基金项目:“十三五”国家重点研发计划“绿色建筑及建筑工业化”重点专项(2018YFC0705300)
第一作者:蒲 静(1996—),女,硕士生,研究方向为工业建筑节能与通风.E-mail:pjjqianxi@163.com 通信作者:袁艳平(1973—),男,博士生导师,教授.E-mail:ypyuan@home.swjtu.edu.com
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China)
industrial building; thermal corridor; buoyancy-driven natural ventilation; non-isothermal heat source
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2022.05.016
与民用建筑不同,工业建筑大多是单层厂房,有较大开敞空间、内部设备多、设备体量大、散热密度高等特点[1-2].由于生产工艺的多样性,厂房内部往往存在不同形式和不同强度的热源,强热源散热可能会导致厂房局部热环境恶劣,造成高排热的需求[3-4].自然通风作为一种被动式通风手段,不仅能改善工作区的空气品质,还可以显著降低建筑能耗[5-7].在工业建筑中已经被广泛采用[8].
目前,国内外学者针对不同类型热源形式对通风效果的影响做了大量研究.学者分别对单个点热源[9-10]、线热源[11]、面热源[12]和体热源[13-14]的房间通风系统进行了分析.而实际建筑中往往包含两个或多个热源,文献[15-16]指出单、双热源形成的垂直温度分布有较大差别,双热源送风参数的计算不能简化为单热源的计算参数,应考虑双热源间距的影响.Cooper和Linden[17]理论推导了含有双互相独立点热源的自然通风房间的热分层流动规律,研究发现,含有两个不等强度的点热源的自然通风房间会形成三个明显的均匀混合的温度分层.热分层高度随着两个点热源的强度之比的变化而变化.倪波[18]通过实验手段研究了置换通风系统中双热源形成的温度场,指出辅热源的存在降低了温跃层的高度和上部区域的温度.学者[19-21]针对含有双热源的房间的对流换热问题,分析了房间尺寸、热源尺寸、热源强度和热源位置等参数对换热的影响.王怡等[22]则对双热源作用下局部排风系统的侧吸罩流场及捕集效率特性进行了研究.Shrinivas等[23]从理论上研究了两个强度不等的局部地板热源的瞬态通风效应变化.Benouis等[24]模拟分析了三个电子元件的热源房间,依次改变进口位置、出口位置和热源位置以确定最优冷却策略.Dou等[25]针对多热源工业建筑,研究了进风口高度和排风速度对浮力驱动混合通风性能的影响,最后确定了改进后通风系统的最优参数.
目前针对热源数量的研究现状表明,单个热源、独立且互相不受影响的双热源、互相影响的双热源以及两热源以上的多个热源成为各个学者的主要研究对象.而针对热源形式,不同体热源也有涉及.但高大带状非等温体热源间相互作用的情况鲜有研究.然而,在工业建筑中,因干燥、烧制等生产工艺的需求,连续排列的多个高温设备将组成具有大长宽比的带状体热源,并在此类热源附近形成高温廊道,如图1所示为厂房热廊道的实景图.高温的工作环境会对工人健康和生产效率产生不良影响[26].基于此,本文以工业热廊道为研究对象,对非等温热源作用下的廊道热压自然通风特性进行研究,相关结果可为此类厂房的自然通风设计提供参考.
在进行缩尺实验之前,需要确保实验模型和实际问题之间能够满足基本的相似定律.即须保证缩尺实验模型和原型建筑达到几何相似性、运动相似性和热相似性三个相似准则.几何相似是最容易达到的相似准则,原型建筑的尺寸被缩小到一个适当的小于1的缩放比例.对于运动相似,实验模型和原型建筑所有对应的流速和加速度的比例系数必须相等.即实验模型和原型建筑中的Pr数、Re数和Ar数相等[27],Ar数是由Gr数和Re数组成.实际工程中,当使用空气作为流体介质时,实验模型和原型建筑中的Pr数是相等的,约等于0.7,但很难同时满足Gr数和Re数相等[28].对于纯热压自然通风,Re数和Gr数不是独立的,Re数与Gr数的平方根正相关[29-30].相关研究表明,在这种情况下,最重要的是确保流动处于完全湍流区(即Re>2.3×103,进入到自模区)[31],即可保证基本的流动与传热现象变化规律相同.Re数的计算公式为
Re=ρuBH/μ (1)
式中:ρ为空气密度,kg/m3; H为厂房高度,m; μ为动力黏性系数,(N·s)/m2; uB为浮力参考速度,m/s,计算公式为[32]
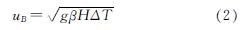
式中:g为重力加速度,m/s2; β为体膨胀系数,1/K; ΔT为温差,℃.
