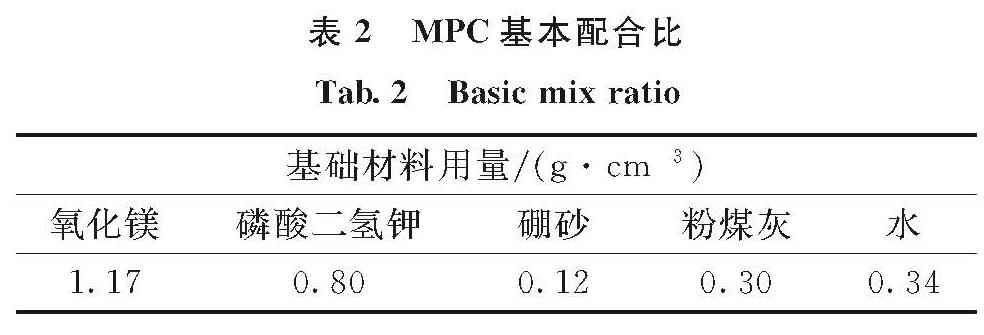
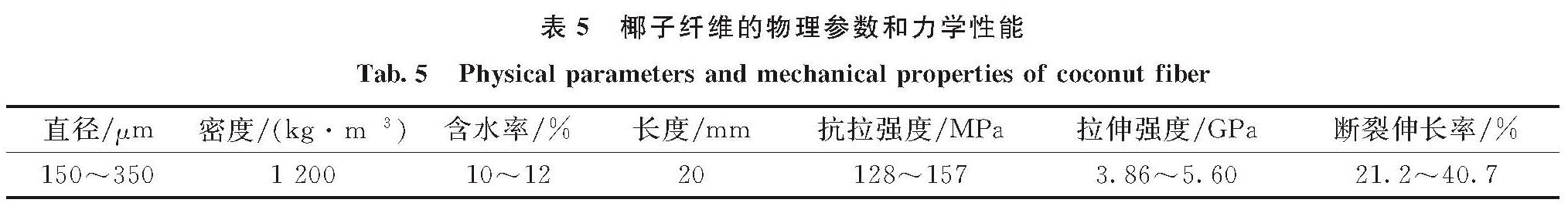
2.1 破坏模式
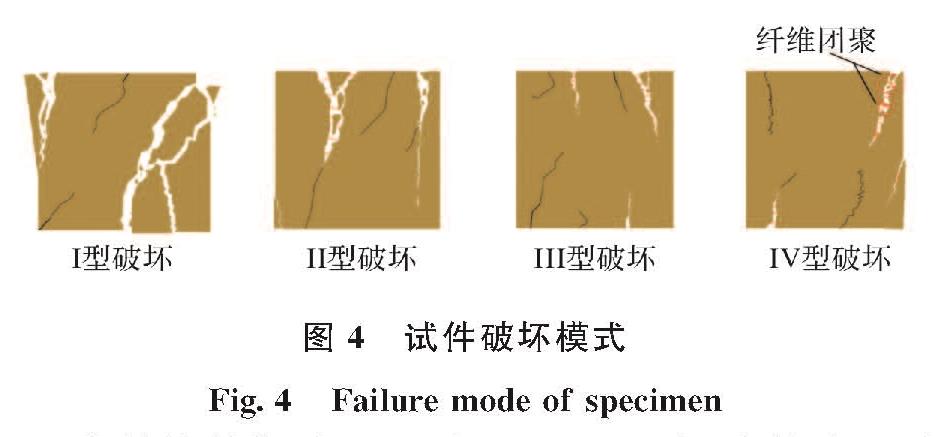
试件的破坏根据试件延性的增长将破坏模式总结为三种形式(见图4).Ⅰ型破坏:当加载力达到峰值时,试件瞬间失效,脆性特征明显.Ⅱ型破坏:与Ⅰ型破坏相似,但由于CF连接在裂缝中,试件破坏时未剥离.Ⅲ型破坏:试件由脆性转变为延性,加载力达到峰值后试件仍能抵抗荷载,试件的裂缝逐渐增多,裂缝宽度小于Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型.Ⅳ型破坏:与Ⅲ型破坏类似,但由于CF掺量过高,使其在MPC中分布不均匀,出现纤维团聚现象.
