基金项目:住房和城乡建设部2022年科学技术项目计划(2022-S-005)
第一作者:王智刚(1971—),男,高级工程师,主要从事绿色建筑和健康建筑方面的研究.E-mail:wangzg@gaokegroup.com 通信作者:李 立(1977—),男,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事绿色建筑和健康建筑方面的研究.E-mail:lili123@gaokegroup.com
(1.西安高新技术产业开发区房地产开发有限公司,陕西 西安 710065; 2.西安建筑科技大学 建筑学院,陕西 西安 710055)
(1.Xi'an High-Tech Industrial Development Zone Real Estate Development Co, Xi'an 710065, China; 2.College of Architecture, Xi'an Univ. of Arch. & Tech., Xi'an 710055, China)
nearly zero energy; public building; Guanzhong; key technologies
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2022.05.010
建筑行业是能源消耗与碳排放“大户”,2018年建筑全寿命周期的能耗和碳排放量分别占全国能源消费总量和碳排放的46.5%和51.2%[1].因此对近零能耗建筑的应用开展研究,有助于加快近零能耗建筑在我国的推广,对于应对能源危机、实现“双碳”目标,具有重要而深远的意义.
近零能耗建筑的理念起源于1976年丹麦Torben V.Esbensen教授提出的“零能耗住宅[2]”,此后多国学者对近零能耗建筑的应用和实施开展了广泛的研究[3-5].我国对于“近零能耗建筑技术”引进较晚,从2002年中瑞超低能耗建筑合作到2019年《近零能耗建筑技术标准》(GB/T 51350—2019)[6]的颁布实施,中国多地完成了近零能耗建筑的实践[7].国内相关学者也对近零能耗建筑技术在我国的应用进行了深入地研究.其中部分学者[8-12]依据近零能耗建筑实例探究了近零能耗建筑技术在不同建筑类型中的应用; 部分研究[13-16]针对不同气候区的气候特点、建筑形式等,探究近零能耗建筑技术的“本地化”,寻求因地制宜的近零能耗建筑设计; 也有学者[17-20]着重于探讨适用于近零能耗建筑的不同技术措施.这些研究促进了近零能耗建筑技术的发展,为近零能耗建筑在不同地区、不同建筑类型的应用提供了参考.
然而,当前对于近零能耗建筑技术的研究大多集中于对近零能耗居住建筑的模拟分析,运用模拟与实测综合分析近零能耗公共建筑的研究还较为缺乏.模拟分析可以为近零能耗建筑的设计提供指导,对多种技术措施下的建筑运行情况进行预测; 而实测分析则通过建筑室内环境检测和运行能效指标评估,反映建筑的实际运行情况,为建筑为各种技术措施的效果进行评价,以此优化建筑的实际运行.因此,结合模拟与实测分析,可对近零能耗建筑技术的效果进行预测与验证,为技术措施的改进提供参考.鉴于此,本文以陕西关中地区已建成的近零能耗公共建筑为例,分析该建筑所采用的关键技术,通过模拟对围护结构的重要节点进行传热分析.此外,结合大量的室内外环境测试和建筑运行数据,分析该建筑在实际运行过程的热工性能和室内环境指标,为关中地区近零能耗建筑的发展提供参考与借鉴.
热桥是指建筑围护结构中某些部位与周边存在传热性能的不同,且在室内外温差下这些部位热流相对密集,造成围护结构内表面温度较低(或较高)的区域.常规节能建筑设计行业常用的节能计算软件有2 种热桥计算形式: 一种为计算线性热桥并代入围护结构的平均传热系数中,简称为热桥计算法,另一种为主断面传热系数与修正系数的乘积,简称为修正系数法[21].本研究采用劳伦斯伯克利国家实验室(LBNL)研发的二维有限元传热分析模型THERM对重要节点进行传热分析,线性热桥传热系数ψ的计算方法如下[22].
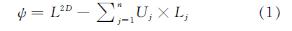
式中:L2D二维热桥的导热系数,W/(m·K); Uj为一维元素的传热系数,W/(m2·K); Lj为适用于二维几何模型中的长度,m; n为一维元素的个数.由于围护结构由多层材料结构组成,根据《民用建筑热工设计规范》(GB 50176—2016)的要求,热桥采用围护结构的平均传热系数按下式计算[23]:
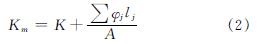
式中:Km为围护结构的平均传热系数,W/(m2·K); K为围护结构平壁传热系数,W/(m2·K); φj为围护结构上的第j个结构性热桥的线传热系数W/(m·K); lj为围护结构第j个结构热桥的计算长度,m; A为围护结构的面积,m2.