根据以上要求,在考虑实验条件与实验安全前提下,确定本文模型实验的几何比例尺为1/20.同时,为保证实型与模型满足相似准则要求,对进空气出口温差分别为5 ℃、15 ℃与25 ℃的实型与模型Re数进行核算,结果如表1所示.
从表中可以看出,全尺寸模型和实验模型的Re数均大于2.3×103,处于完全湍流区范围内.因此模型实验的进出口温差在5~25 ℃范围时,能对应绝大部分的实型建筑自然通风工况,可以按此缩尺比例进行缩尺实验.为了保证模型实验和实际建筑相似,Ar数应该相等,即(Ar)1=(Ar)2,其计算公式为
Ar=gHβΔT/u2B (3)
式中:下标1代表模型实验; 2代表实际建筑.
模型的几何比例尺为1/a,即l2=a·l1,温度比例尺为1,即T1=T2; 于是速度比例尺:u2=u1a1/2,风量比例尺:G2=G1a5/2.最终得到模型的各种相似比例尺列于表2.
本文的模型实验台是参照某建陶厂窑炉车间按1:20的比例设计,长×宽×高=2.5 m×0.75 m×0.5 m.围护结构由金属夹芯板制成,模型地面做近似绝热处理.x方向两侧外墙及屋顶分别设2个进风口和2个排风口,进风口底部贴地,排风口中心间距为0.325 m,4个风口尺寸均为长×宽=2.5 m×0.075 m.两热源贴地放置,水平间距为0.25 m,热源尺寸为长×宽×高=2.5 m×0.15 m×0.2 m.模型示意图如图2所示.
实验过程中分别在三条廊道的正中间位置各布置一个测点,水平方向总计3个测点; 垂直方向每隔0.05 m布置一个测点,总计9个测点,测点布置示意图如图2所示.测试仪器采用K型热电偶与安捷伦34980A数据采集仪,仪器测量范围为-50~300 ℃,精度为±0.5 ℃.
本文的物理模型即为上文2.2节所提的三维实验模型,为方便下文分析,定义左侧热源为1号热源,右侧热源为2号热源.
由于本文研究厂房涉及大面积热源散热的传热问题,因此采用增强型壁面函数.为了保证y+≈1,在热源近壁区域划分较密的网格密度.本文采用ICEM网格划分软件进行处理,网格示意图如图3所示.其中最小网格尺寸为0.8 mm,最大网格尺寸为20 mm,网格增长率不超过1.2.对于热壁面相邻的网格单元,y+平均值在1左右,最大值不超过3.
参照建陶厂窑炉车间的实测概况[33],本文边界条件设定如下.
(1)壁面
在粘性流动中,所有壁面都默认采用无滑移的边界条件.设定热源除底面外,其他三面均匀散热,热源边界采用定壁温边界,定义热源的表面温度,表面发射率ε为0.85.厂房围护结构的设置与实验模型的一致,环境温度为室外气温25 ℃,四面外墙和屋面传热系数设定为0.83 W/(m2·K),表面发射率ε为0.85,地面设为绝热面.
(2)进、排风口
由于浮升力驱动热压自然通风的进、排风口的速度是未知的,因此自然进、排风口边界条件采用压力边界[34].定义进、出口空气温度为室外气温25 ℃,相对静压取值为0 Pa,湍流强度为5%,特征尺寸为风口高度.
控制方程由连续性方程、动量方程和能量方程组成.这些稳态方程用计算流体动力学软件ANSYS FLUENT 17.0.求解器采用有限体积法和二阶迎风格式[35].采用SIMPLE算法实现了压力-速度的耦合计算[36].湍流效应采用Realizable k-ε模型进行模拟[37-39].
由于热源表面温度较高,必须考虑辐射影响.Fluent软件提供5种辐射模型,包括离散传输辐射模型(DTRM)、P-I辐射模型、Rosseland辐射模型、S2S辐射模型和离散坐标(DO)辐射模型.其中S2S辐射模型常用于封闭空腔中不考虑介质影响的辐射换热问题,该辐射计算模型假定所有表面均为漫灰表面[40-41].由于通常条件下,空气对于热辐射近似透体[42-43],因此可选用S2S模型予以计算空气的物理性质被假定为常数,假设空气是不可压缩的,由温差引起的密度变化采用Boussinesq假设[44].除了动力方程中的浮力项外,Boussinesq假设认为密度是常数.此外,由于厂房是热压为驱动力的被动式自然通风方式,所以必须加上完全浮力影响(Full Buoyancy Effects)选项.