图4 试件破坏模式
Fig.4 Failure mode of specimen
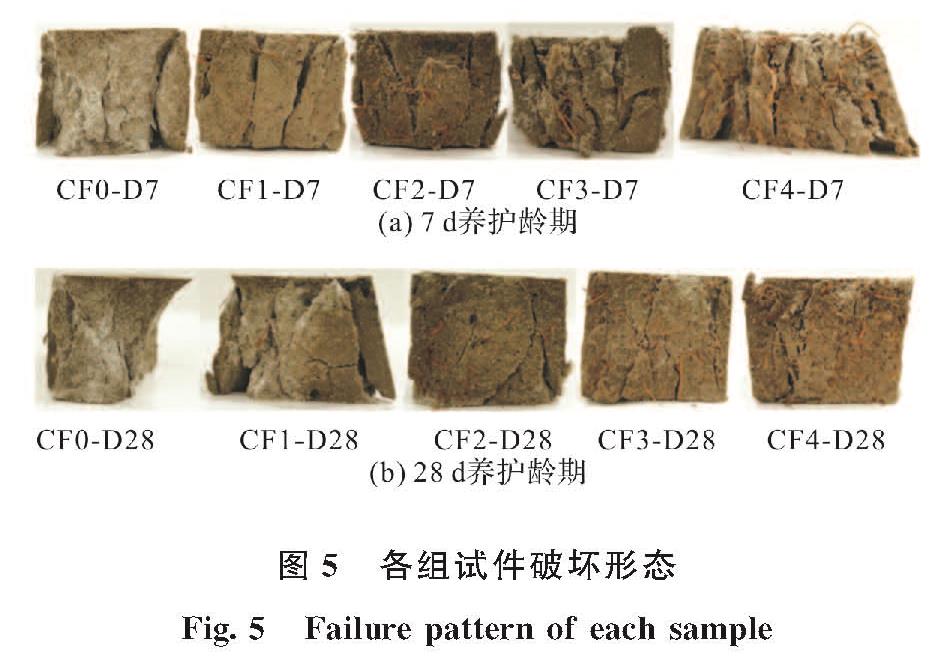
在养护龄期为7 d时,CF0-D7组试件表现为Ⅰ型破坏,试件破坏形态见图5(a),在受压过程中竖向试件侧表面中间区域首先产生微小裂缝,随着荷载的逐渐增大伴有水泥碎块剥落,当加载到峰值应力时,裂缝扩大并迅速贯通,伴随突发性崩裂,产生较大的压碎破坏声响,边角混凝土压碎明显.从试件的应力-应变曲线,图 11(a),也能发现试件达到峰值应力后,试件在微小应变内破坏,应力迅速下降为0; CF1-D7组试件破坏表现为Ⅱ型破坏,与Ⅰ型破坏现象基本一致,但由于CF将破裂的碎片连接在一起,试件并没有分裂成独立的碎片; 随着试件CF掺量的继续增加(CF2-D7、CF3-D7),试件破坏发展为Ⅲ型破坏,试件破坏具有一定的延性特征.在试验过程中,随着荷载的增加,裂纹以一定的速度扩展,并扩展到一定的宽度形成裂缝,可观察到部分CF从MPC基体中拔出,且由于纤维的连接,破裂的碎片并没有分裂成独立的碎片; 当纤维掺量超过3%时(CF4-D7)表现为Ⅳ型破坏,试件仍具有较大延性,但由于CF掺量过高导致MPC砂浆流动性差、CF分布不均匀,一些缠绕成团的CF出现在裂缝中.
图5 各组试件破坏形态
Fig.5 Failure pattern of each sample
当养护龄期为28 d时,试件随CF掺量变化的破坏形态与7 d养护龄期下试件的破坏形态基本一致.但相同CF掺量的试件中,28 d养护龄期的试件比7天养护龄期下的试件脆性都更大,破坏时的裂缝宽度更窄.并且从图 11中可观察到28 d养护龄期下峰值应力对应的应变均小于7 d养护龄期.另外从试件破坏面来看28 d养护龄期试件内部孔隙明显小于7 d养护龄期试件,28 d养护龄期试件内部结构更加致密.
2.2 抗压强度
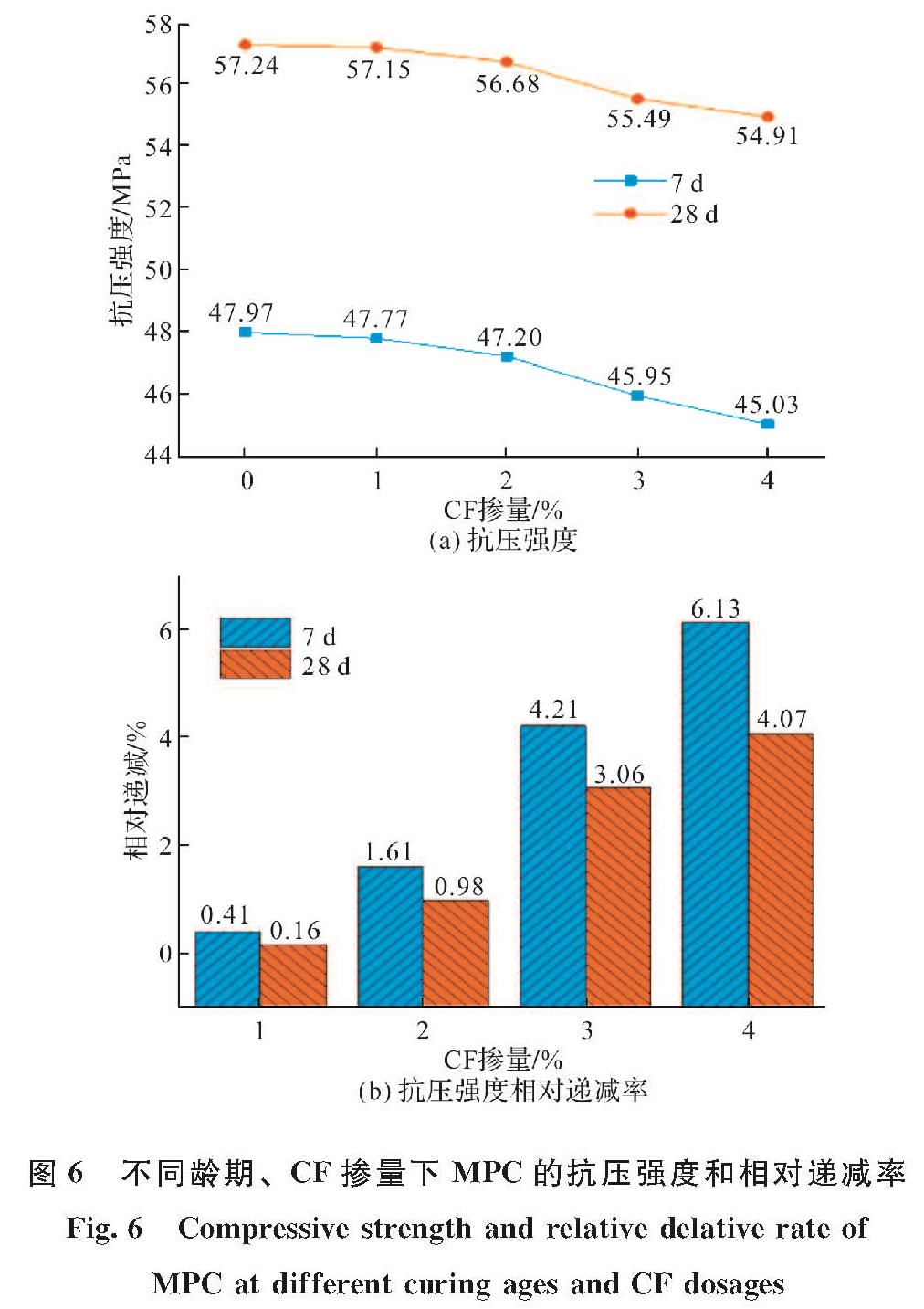
图6(a)给出了7 d、28 d养护龄期下各组试件的平均抗压强度(Average Compressive Strength,简称ACS).在7 d养护龄期下,随着CF掺量从0增加到4%,试件ACS从47.97 MPa持续减小到45.03 MPa.在不同CF掺量(1%、2%、3%、4%)下对应的ACS递减率分别为0.41%、1.61%、4.21%、6.13%,如图6(b)所示.
