2.1 Hoek-Brown常数及广义H-B准则
Hoek-Brown强度准则是霍克等人在参考Griffith经典强度理论的基础上,通过大量岩石三轴试验提出的岩体非线性破坏经验准则,其综合考虑了岩体结构面和应力状态等对岩体强度的影响,系统解释了拉应力区、低应力区和最小主应力对岩石强度的影响机理,对各向异性岩体或深埋破碎岩体均适用,其强度估算的普遍公式为[11]
σ1=σ3+σci((mb)/(sci)σ3+s)α (1)
式中:σ1,σ3为岩体破坏时的最大主应力和最小主应力; σci为组成岩体完整岩块的单轴抗压强度; mb为岩体的Hoek-Brown参数,取值为0.000 000 1~25; s为与岩体质量有关的常数,取值为0~1; α为有关岩体结构的参数.
mb、s和α与岩体结构面情况相关且相互独立,可由岩体地质强度指标GSI值和扰动程度D求得.对于严重扰动岩体D取1,施工无扰动时D取0.其判别公式为
s=exp((GSI-100)/(9-3D)) (2)
mb=miexp((GSI-100)/(28-14D)) (3)
α=1/2+1/6(e-GSI/15-e20/3) (4)
式中:mi为完整岩块的Hoek-Brown常数; GSI为地质强度指标[12-13].
考虑爆破开挖及应力松弛对岩体影响,岩体变形模量的估算可采用如下的公式.
当σci<100 MPa时
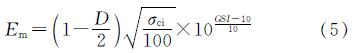
当σci>100 MPa时
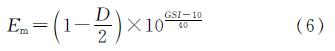
为了更好地探讨岩体地质强度参数对隧道洞身位移的变化影响规律,取GSI分别为30,50,70,90,对应围岩等级为Ⅴ、Ⅳ、Ⅲ、Ⅱ级,并结合霍克布朗屈服准则及《公路隧道设计规范》采用软件RocLab估算的岩石力学强度参数如表1所示[14-16].
表1 基于GSI分类系统和H-B准则确定的围岩力学参数表
Tab.1 Mechanical parameters of surrounding rock determined based on GSI classification system and H-B criterion
2.2 有限元弹塑性模型
为了更好地反应空间效应,采用有限元软件Midas GTS对不同岩石强度参数下隧道施工变形展布规律展开系统性数值分析研究[17-18].隧道围岩按均质弹塑性材料考虑,采用Mohr-Coulomb屈服准则,用实体单元模拟.Ⅴ级软弱破碎围岩带开挖前需进行超前支护,超前小导管和超前注浆对围岩的加固效果通过将洞周围岩弹性模量提高42%~56%,粘聚力提高35%~51%,内摩擦角提升2.3~3.4°来等效模拟[19],注浆加固范围为拱顶及上拱腰环向120°区域.3 mφ22系统锚杆采用植入式桁架并视为线弹性材料.初期支护采用板单元模拟,厚度为30 cm,其强度通过将18号型钢拱架和钢筋网的弹性模量等效到喷射混凝土的衬砌弹性模量中计算.支护力学参数如表2所示.
表2 支护力学参数
Tab.2 Mechanical parameters of supporting
象君山深埋隧道ZK55+845~ZK55+915段平均埋深200 m,为简化计算,取上部隧道埋深50 m建模,其他埋深通过在上部边界施加均布荷载q=γh=5 MPa等效土体自重,水平构造地应力通过侧压力系数K来实现,K取1.2.考虑到模型开挖边界效应,模型隧道底面距土体底部边界为4倍洞径,左右边界至隧道中心线约为3.5倍洞径,纵向方向取50 m的开挖长度,建立模型尺寸为100 m×50 m×100 m.边界约束条件为:模型前后、左右和底部边界施加垂直于围岩面的法向约束的位移边界,顶面为自由边界.
为了深入考虑开不同挖工法对岩体变形机制的影响,对三台阶法、CRD法、环形预留核心土法及三台阶临时仰拱法进行有限元模拟开挖(开挖循环进尺为1 m),并对岩体力学性质与变形状态进行动态分析.
各开挖工法模型洞室网格细部划分如图2所示.
图2 各开挖工法模型洞室网格细部划分示意图
Fig.2 Diagram of mesh division of each excavation method
2.2.1 围岩变形分析
图3为不同岩石强度参数下采用四种开挖工法对隧道开挖结束后中间断面洞周沉降和收敛变形的影响.根据结果所示,对于围岩破碎、节理发育的软弱岩体,采用CRD法或三台阶临时仰拱法开挖时隧道拱脚收敛位移约为三台阶或环形预留核心土开挖时拱脚位移的2%~3%,墙腰水平收敛位移约为后者的9%~14%,拱顶沉降也随开挖工法的改变有缓慢下降的趋势.当GSI为50时,岩石强度相对良好,此时采用CRD法及三台阶临时仰拱法对变形的控制效果虽然不如较差围岩时表现突出,但均明显优于三台阶与环形预留核心土开挖.当GSI为50和GSI为70时,对于稳定岩体,无论采用何种开挖工法都能很好地控制变形,且洞周变形已经趋于稳定.因此当围岩强度较差时,优先采用CRD法或环形预留核心土法进行开挖,对大变形有良好控制效果,当围岩具有一定强度时,由于不同开挖工法对围岩变形控制效果区别不大,且围岩有不错的自承能力,因此,可以采用三台阶法或全断面法开挖,成环较快,工期较短,节约造价.
