基金项目:国家自然科学基金青年项目(52108063); 国家自然科学基金面上项目(51978551); 陕西省自然科学基础研究计划项目(2021JQ-568)
第一作者:刘 冬(1984—),女,博士(后),教授,硕士生导师,主要研究基础教育空间格局.E-mail:396705240@qq.com 通信作者:张堂基(1995—),男,硕士研究生,主要研究基础教育空间格局.E-mail:785732297@qq.com
(1.西安科技大学 建筑与土木工程学院,陕西 西安 710054; 2.陕西华地勘察设计咨询有限公司,陕西 西安 710020; 3.西安建筑科技大学 建筑学院,陕西 西安 710055; 4.成都市市政工程设计研究院,四川 成都 610023)
(1.Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Xi'an University of Science and Technology,Xi'an, 710054, China; 2.Shaanxi Huadi survey and Design Consulting Co.,Ltd,Xi'an, 710020, China; 3.Department of Architecture, Xi'an Univ. of Arch.& Tech., Xi'an, 710055; 4.Chengdu Municipal Engineering and Research Design Institute, Chengdu 610023, China)
point of interest(POI); spatial layout; school supply; coverage unit
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2022.05.007
随着国家中心城市、国际化大都市等建设目标的推进,以及“史上最宽松”户籍新政、百万大学生留西安等各种利好政策的实施,截至2019年底西安市常住人口数量已破千万.在审视创造出人口新的增长极,西安市正式迈入“超大城市”圈的同时,因人口迅速扩张引发的基础教育设施空间承载能力不足、资源分配不均、资源差距较大等一系列教育不公平现象愈发突出.2019年10月18日,西安市发布《基础教育提升三年行动计划(2019—2021 年)》,明确要求要通过优化布局等措施加快推进区域教育均衡发展.因此,如何审视西安市基础教育资源的空间布局现状,准确判断当下的学位供需矛盾,满足人民群众对优质均衡教育的热切期盼,在最短时间合理做大优质教育资源总量,有效化解“择校热”,显得尤为紧迫与重要.
空间分析是ArcGIS地理处理中的核心模块,通过对空间信息的提取、表现和传输,为有效地获取、科学描述和认知空间特性提供技术平台,并为调控空间资源的配置提供可视化的决策依据.目前,GIS空间分析技术在基础教育的布局优化、资源配置、可达测度及学区划分等方面已有较多应用.陈芸芬[1]利用GIS空间分析技术定量分析了兰州市基础教育资源空间分布特征及其布局效率.邵艳[2]建立了基于GIS的天津市基础教育均衡发展决策支持系统.孔云峰[3]使用GIS模拟学校与学生的最佳配置.艾文平[4]依托GIS交通网络路径分析对现状学区学位进行自动优化派位,并得出了不同模型下的学校学位最优派位的方案以及学区最优划分的分布图.此外,兰峰[5]基于空间失配理论运用健康距离模型,衡量了2009-2015年西安市九城区小学教育资源的失配程度及时空格局演化.王峡[6]汇总分析了西安市城市小学通学出行的时空特征,总结出30种家庭通学出行活动路径,初步提出了与家庭通学出行的城市小学布局思考.
随着互联网信息技术的发展与应用,兴趣点(Point of Interest,POI)信息资源规模的快速增长,其作为代表真实地理实体的点状空间数据,更有利的呈现了“要全体不要抽样”的大数据特征,对提升空间信息服务与完善实施管理具有重要作用.目前,POI数据在城市设施格局研究方面已有较多应用,主要表现在城市商业设施、公共服务设施和生活服务设施等空间格局分析上,表征城市各要素的分布状态,从空间角度进行客观描述.
总体上看,国内学者对基础教育设施从不同角度和不同方法进行了不同尺度的研究.但缺少从城市宏观层面到区域中观层面,再到居住单元微观层面的整体空间特征把握.因此,本研究综合POI数据和GIS空间分析技术所兼具的规模化、可视化优势,基于2020年西安市中心城区小学315条POI数据信息,分别对中心城区的宏观分布、下辖六区的中观供给、小学单元的微观覆盖三个层面的现状特征进行梳理和识别,以期为中心城区小学布点优化和调整提供更为准确的依据,进而对西部城市中心城区基础教育资源的布局优化有所启示.