图6 不同龄期、CF掺量下MPC的抗压强度和相对递减率
Fig.6 Compressive strength and relative delative rate of MPC at different curing ages and CF dosages
CF掺量对MPC抗压强度的影响可以解释为MPC内部发生着如下水化反应.
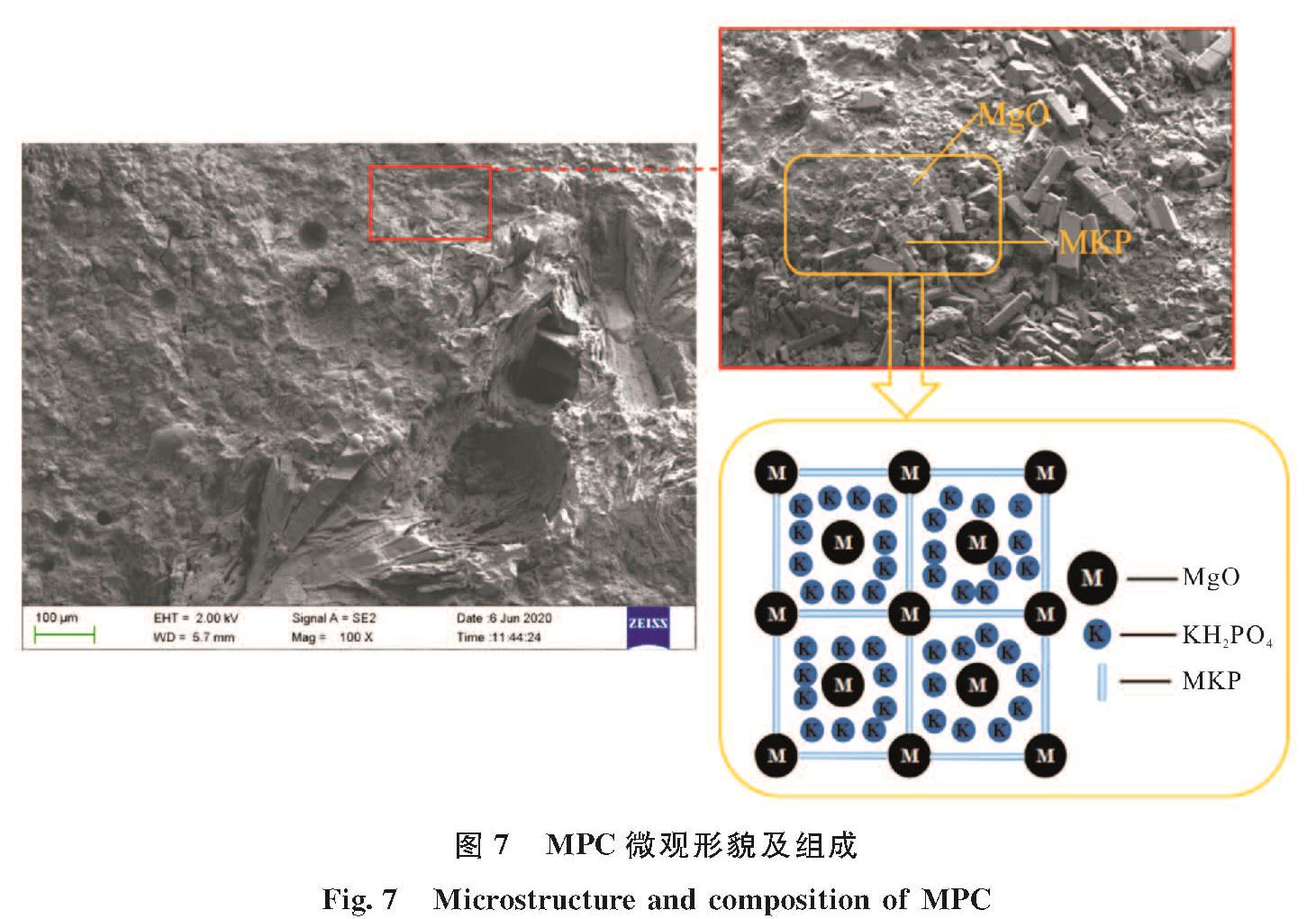
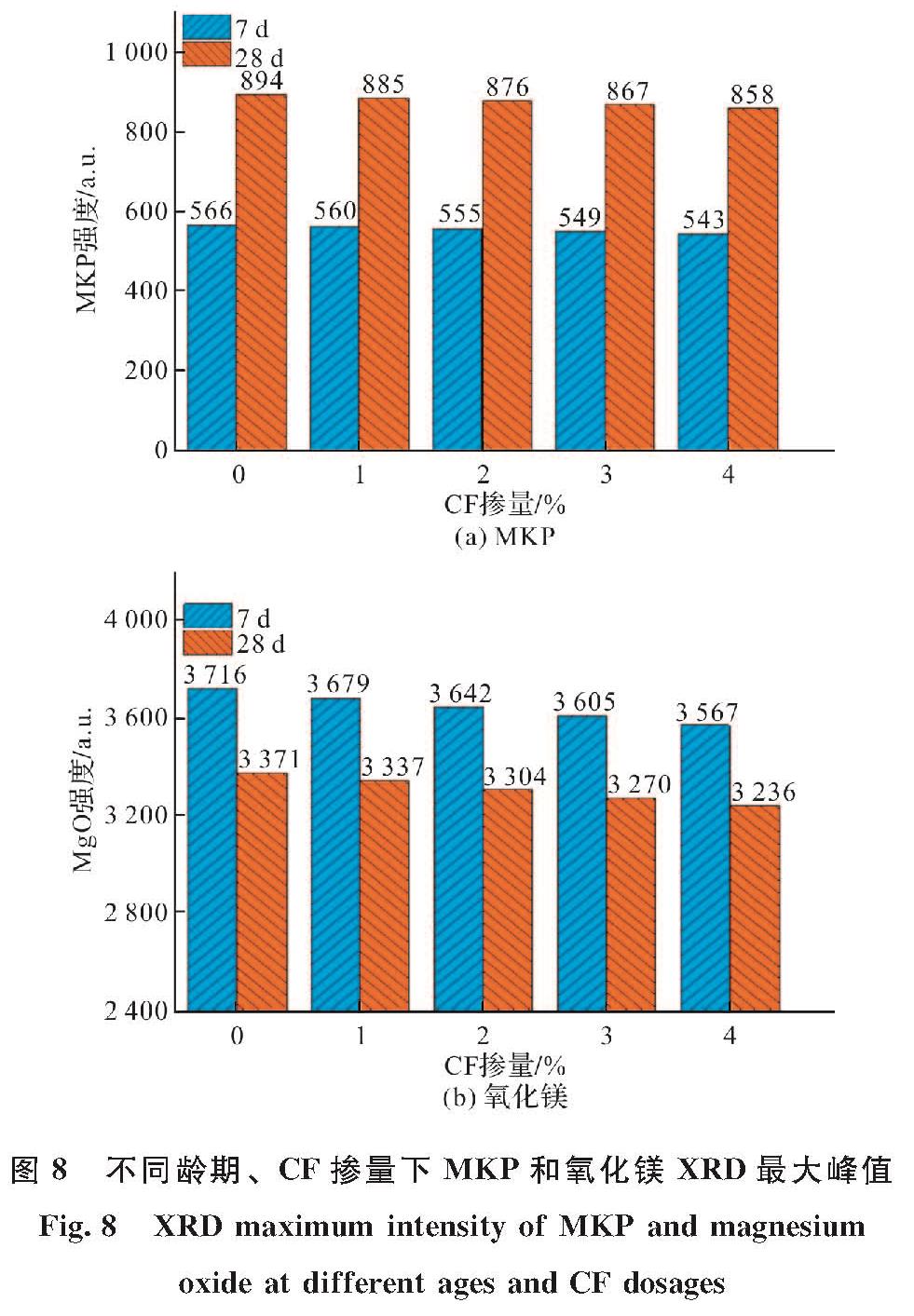
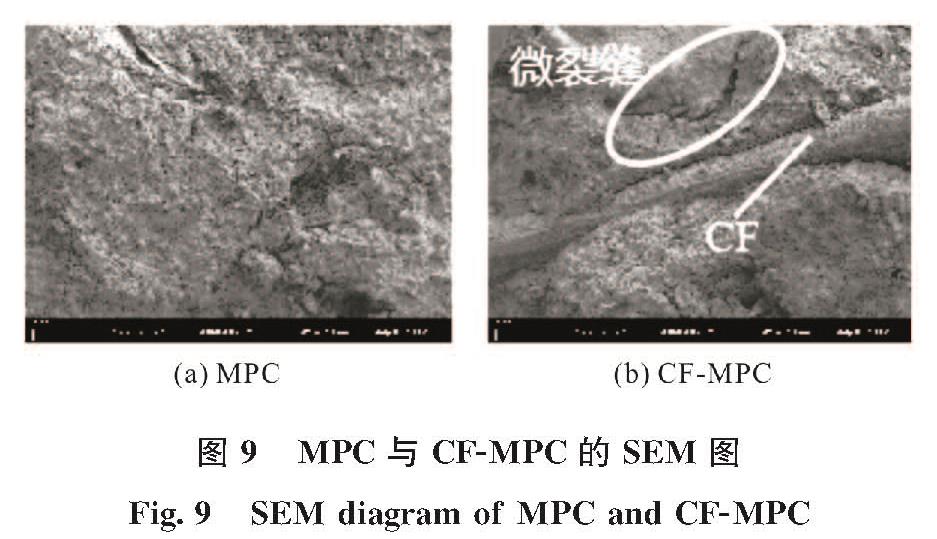
MgO+KH2PO4+5H2O=MgKPO4·6H2O其中,主要水化产物六水磷酸钾镁(MgKPO4·6H2O,简称MKP)包裹着未反应的MgO和KH2PO4形成的晶体结构如图7所示,是提供MPC机械强度的主要部件[30].而图8(a)XRD分析中,同一龄期下MKP含量随CF掺量的增加而递减,当CF掺量从0增加到4%时,MKP的最大衍射强度从566.12 a.u.下降到543.36 a.u.,导致MPC抗压强度的损失,这主要是因为随着CF体积掺量的增加,MPC在CF-MPC中的占比相对有所下降,导致水化产物MKP也相对下降; 此外,通过图9 MPC及CF-MPC的SEM图可发现随着CF的掺入,过高掺量(4%)时会出现CF分布不均匀和CF团聚的现象,致使结构整体性降低,CF周围出现了较大的微裂缝,导致MPC整体抗压性能下降.