图3 不同岩体强度下各工法洞周位移变化
Fig.3 Variation of circumferential displacement under different rock mass strength
可以明显看出,对于稳定性差的软岩(GSI=30),采用三台阶或预留核心土法开挖时,由于没有临时支撑抵抗围岩向临空面挤压变形的压力,且围岩自身承载力不足,开挖断面支护后,在围压作用下,支护结构脚部将产生向下的位移,围岩松弛区域扩大且洞周产生大变形,变形以拱脚处最为突出.因此必须加强软弱围岩开挖时对拱脚的补强,提高基底承载力,脚部围岩补强以减少接地应力(加肋钢支撑)为目的或提高拱脚承载力(打入脚部锚杆或水平锚管等)为目的,而对于稳定性好、强度高的围岩拱脚变形量相对拱顶沉降量较小[7].而三台阶临时仰拱法以及CRD法通过分割隧道面并设置临时支撑使隧道暂时形成早期闭合构造,有效地减少了拱腰与拱脚变形,但是在断面成环及拆除临时支撑时这两种方法将产生较大变形量,施工过程中因根据围岩变形情况进行小心作业.
2.2.2 围岩主应力状态分析
分析不同地质强度指标GSI下的围岩主应力变化趋势,如图4所示,当岩体地质强度较差(GSI=30)时,采用三台阶法开挖将产生较大的压应力,不利于围岩稳定,洞周也将产生较大变形量,结合图3,其拱脚收敛达到101.3 cm,墙腰收敛达到61.44 cm; 随着围岩强度的提高,采用三台阶法开挖对围岩应力的控制效果趋于稳定,此时沉降与收敛变形量也显著减少.采用三台阶临时仰拱法、CRD法及环形预留核心土法开挖后,围岩最大主应力和最小主应力值随岩体强度的增加变化不大,相对于强度较高围岩此时对Ⅴ级软岩也有明显的应力控制效果.因此采用三台阶法开挖方式对地质强度要求较高,对于深埋Ⅴ级软岩隧道,不宜采用三台阶法施工,此时无论是围岩应力或者洞周变形均不能得到有效的控制,若应力过大超过围岩抗压强度,岩体将产生塑性松弛区域且丧失稳定.
图4 各工法围岩主应力随岩体强度变化趋势
Fig.4 Main stress of surrounding rock varies with the strength of rock mass
考虑实际工程Ⅴ级破碎软岩围岩施工变形大,技术要求高,因此,对GSI=30时软弱围岩模拟结果作主要分析.根据圣维南原理,提取模型中间断面围岩最大主应力和最小主应力值,根据表3,结果表明采用CRD法开挖对围岩最大主应力的控制效果相对于三台阶法和环形预留核心土法提升了39.9%和3.7%,最小主应力的控制效果提升了49.7%和29.3%.采用三台阶临时仰拱法开挖对最大主应力的控制效果相对于三台阶法和环形预留核心土法提升了39.8%和3.6%,最小主应力的控制效果约提升了57.8%和40.5%.
表3 中间断面围岩主应力状态
Tab.3 principal stress state of surrounding rock in middle section
根据各监测点主应力提取结果,由图5可知,无论采取哪种工法开挖,相对于其他监测点,拱脚都是压应力值较大处,尤其是三台阶法施工在拱脚处最容易发生围岩流变现象,拱腰也由于台阶开挖产生狭窄三角区导致应力分布较大,其拱顶及拱腰应力值则相对较小.环形预留核心土法、CRD法和三台阶临时仰拱法对各监测点应力整体控制效果显著优于三台阶法; 由于中隔墙和临时仰拱的存在,CRD法拱顶的应力值较大而对拱腰应力值控制效果最好,三台阶临时仰拱法在拱腰位置处应力值较大,但其对拱脚应力的控制效果在四种开挖工法中最优.因此,在施工过程中,采取不同的开挖工法时,应加强对其相应位置应力集中处进行补强增强其承载能力,可以通过打入锁脚锚杆或在拱脚和临时支撑处围岩内补强注浆进行加固.
图5 围岩各监测点主应力提取结果
Fig.5 Principal stress of surrounding rock's monitoring point
2.2.3 围岩塑性区分布分析
分析不同工法对Ⅴ级软岩状态下塑性区范围的控制效果,由围岩塑性区结果图6可知,三台阶法产生的塑性范围最大,主要集中在两拱腰、拱底与拱脚,在拱脚与拱底产生严重破坏区,在这个位置处需加强支护.CRD法和三台阶临时仰拱法能够有效减小塑性区范围,且在拱脚处,CRD法开挖有对拱脚变形控制效果最为良好,三台阶临时仰拱法也有减弱此区域内围岩塑性延展的趋势.开挖结束后,三台阶、三台阶临时仰拱和预留核心土开挖法的塑性区厚度和向岩体深部扩展趋势有向注浆加固区域缓慢减小的趋势,拱顶区域内塑性变形最小,说明超前注浆加固能够有效地控制岩体产生塑性流变; 而CRD法开挖由于中隔壁的存在,明显抑制住了拱脚和拱顶钢支撑处的塑性区发展,拱顶的塑性区厚度相对于拱腰有所增大,但整体来说洞周变形远小于其他工法开挖.
图6 Ⅴ级围岩塑性区分布图
Fig.6 Ⅴ grade surrounding rock plastic separation layout