西安地处关中平原中部,是中国西北部最大的中心城市,下辖11个区、2个县和7个国家级及省级重点开发区,总面积10 752 km2(含西咸新区).本文研究区域为西安市中心城区,位于E108.47°08'~109°27',N33°79'~34°45'之间,是黄河流域中部关中盆地城市,总面积为836.02 km2,辖碑林区、雁塔区、新城区、未央区、莲湖区、灞桥区六个区,并包括西安高新技术产业开发区、经济技术开发区、曲江新区、浐灞生态区和国际港务区五个开发区(图1).
本研究的主要数据包括西安市中心城区小学POI数据、居住单元POI数据、下辖六区行政区划矢量数据、面积及常住人口数据.其中:中心城区小学POI数据与居住单元POI数据均由百度API开放接口获取,且通过百度在线地图进行矫正,共获取315 个小学(图2)和8 882个居住单元(图3)的空间位置信息; 同时,利用QGIS软件将上述获取的POI数据坐标转换为WGS1984坐标,以便于研究分析.西安市中心城区基础地图数据来源于国家地理空间数据云,并基于区级行政区划进行矢量化处理; 此外,中心城区及下辖六区面积与常住人口数据均来源于《西安市统计年鉴2019》(表1).
为准确、有效地梳理和识别西安市中心城区小学空间布点特征,本研究采用平均最近邻、核密度和标准差椭圆三种方法对宏观层面的空间集聚、热点分布和分布方向进行量化描述.
(1)平均最近邻(ANN)
平均最近邻(Averag Nearest Neighbor,ANN),根据空间统计中每个要素与其最近邻要素之间的平均距离计算其最近邻比率,体现为“平均观测距离”与“平均预期距离”的比值.即,在测算西安市中心城区315 个小学POI位置之间的距离基础上,得出最近邻距离的平均值(即平均观测距离),以识别中心城区范围内小学空间布点的集散程度.如果该平均值小于假设随机分布中的平均距离(即平均预期距离),说明最近邻比率ANN<1,则将所分析的要素分布视为聚类要素.反之,说明最近邻比率ANN>1,将所分析的要素分布视为分散要素.Z得分和P值结果用以统计量度显著性,从而判断是否接受零假设.计算公式为
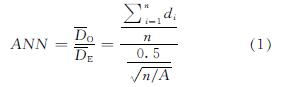
式中:D^-O为平均观测距离、D^-E为平均预期距离.
(2)核密度分析法(KDE)
核密度分析(Kernel Density Estimation,KDE),根据使用空间核函数聚点或折线要素计算每单位面积的量值,体现为不同搜索半径下每个栅格的密度值,用以反映当前空间下的要素集聚状态.即,测算西安市中心城区315个小学POI的分布密度来模拟其在空间的分布状况,以识别中心城区范围内小学空间布点的高密度区域.密度值随着学校中心辐射距离的变化而变化.计算公式为
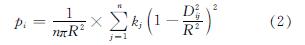
式中:kj为要素j的空间权重,Dij为空间点i和研究对象j的距离,R为搜索半径.
(3)标准差椭圆法(SDE)
标准差椭圆法(Standard Deviational Ellipse,SDE),根据椭圆的中心、长轴、短轴、旋转角等参数,定量描述要素空间分布中心性和方向性等特征.即,测算西安市中心城区315个小学POI空间分布的椭圆模型,以识别中心城区范围内小学空间布点的未来发展走势.椭圆的大小反映小学空间分布的聚集程度,旋转角反映小学分布的主导方向.计算公式为
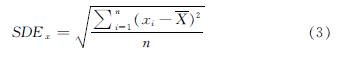
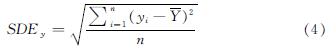

式中:θ为旋转角,表示小学POI空间分布的方向性; SDEx、SDEy分别表示标准差椭圆的长轴与短轴.