当养护龄期为28 d时,ACS随CF掺量的变化趋势与7 d养护龄期下基本一致.如图6(a)所示,随CF掺量从0增加到4%,ACS从57.24 MPa持续降低到54.91 MPa.在不同CF掺量(1%、2%、3%、4%)下对应的ACS相对递减率分别为0.16%、0.98%、3.06%、4.07%,相比7 d养护龄期的相对递减率较小.这主要是因为28 d养护龄期下MPC水化反应更充分,MPC基体内部和MPC与CF之间粘结力均增强,未掺CF的MPC抗压强度基数较大,因此CF对MPC抗压强度缩减的影响较小.而如图6(a)所示,当CF掺量相同时,试件抗压强度随龄期增长明显增大,这主要是因为28 d养护龄期下试件水化反应更加充分,产生更多MKP包裹的晶体结构,提高了抵抗外部压力的能力.
图7 MPC微观形貌及组成
Fig.7 Microstructure and composition of MPC
图8 不同龄期、CF掺量下MKP和氧化镁XRD最大峰值
Fig.8 XRD maximum intensity of MKP and magnesium oxide at different ages and CF dosages
图9 MPC与CF-MPC的SEM图
Fig.9 SEM diagram of MPC and CF-MPC
2.3 应力-应变
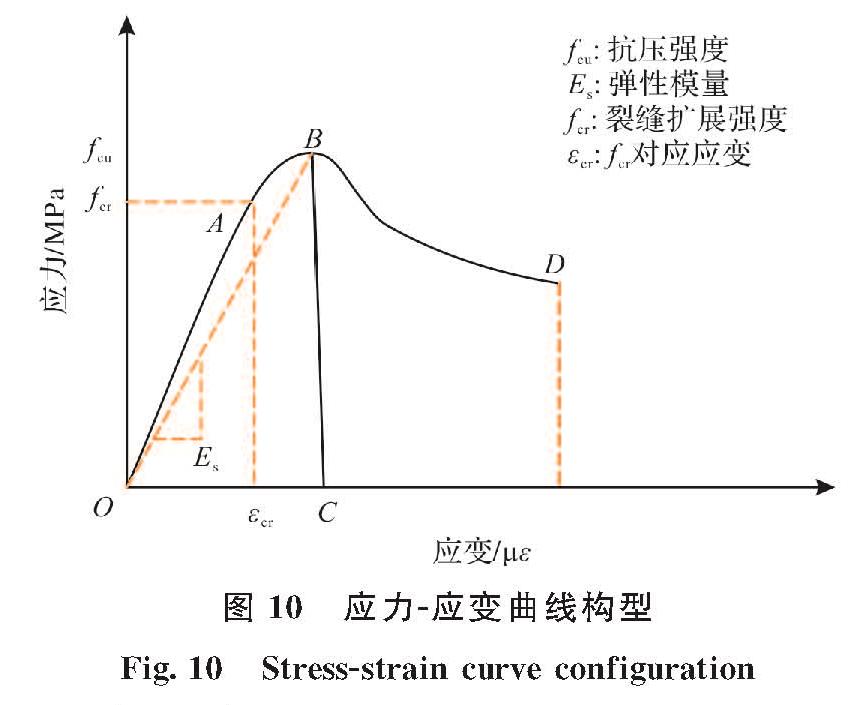
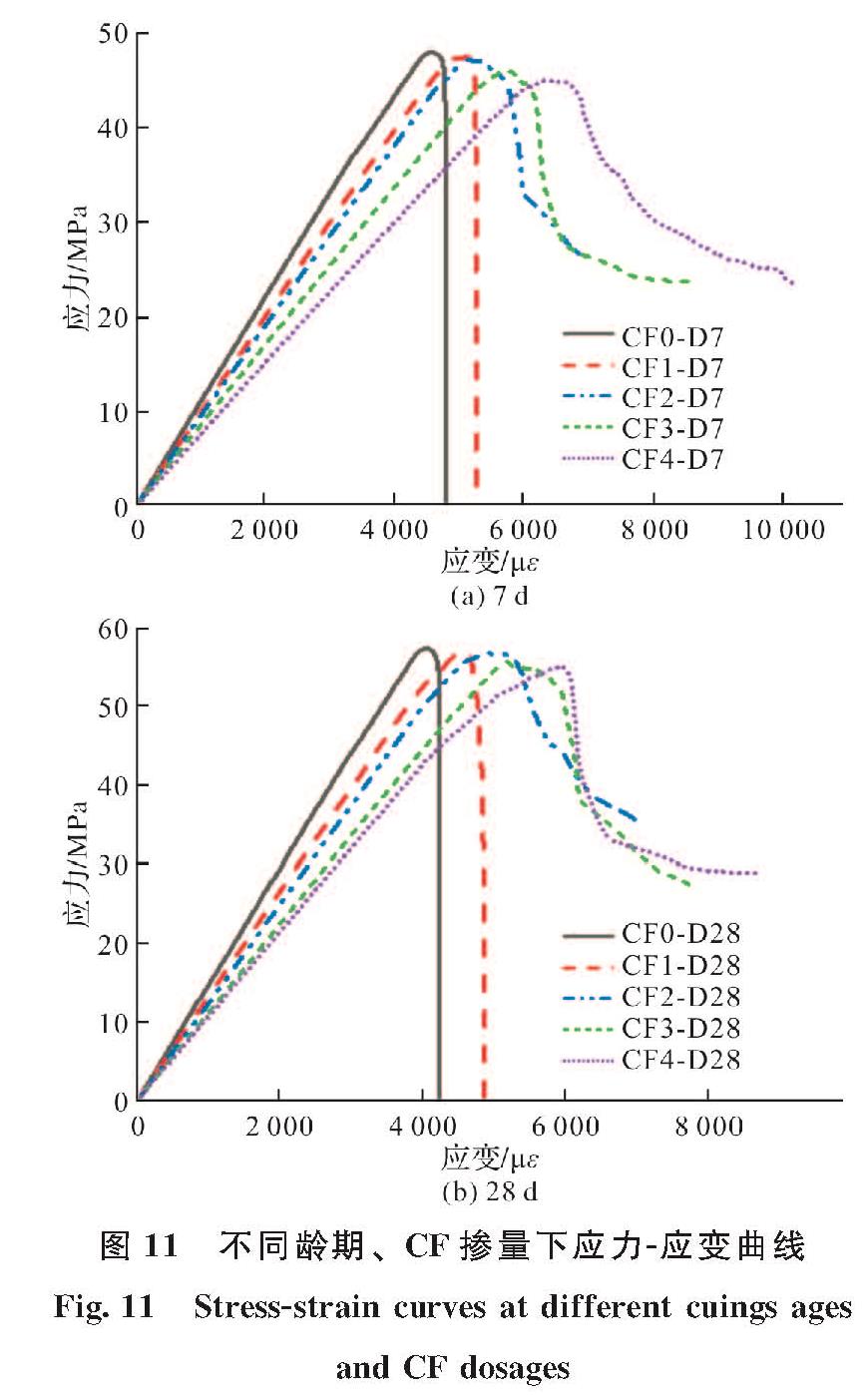