在迭代计算过程中,对廊道关键位置的空气温度进行监视,确保温度值不随迭代过程而发生大幅波动,且系统的流入量与流出量的差值小于总流量的0.1%,则可认为达到收敛状态.
网格数量是影响数值模拟计算准确性的一个关键因素,为了验证数值模拟结果与网格数量无关,本文分别采用了41万、53万和74万网格对网格独立性进行验证.图4表示两热源表面温度均为80 ℃时,不同网格数下中间廊道的垂直空气温度变化.从图中可以看出,在不同网格数下,中间廊道垂直温度变化趋势一致,其中41万网格的空气温度计算结果偏高,53万网格和74万网格的计算结果基本一致,计算相对误差在5%以内.考虑到网格的数量越多,迭代所需的时间就越多.因此,下文的数值模拟中选择53万网格进行计算.
以上文建立的数值计算模型以及实验过程中的测试数据作为边界条件,通过对比侧边廊道和中间廊道垂直温度分布来验证数值模拟方法的有效性.图5显示了两热源表面温度均为80 ℃时,侧廊道和中间廊道垂直温度的模拟值和实验值的对比.从图中可以看出,厂房两廊道沿垂直方向测点空气温度的模拟值和实验值基本一致.从而验证了本文所用CFD数值模型的准确性与可靠性.
左侧1号热源表面温度保持80 ℃不变,分别设定右侧2号热源表面温度为80 ℃和120 ℃,对比分析热廊道厂房内部两等温热源与非等温热源的自然通风特性.
图6为两热源在等温与非等温作用下的厂房温度场和速度场分布对比.从流场图可以看出,从侧墙进入室内的空气流经热竖壁后被加热膨胀,空气密度减小,热压作用使得其以自然对流的形式向上升腾,此时气流贴附热源的上升速度较大.气流脱离热竖壁后,在热源上方分成了两股空气流,一部分热空气继续向上运动从天窗排出厂房,另一部分由于热源障碍物的遮挡,在中间廊道顶部产生下降流,同时热竖壁的近壁气流上升形成了方腔回流循环.两高大带状热源贴地放置,使得浮力羽流的下方无空气补给,热量因此囤积在中间廊道.
图6 等温热源与非等温热源的厂房温度场和速度场分布(模拟工况设置:Ta=25 ℃, Tw1=Tw2=80 ℃和Tw1=80 ℃, Tw2=120 ℃)
Fig.6 Distribution of temperature contour and velocity field in plant with isothermal and non-isothermal heat sources
从图中可以看出,中间廊道空气温度较高,其次是廊道上方空间,侧廊道空气温度最低,与室外环境温度接近; 空气流速的大小分布则相反,侧廊道的空气流速最高.沿厂房x方向三个截面的温度场和速度场差异较小.当两热源强度相等时,温度场和速度场均以厂房中轴线呈对称分布.当两热源强度不等时,温度场和速度场的分布表现出差异性,中间廊道及热源上方的流场形态发生了改变; 高温热源侧的气流在热浮升力作用下直接向上运动由顶部排风口排出; 低温热源侧的气流则被诱导降沉至中间廊道,以减缓中部区域的热堆积,中间廊道内部对称分布的两涡流变成了靠近低温热源一侧的单个涡流.
根据上述分析,可将自然通风热廊道厂房在非等温热源作用下的空气流动简化,并在热源高度处作虚线所示的假想面,如图7所示.从图中可以看出,侧廊道流场属较为典型的热壁诱导/非对称热通道的自然对流流场,中间廊道则因近壁气流上升、远壁空气降沉而形成半封闭方腔的回流循环.侧廊道由进风口、外墙、单热源竖壁、地面和顶部假想面构成一个封闭体,中间廊道则是由左右两热源竖壁、地面和顶部假想面构成一个封闭体.
如表2所示,左侧1号热源表面温度保持120 ℃不变,分别设定右侧2号热源温度为100 ℃、80 ℃、60 ℃和40 ℃,分析热廊道厂房内部两热源的不同温度差异对自然通风特性影响.