本次测试主要对建筑外围护结构整体气密性能进行检测,依据《建筑物气密性测定方法风扇压力法》[24],采取压差法进行检测.测试前需计算建筑内部体积、围护结构总面积、墙与屋顶面积、地板净面积等,并记录室内外温度、风速、风压等相关计算参数.测试过程中需关闭被测空间所有有影响的外部开口,打开所有的内门; 关闭带有内部风口的供暖装置、机械通风器和空调系统,并封闭机械通风末端和空调系统末端.建筑气密性的检测结果需要计算应符合50 Pa和-50 Pa压差下的换气次数,计算过程如下.
N+50=L+50/V# (3)
N-50=L-50/V# (4)
式中:N+50、N-50分别为室内外压差50 Pa和-50 Pa下房间的换气次数h-1; L+50、L-50分别为室内外压差50 Pa和-50 Pa下空气流量的平均值,m3/h; V为被测房间或建筑的换气体积,m3.建筑或被测空间的换气次数应按下式计算.
N50=(N+50+N-50)/2# (5)
式中:N50为室内外压差50 Pa条件下,建筑或房间的换气次数.
在进行室内环境测试和建筑能耗监测的过程中,需要对设备运行的启闭规律和人员在室率进行相应的设置.由于该研究所涉及的测试和监测周期较长,运行期间的人员在室率,设备运行时刻表大致符合《公共建筑节能设计标准》(GB50189-2015)的运行要求,其中工作日如图1所示,节假日全时间段仅有采暖温度设置为5 ℃低温运行.
本文选取陕西省西安市高新区已建成的TG幼儿园为研究对象.该项目总建筑面积7 473.8 m2,地上3层建筑面积4 710.0 m2为教室、幼儿活动室、寝室等; 地下1层2 763.8 m2为地下车库.建筑结构为框架结构,建筑设计为南北朝向,建筑体形系数为0.21,各朝向窗墙面积比为东0.23,西0.09,南0.43,北0.27,符合紧凑型设计原则.该项目作为近零能耗建筑,要求设计建筑比基准建筑本体节能率不小于30%,综合节能率不小于60%,且可再生能源利用率不低于10%.为实现近零能耗建筑目标,设计方案参照《近零能耗建筑技术标准》(GB/T 51350—2019),并荣获中国建筑节能协会的近零能耗建筑认证,项目的实施对陕西省绿色建筑行业起到示范引领的作用.
近零能耗建筑设计的出发点是降低建筑能耗的同时提高其能效,本文对建筑的围护结构热工性能、气密性设计、主动式能源系统和可再生能源利用等进行了分析,主要节能设计技术措施如下.
近零能耗建筑应采用保温性能更高的围护结构.围护结构保温性能的确定遵循性能化设计原则,通过计算后确定的围护结构方案为:外墙采用200 mm厚加气混凝土砌块+250mm厚石墨聚苯板,保温层双层错缝粘贴,固定形式为粘贴+断热桥锚栓,平均传热系数为0.15 W/(m2·K); 屋面采用120 mm厚钢筋混凝土砌块+250 mm厚高容重石墨聚苯板,保温材料分层错缝干铺,屋面设置隔汽层和防水层,采取保温防水一体化的干法施工工艺,屋面平均传热系数为0.14 W/(m2·K); 外窗采用外挂式木索结构被动式窗,选用铝包木型材,玻璃采用三玻两腔6 Low-E+16 Ar+6 Low-E+16 Ar +6 Low-E; 夏季太阳得热系数0.33,冬季太阳得热系数0.46; 整窗传热系数1.0 W/(m2·K).外墙、屋面女儿墙及外窗的结构做法详图见图2.
建筑外围护结构保温性能提高后,热桥成为影响围护结构保温效果、室内环境舒适度及建筑能耗的重要因素.对易产生热桥的部位如外保温的铺贴及固定方式与固定锚栓、墙角处、外墙上固定龙骨支架等不同部位均采取相应的削弱或消除热桥的措施处理,以保证建筑整体尽量无热桥,最大限度减少因热桥对建筑节能及舒适度的影响.本研究采用THERM对外围护结构的重点部位进行二维传热分析,得到不同节点的热损失分布情况.如图3所示,采用无热桥的节点处理后,节点a-e 的外边界和内边界间无明显的热桥,尤其消除了保温与墙体之间的金属连接件所带来的热桥影响,线性热桥传热系数值ψ分别为0.146,0.187,0.114,0.163,0.632均能较好的符合《近零能耗建筑技术标准》(GB/T 51350—2019)的要求.