如图 10所示,试验得到的应力-应变曲线可总结分为三个阶段:近似弹性阶段(O~A)、裂纹稳定扩展阶段(A~B)和软化下降阶段(B~C,B~D).根据应力-应变曲线可得到各个阶段的弹性模量.当MPC中不掺CF或者掺量较少(1%)时,软化下降阶段表现为B~C,试件如本文2.1所述试件表现为明显的脆性特征.而随CF掺量的增加,应力-应变软化下降阶段表现为B~D,这主要得益于椰子纤维的掺入改善MPC的延性.
图 10 应力-应变曲线构型
Fig.10 Stress-strain curve configuration
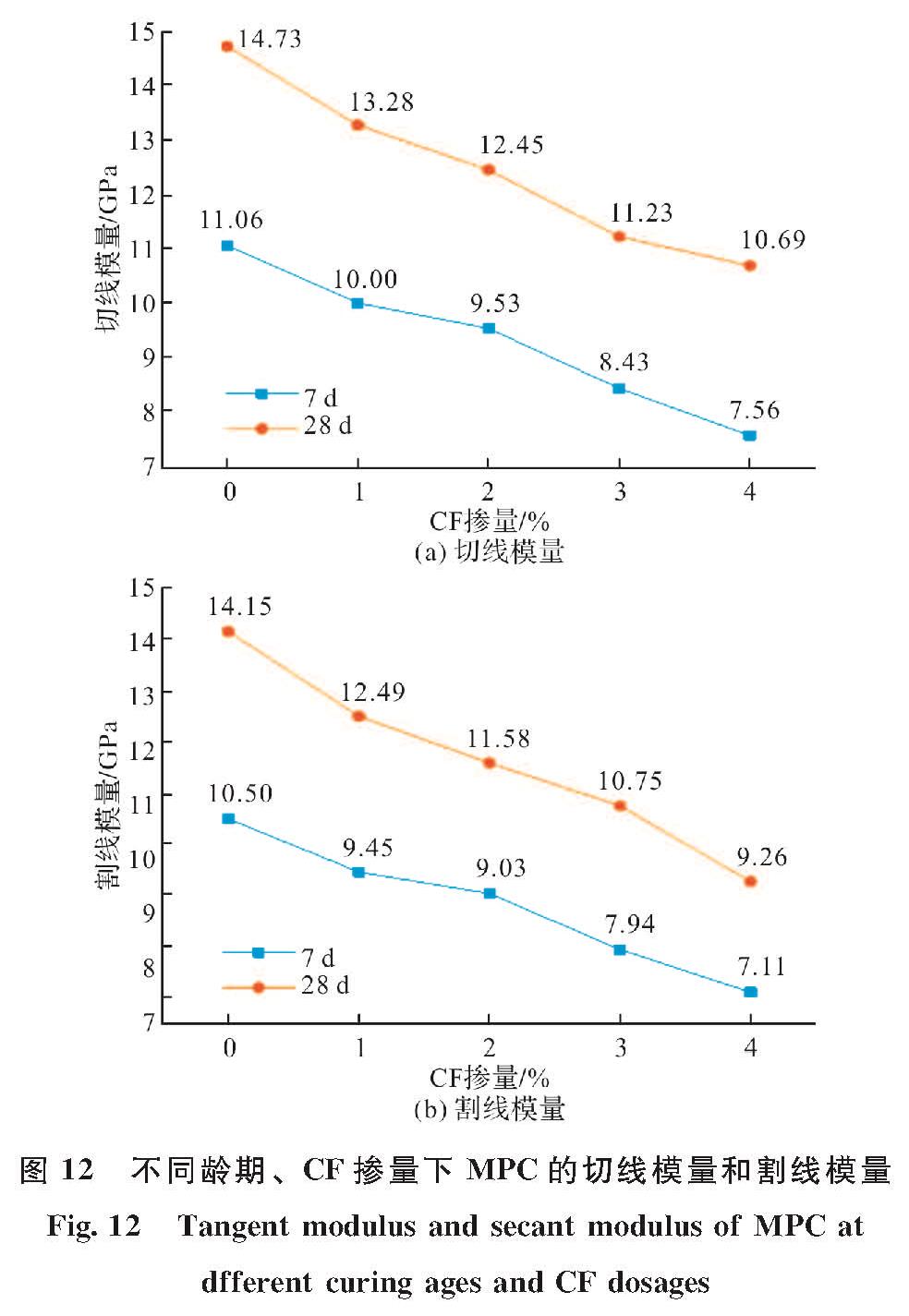
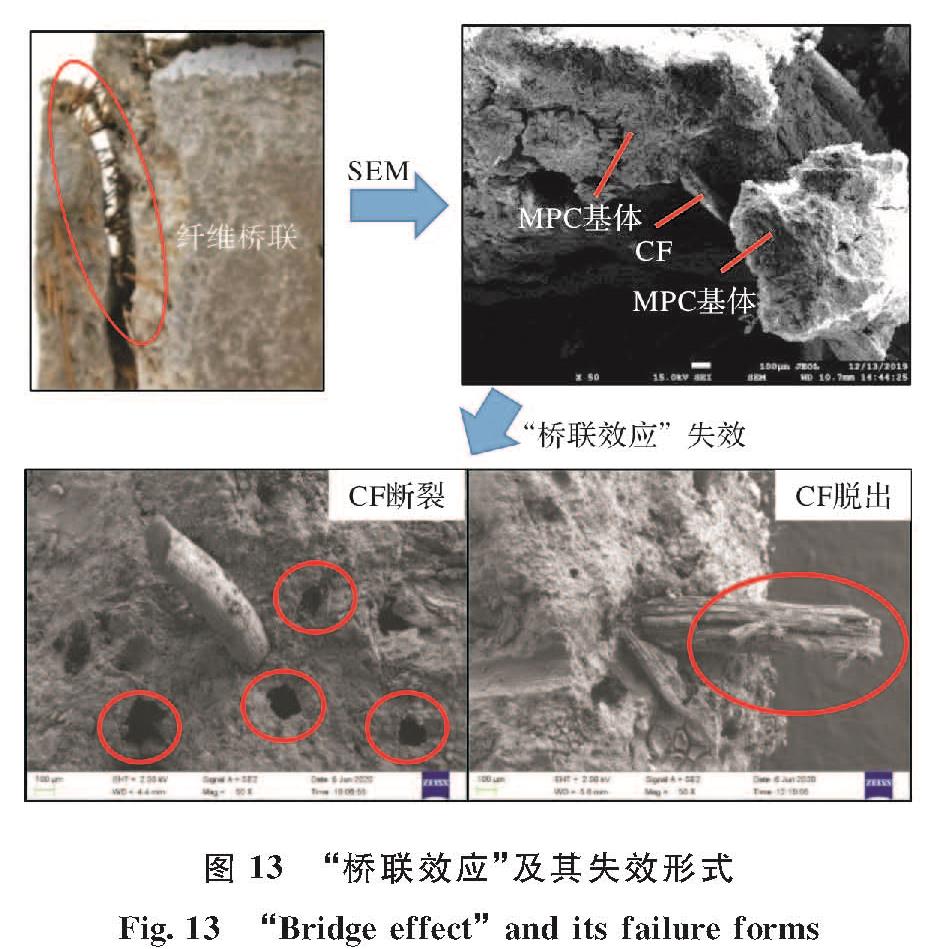
图 11(a)为7 d养护龄期下不同CF掺量试件的应力-应变曲线,所有试件的应力-应变曲线在弹性阶段(O~A)相似,都可以看作是一个近似线性上升阶段.如图 12(a)所示,随着CF掺量从0增加到4%,切线弹性模量(E)从11.06 GPa下降到7.56 GPa.根据复合材料理论[31],较低模量的CF掺入MPC,使整体弹性模量降低.随着载荷的增加,应力增大到A点,裂纹处局部应力超过了基体局部的抗裂能力,基体中出现了一些微小裂纹.进入下一阶段(A~B)后,尽管弹性模量随着应力的增加而逐渐下降,但由于基体间的粘结力和CF与MPC之间的“桥联效应”(图 13)未达到极限,基体承载力仍在增大.此外,从图 11(a)中可以看出,随着CF掺量的增加,A~B阶段对应的应变范围也在增加,MPC中裂缝的开展被延缓.割线模量(Es)的变化也可以用来表现CF掺量对微裂纹的限制作用.如图 12(b),CF掺量从0增加到4%,7 d养护龄期下Es由10.50 GPa减少到7.11 GPa.
图 11 不同龄期、CF掺量下应力-应变曲线