另外,在下辖六区中观层面,通过各区人口密度与学校密度进行叠加,以判断各区学校数量供给是否合理.在小学单元微观层面,通过缓冲区加泰森多边形的方法,划分315 个小学POI的覆盖范围,并利用空间连接工具对各小学覆盖范围内的居住单元数量进行统计,以判断各小学覆盖效率.
(1)整体空间离散特征显著
根据公式(1),通过对最近邻比率ANN的计算,可识别中心城区小学空间布点的集散特征.由计算得出,最近邻比率ANN=1.302 844>1,且Z为10.282 655>0,P值小于0.1.
该结果表明中心城区范围内小学空间整体呈离散分布,随机产生此离散模式的可能性小于1%.(图4)
(2)空间结构呈单中心格局
根据公式(2),通过对中心城区小学空间布点的核密度分析,可以判断小学的空间结构形态与布点格局.由自然间断法分级计算得出,核密度值大于33 600.461 21的红色高密度集中区主要在新城区、碑林区和莲湖区(图5).同时,对中心城区的人口密度分布进行研究可看出主城区内的人口密度较大,相对应的新城、碑林和莲湖三区人口密度值分别为2.717 2、2.633 2和1.946 63(图6).
该结果表明中心城区小学呈“内密外疏”的单中心空间结构,且小学空间布点的核密度与城区人口分布密度有较强的正关联性.
(3)分布态势沿东北—西南方向
根据公式(3),通过对中心城区小学空间分布的标准差椭圆分析,可以观测小学空间布点的分布方向.由计算得出,小学POI标准差椭圆旋转角为67.26°,长轴长度为9.93 km,短轴长度为7.97 km(图7).该结果表明中心城区小学现状及未来空间分布主要沿东北—西南方向.另外,对中心城区居住单元的标准差椭圆进行计算得出,标准差椭圆旋转角为49.99°,长轴长度为7.71 km,短轴长度为6.11 km(图8).该结果表明中心城区居住单元现状及未来主要沿东北—西南方向分布.
综上数据结果可以发现:中心城区小学POI的分布方向与居住单元POI的分布方向具有一致性,均沿东北—西南方向.
(1)人口聚集与学校分布密度一致
通过对中心城区下辖六区的人口与学校数量的计算,得出各区的人口密度与学校密度值(图9).可以看出:六区相比较而言,学校密度较高的依次是碑林区、莲湖区和新城区,且这三区人口密度亦较高.该结果表明中心城区学校密度与人口密度有较强的关联性,且该结果与中心城区小学POI的核密度分析结果一致.同时,将人口密度数据与学校密度数据进行可视化叠加,可以看出中观层面满足高密度人口分布对应高密度学校分布的量化特征(图 10).
图9 中心城区人口密度与学校密度对比统计图
Fig.9 Comparison of population density and school density in central urban areas
图 10 中心城区人口密度与学校密度叠加分布图
Fig.10 Overlay distribution of population density and school density in central urban
(2)各区学位供给差异明显
中心城区人口集聚密度与学校分布密度保持一致,但并不能说明学校数量与人口数量的匹配程度,即各区的学区供需情况.因此,本研究以学位正负值为界定,通过测算学位供给与学位需求的差值来判断各区学位供给是否满足需求.同时,在进行数值计算时,根据西安市2019年人口出生率12.47‰的6倍计算入学人口,以及《城市居住区规划设计标准》和《中小学校设计规范》要求,取城市完全小学平均用地面积7 000 m2,生均面积9.3 m2/人[9].则学位供需测算公式为
学位需求数=常住人口数量×12.47‰×6(6)
学位供给数=(7 000)/(9.3)×学校数量(7)
学位正负值=学位供给数-学位需求数(8)
根据学位供需测算公式(6)~(8),可计算出下辖六区的学位供需情况(表2).从表中可以看出:下辖六区学位正负值均小于1,说明六区现阶段均无法满足现状就学人口需求.其中,供需差距最大的是雁塔区,即使学位供给数量在六区中已排第二,但由于实际需求人口较多,则导致供给严重不足,这与当下雁塔区的经济社会发展也存在一定联系.此外,新城区、碑林区和莲湖区虽然学校密度较大,但通过供给预测数据发现三区的学位供给数量却排名靠后.究其根源为新城区、碑林区和莲湖区处主城区,用地规模有限,实际学位供给能力有限.综上,下辖六区中观层面上亟待解决分布数量不足的问题,以满足基本的学位供给.