表3 两热源温度差异的模拟工况设定(单位:℃)
Tab.3 Setting of simulation condition with different temperature difference between two heat sources(unit:℃)
图8 两热源温度差异变化的x=1/2 L截面温度场和速度场分布
Fig.8 Distribution of temperature contour and velocity field at x=1/2 L plane with different temperature difference between two heat sources
如图8所示为两热源温度不同差异的x=1/2 L截面温度场和速度场分布.随着两热源温差的增大(即右侧2号热源表面温度的降低),厂房内部余热量减小,整体空气温度降低,中间廊道区域尤其明显.两热源温差大小会一定程度影响热廊道厂房的速度场,进而对中间廊道的空气温度分布均匀度产生进一步的影响.此外,中间廊道中轴线左右两部分区域的空气温度差异逐渐增大,廊道上方左右两股气流的汇合位置逐渐向高温热源侧偏移.
在两热源温度差异变化的过程中,侧廊道流场仍属热通道自然对流,中间廊道则是半封闭方腔的回流循环.图9为两热源不同温度差异下,厂房左、右两侧廊道的热压通风量变化.对于热压自然通风建筑,随着热源表面温度的升高,房间内部热压作用增强,内外压差增大导致通风量增大.随着两热源温度差异的增大(即2号热源表面温度的降低),厂房整体通风量减小,这一变化趋势与热压自然通风原理符合.当两热源温度差异增加3倍时,左边1号热源侧廊道风量降低了15.5%,右边2号热源侧廊道风量降低了19.1%.虽然左边1号热源的温度未变,但由于右边2号热源表面温度降低,厂房整体余热量减小,故左侧廊道的通风量同样减小.可见对于热廊道厂房,侧廊道的通风量不仅与其内部热源强度有关,附近热源散热同样对其通风量有影响.
图9 两侧廊道风量随两热源温度差异变化
Fig.9 Distribution of ventilation rate of two side corridors with different temperature difference between two heat sources
由前文的分析得到,侧廊道的顶部即为通道流的出口,中间廊道的顶部既是方腔流的进口也是出口,通过比较两廊道顶部开口处的空气温度和速度变化,分析两热源温度差异变化对廊道自然通风效果的影响.图 10表示侧通道和中间方腔的上部开口竖向速度和温度随两热源间温度差异变化,从开口的竖向速度分布可以看出,贴壁处,由于黏性作用流体速度为零; 在靠近两端冷、热壁处时,均存在一个峰值速度; 壁面温度越高,对流换热越强烈,峰值速度越大.随着与热(冷)壁距离的增加,开口竖向流动速度逐渐减小(增大).开口的温度分布可以看出,贴壁处的流体温度等于壁面温度,在离开壁面的方向上流体温度逐渐变化,直至周围环境温度.
侧通道:从开口竖向速度分布可以看出,冷空气在侧通道的运动主流区集中于热壁侧,随着右热源温度的降低(两热源温度差异的增大),厂房内部热压作用减弱,左、右两侧通道在顶部出口主流区的竖向速度均有所降低,峰值速度的出现位置基本不变.从开口温度分布可以看出,两侧通道的主流区出口温度差别较小.
中间方腔:竖向速度为负值即代表空气进口,竖向速度为正值即代表空气出口.从竖向速度分布可以看出,由于方腔左壁面温度高于右壁面,以厂房中轴线为基准,冷气流大多从方腔顶部的左侧进入,在壁面附近排出,方腔中轴线左热壁侧的进、出口速度及峰值速度均大于右侧.从开口温度分布可以看出,沿水平方向开口空气温度的变化较小,随着右热源温度的降低,方腔的进、出口温度随之降低.
本文通过CFD数值模拟研究了非等温热源作用下,工业车间热廊道的热压自然通风特性,得出了以下结论:
(1)热廊道厂房在双等温热源的自然通风情况下,侧廊道流场属热壁诱导的非等温热通道自然对流流场,中间廊道则因近壁气流上升、远壁空气降沉而形成半封闭方腔的对称回流循环.而非等温热源一定程度上改变了自然进风路径:高温热源侧的侧廊道进风气流因浮力向上迁移,低温侧的气流被诱导降沉至中间廊道;
(2)侧廊道的热压通风量不仅取决于临近侧热壁的散热强度,还将显著地受到其廊道对侧热源散热强度的影响;
(3)随着两热源温差的增大,中间廊道中轴线左右两侧空气温度差异增大,热源上方左、右两股气流的汇合位置由厂房中间区域逐渐向高温热源侧偏移.
综上所述,在布置生产厂房内部的条、带状高温生产设备时,应注意热源温度差异对廊道工作区热环境的影响,尽可能将操作岗位集中于侧廊道,并在中间廊道靠近高温热源侧设置作业时段的主动降温措施.本文的研究结果可为工业热廊道的自然通风设计提供参考依据.