Fig.11 Stress-strain curves at different cuings ages and CF dosages
图 12 不同龄期、CF掺量下MPC的切线模量和割线模量
Fig.12 Tangent modulus and secant modulus of MPC at dfferent curing ages and CF dosages
图 13 “桥联效应”及其失效形式
Fig.13 “Bridge effect” and its failure forms
当曲线达到峰值应力B点后,试件进入软化阶段.这个阶段应力-应变曲线产生了不同变化:试件CF掺量为0和1%时,曲线在极小的应变范围内应力急剧下降到点C,试件破坏; 当CF掺量超过1%时,试件应力缓慢下降到点D,试件表现出更大的极限应变且仍有较大残余强度.试件软化阶段的差异主要是因为CF掺量的不同,CF掺量较少时(在本研究中小于1%),“桥联效应”较弱,CF对MPC应力-应变行为的影响可以忽略不计.从试件破坏面可以看出,CF1-D7组试件受压过程中大部分CF迅速脱出,裂纹迅速扩展,直至试件破坏.随着掺量的增加,裂纹所在截面的CF数量增加,使得“桥联效应”增强,限制了裂缝的扩展.图 11(b)为28 d养护龄期下不同CF掺量试件的应力-应变曲线,其整体变化趋势与7 d养护龄期下相似,都是经过近似弹性阶段(O~A)后呈现出了较为明显的差别,随荷载的逐渐增加达到峰值应力,低于1%CF掺量的试件发生了脆性破坏,应力突变降至0,而高于1%掺量试件仍能承受一定荷载,这主要是一定掺量的CF能够增强CF与MPC之间的联系,使试件具有了一定的延性.