(1)微观覆盖效率不高
根据《城市居住区规划设计标准》,小学是十分钟生活圈必须配套的服务设施,服务半径不宜超过500 m.因此,可通过小学服务范围内居住单元数量分析小学单元的微观覆盖特征.为保证各小学在划分覆盖范围时互不重合,本研究利用500 m缓冲区和泰森多边形相交的方法,得到中心城区315个小学的覆盖范围(图 11).可以发现:中心城区小学覆盖范围存在大量盲区,无法全面覆盖8 882个居住单元.经统计得出,处于覆盖范围内的居住单元数量为4 315个,占比仅为48.58%不足一半.该结果表明西安市中心城区现状小学单元覆盖效率较低.
(2)覆盖居住单元数量不均
本研究利用空间连接工具统计中心城区315个小学覆盖范围内居住单元的数量,并采用自然间断法划分了5 个区间量级(图 12),用以对比各覆盖范围内居住单元的数量差异.经统计得出,中心城区315个小学覆盖范围内平均有14 个居住单元; 其中,覆盖居住单元数量较多的小学主要分布在碑林、莲湖和新城区.未央和雁塔各有1 所小学覆盖的居住单元数量超过40个.另外,由频数统计图可以看出(图 13),碑林区有1所小学覆盖居住单元可达76 个; 还有39 所小学没有覆盖任何居住单元,占比高达12.38%.该结果表明现状小学居住单元覆盖数量差异较大,不均衡问题突出.
图 12 中心城区小学POI覆盖范围内居住单元统计
Fig.12 Statistics of residential units within the coverage of primary school POI in central urban area
(1)宏观层面研究得出:西安市中心城区小学布点离散特征显著,空间上呈“内密外疏”的单中心格局且主要沿东北—西南方向发展.这是基于优质教育资源和人口的双向正反馈逻辑不断极化的结果,同时,随着《大西安2050空间发展战略规划》南控、北跨、东拓、西进空间发展格局的不断演变,小学教育资源沿东北—西南的分布发展方向也是西安市未来城市发展与空间结构变化趋势的体现.
(2)中观层面研究得出:小学数量不足,不能满足现状就学人口需求.西安市中心城区下辖六区的交通条件、人口密度、学校分布等情况差异较大,同时缺失空间度量标准,致使中观层面小学供给与现实需求不相匹配.亟待加大办学建校力度,或改建扩增现有部分小学的供给能力,以弥补小学教育资源的短缺.
(3)微观层面研究得出:各小学单元覆盖效率较低,且覆盖范围内居住单元数量不均衡.现行指导小学建设的规范主要包括《城市居住区规划设计标准》、《中小学校设计规范》及《城市普通中小学校校舍建筑设计标准》,既有相关标准的指标各有侧重,且缺乏有效衔接.即使相关规范和标准虽有说明,但由于监管力度有限或利益诱引,未在居住区的规划中体现出强制执行力,致使小学在学区覆盖上与居住单元联系不够紧密,实际覆盖效率偏低.
在快速城镇化和全面放开二孩政策背景下,城市空间结构、人口规模和空间分布也产生了相应的变化,且随着教育改革从“足量”向“量质均衡”的提升,原有基础教育资源的空间配置布点已不能满足人们的需求.因此,引入小学位置的兴趣点数据,精细化审视西安市中心城区小学空间布点现状特征,其实质是对过往布局方法、学位配比、调控策略、实施执行等多方面的反思,更是对如何进行小学布点的科学性和可操作性的启发.