建筑气密性对于降低建筑能耗、提高室内环境质量起到关键性作用.项目在建筑设计阶段明确标注气密层的位置,保证气密层连续,并包围整个外围护结构(图4).
项目气密性设计涉及到采用高气密性的建筑外门窗,外门窗与洞口之间缝隙的气密性处理,维护结构洞口、接线盒、管线穿越处等易发生气密性问题的部位,不同围护结构交接处、以及排风等设备与围护结构交界处的密封节点设计等.典型的气密性设计涉及的节点做法见图5.
项目采用高效热回收新风系统,通过回收利用排风中的能量降低新风负荷需求(图6).全热回收效率75%,单位风量风机耗功率0.19 W/(m3/h),满足近零能耗标准要求,初级过滤效率大于90%,中级PM2.5过滤效率达到95%.
空调采用直流变速多联式中央空调系统,主机采用直流变速、变制冷剂流量空调系统,可根据房间负荷自动调节.多联机制冷性能系数为3.65>2.8,制冷综合性能系数IPLV为8.5>6.0,制热性能系数COP>1.8,均满足节能标准要求,最大程度地降低建筑供暖供冷设备能耗.
为实现近零能耗建筑的能效指标,项目在屋面设置了高效的太阳能光伏系统和太阳能+空气源热泵集中供应热水系统.光伏发电系统由1个光伏子系统构成,共设置光电转换效率超过16%的多晶硅电池组件400块(图7).光伏板面积约200 m2,设计总装机容量峰值不小于25.5 kWP(峰值).太阳能+空气源热泵集中供应热水系统设计为产热量6 000 L/d.同时这些太阳能设备与新风系统机组还共同构成了屋面的遮阳构件,在降低顶层建筑的能耗方面发挥了重要的作用.
通过对该建筑1~3层室内环境和室外环境进行测试,是检验和评价近零能耗建筑综合性能的有效途径.因此,本研究以室内环境指标温度、湿度、PM2.5、二氧化碳浓度背景参数,并作为本次分析依据的背景环境因素.测试设备型号与精度参数如表1所示,数据采样频率为4次/h(每天采样为96次).本次测试从2020年12月1日至2021年5月31日,其中12月~3月期间室内维修及监测设备调试、断网等情况造成部分数据缺失,根据原有数据对缺失数据进行修复和插值处理.其中对1、2层最低温湿度数据进行了少量的插值处理,对3层最低温度和最低湿度数据进行了数据修复性替换,其中12月10日至12月15日数据为6 d均值; 12月16日和17日的数据为2日均值; 1月22日至1月24日为3 d均值,5月18日至5月24日为7 d均值,5日28至5月31日为4 d均值.
本研究采取压差法对外围护结构整体气密性能进行检测,测试时将ZN-07与一台风机连接进行检测.选择建筑的主出入口为鼓风门的安装位置,安装鼓风门、风机、检测主机等设备,将检测主机和风机通过等压管、数据线与安装TECTITE检测软件的电脑连接.本次测试通过输入不同的检测压差值,测试建筑压差检测间隔为±5 Pa,检测范围为±25 Pa~±60 Pa.此外,分别进行负压检测和正压检测,负压检测时风机向室外鼓风,正压检测时风机向室内鼓风,通过主机对各个压差下的空气流通量进行数据采集,并对取样点进行拟合得出建筑物在室内外压差50 Pa时的空气渗透量.通过气密性测试,取得负压0.24次/h,正压0.25次/h,平均换气次数0.25次/h的结果,因此该项目具有良好的气密性.
如图8所示,通过对该项目室内1~3层室内最低温度、室内最高温度和室内平均温度与室外最低温度和最高温度的曲线进行比较分析,进而分析该建筑的热工性能.就整体的趋势而言,在室外温度变化波动较为剧烈的情况下,项目1~3层的总体温度波动较小.室外最低温度和最高温度从12月到5月波动上升,室外最低温度-9.05 ℃,室外最高温度36.68 ℃,而室内每层温度最低温度和最高温度在20~26 ℃之间波动,围护结构具有良好的抗外扰能力.此外,就整体建筑而言,1~3层的总体变化趋势较为一致(图8d),由此可知建筑空间的整体热稳定性较好,建筑内部的温度分布较为均匀,进而能有效改善人居环境的舒适度.