2.4 能量吸收
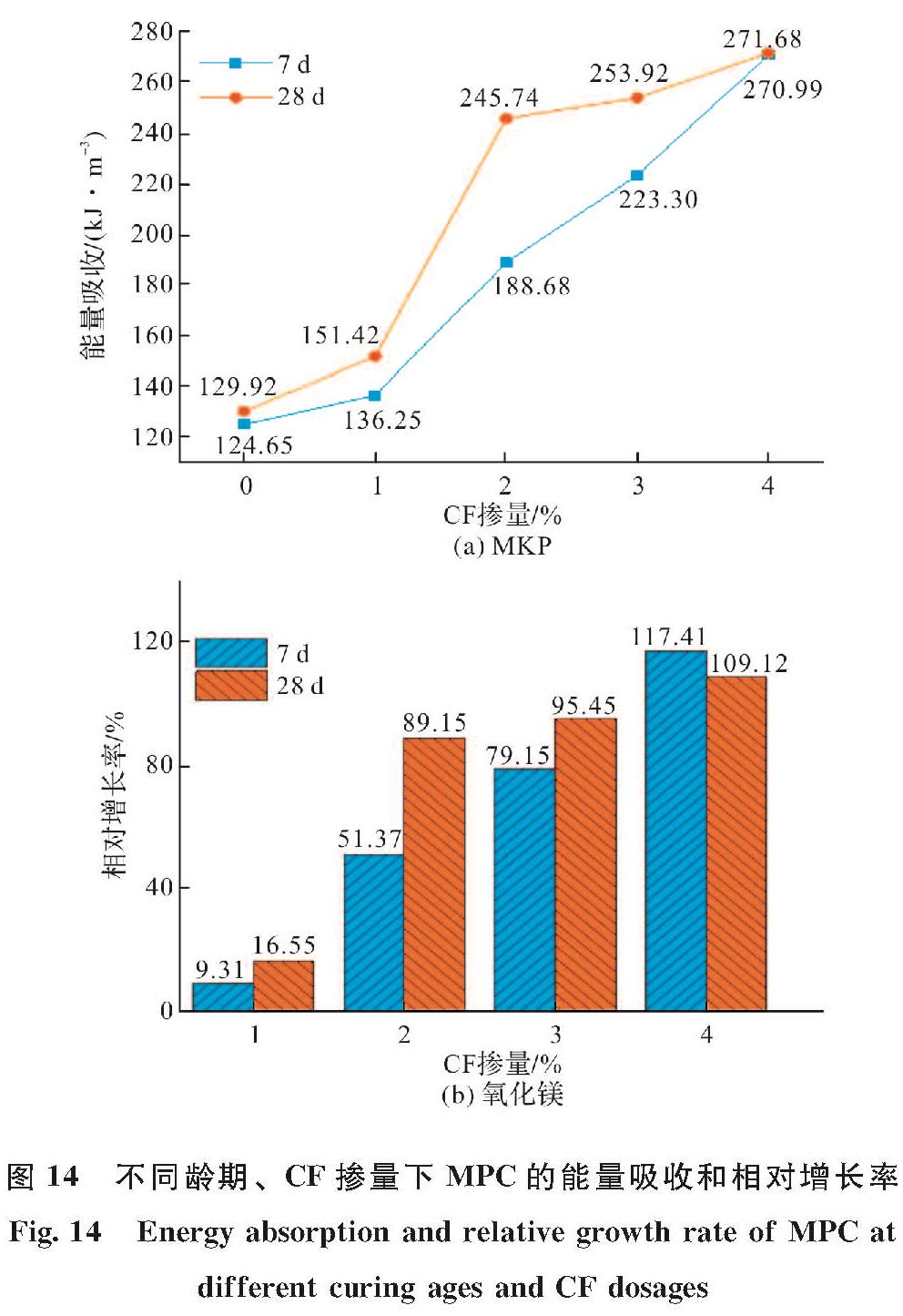
图 14为7 d、28 d养护龄期下不同CF掺量试件的能量吸收情况,能量吸收定义为图7所示的应力-应变曲线下面积的应变能.在本研究中,为计算O-B-D阶段所包围的面积,D点的应变限制在7 000.从图 14(a)可清晰观察到,7 d养护龄期下,随着CF掺量从0增加到4%,能量吸收从124.65 kJ· m-3递增到270.99 kJ·m-3.在不同CF掺量(1%、2%、3%、4%)下对应的能量吸收递增率分别为9.3%、51.4%、79.1%、117.4%,如图 14(b)所示.
图 14 不同龄期、CF掺量下MPC的能量吸收和相对增长率
Fig.14 Energy absorption and relative growth rate of MPC at different curing ages and CF dosages
随CF掺量增加能量吸收递增显著主要是因为2.3中提到的MPC基体与CF之间的“桥联效应”增强.如图 13所示,加入CF后基体之间的联系增强,这主要得益于其内部晶体产物与CF的连接.若基体中裂纹持续发展,CF会脱出基体或断裂,且无论是裂纹的形成、CF的脱出或断裂都会造成能量消耗,并随着CF掺量的增加,“桥联效应”随之增强,能量消耗也会更大.
28d养护龄期下,其整体变化趋势与7 d养护龄期下相似,随着CF掺量从0增加到4%,能量吸收从129.92 kJ·m-3递增到271.68 kJ·m-3.在不同CF掺量(1%、2%、3%、4%)下对应的能量吸收递增率分别为16.5%、89.2%、95.4%、109.1%,相较于7 d养护龄期的能量吸收,1%至3%CF掺量的能量吸收递增率均有所增加,而由于0掺量的MPC试件在28 d养护龄期下能量吸收相对7 d养护龄期较高,尽管4%掺量的能量吸收值大于7 d养护试件,但能量吸收增长率表现略低,如图 14所示.