建筑湿度是影响环境舒适性的重要环境参数之一,对项目空间的湿度进行测试,进而分析空间湿度的分布范围.如图9所示,根据测试所得项目的室内1~3层室内最低湿度、室内最高湿度与室外最低湿度和最高湿度的曲线进行对比分析.室外湿度整体的波动较为剧烈,最低为9.39%,最高为96.11%.室内每层温度最低湿度和最高湿度基本在30%~60%间波动,总体的空间湿度波动幅度相对较小.就整体的测试数据变化趋势而言,1层的波动幅度大于3层的波动幅度,2层的湿度稳定性最佳.此外,项目1~3层的湿度总体变化趋势与室外的变化较为一致,但室内湿度变化随季节变化的幅度得到了有效的削弱,进而提升了室内空间热湿环境的稳定性.
在提升建筑气密性的同时,有效保证室内空气质量对建筑中人员的身体健康具有重要的意义,本研究对项目的室内PM2.5浓度和CO2浓度进行了长期测试,测试结果如图 10所示.从11月15日至12月10日测试得出项目室内1~3层室内和室外PM2.5数据进行分析(图 10(a)).总体而言,1~3层空间的室内PM2.5浓度低于室外空间,仅有部分时间的2层空间PM2.5浓度数值高于室外的数值.此外,进一步分析测试周期中室内空间的CO2浓度数据(图 10(b)),参照欧洲标准EN 15215-2007,在我国近零能耗建筑中,对于人员密集场所二氧化碳的体积浓度控制要求,满足《近零能耗建筑技术标准》GB/T 51350—2019关于CO2的人员长期停留区域室内二氧化碳体积浓度的900 ppm,整体室内空气质量达到“优等”水平.
在能耗监测的时间段内,对每层VRV空调、VRV末端、照明及设备、新风系统、电辅热(12月开启9 d,1月31 d,2月20 d)的每月各项能耗进行统计,光伏发电量减去总能耗即剩余的光伏发电量.如图 11所示,经过对测试数据进行分析,该建筑在冬季的采暖能耗指标约为10.5 kWh/(m2·a),远低于《近零能耗建筑技术标准》GB/T 51350-2019中寒冷地区限值为15 kWh/(m2·a)的要求.此外,由于该项目位于寒冷气候区,在冬季采暖季对建筑自然通风工况进行测试,能有效评价该建筑物的被动式节能潜力.本研究选取关中地区最冷月(1月11日—1月18日)进行对该建筑的自然通风工况下的室内温度进行测试,测试结果如图 12所示.根据数据分析可知,室外温度日最高温度低于15 ℃,最低温度接近0 ℃,室内各层平均温度均维持16~20 ℃; 采用高效的围护结构能有效提升建筑空间的稳定性,在有效保证室内空间的舒适度,降低建筑物的能源消耗,具有较好的节能潜力.
根据对该项目的光伏发电监测数据进一步分析,从12月1日至5月31日,共计发电182 d,平均每天发电68.9 kWh.其中在2月24日发电量最少为3.9 kWh,4月28日发电量在为最大148 kWh.经过测试分析,该项目的可再生能源利用率约为18.47%,满足《近零能耗建筑技术标准》GB/T 51350-2019中近零能耗公共建筑的可再生能源利用率≥10%的要求,在此基础上为建筑空间清洁能源替代提供了更加有效的保障.
以陕西关中地区的某典型近零能耗公共建筑为例,分析了该地区的近零能耗公共建筑设计关键技术.结合有限元模拟分析围护结构的重要节点,并通过实测分析建筑环境参数和运行数据进一步论证设计方案的可靠性.基于此,得出以下结论:
(1)对该建筑的关键节点进行二维传热分析,通过无热桥设计的关键节点能有效降低围护结构的热损失,各个节点的线性热桥传热系数ψ均能满足标准的限值;
(2)对该建筑运行效果进行实测可知:在被动式建筑设计、主动式高性能能源系统和可再生能源利用三个重要技术路径指导下,项目采取多项关键节能技术,达到了良好的气密性和稳定舒适的室内环境,满足了近零能耗建筑要求;
(3)结合各项能耗和太阳能发电的监测数据分析可知:结合可再生能源利用,该建筑在少量能源消耗的情况下能较好的维持室内环境的热舒适.