基金项目:中国工程院战略研究与咨询项目(2022-XZ-38); 中国博士后科研基金项目(2021M702551); 西部绿色建筑国家重点实验室自主研究基金课题项目(LSZZ202201)
第一作者:杨 雯(1990—),女,博士,讲师,从事建筑技术方面研究.E-mail:yangwen@xauat.edu.cn 通信作者:刘加平(1956—),男,博士,教授,从事建筑技术方面研究.E-mail:liujiaping@xauat.edu.cn
(1.西部绿色建筑国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710055; 2.西安建筑科技大学 建筑学院,陕西 西安 710055)
(1.State Key Laboratory of Green Building in Western China, Xi'an 710055, China; 2.School of Architecture, Xi'an Univ. of Arch. & Tech., Xi'an 710055, China)
building heating energy consumption; spatial autocorrelation analysis; temporal and spatial distribution; influence factor
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2022.06.005
“一带一路”为2013年中国提出建设的“新丝绸之路经济带”和“21世纪海上丝绸之路”简称,其包含北线、中线、南线和中心线四条线路,本文的研究区域为中心线和中线的西部地区,包括陕西、青海、宁夏、甘肃和新疆.其中,除陕西的汉中、安康和商洛以及甘肃的陇南属于夏热冬冷地区,其他均为严寒和寒冷地区(集中供暖).汉中、安康、商洛无集中供暖,由于陇南市的统计年鉴和政府文件中存在供暖能耗信息,因此,本文的统计信息包括陇南市.截止到2016年,建筑供热能耗已经占到了建筑能耗总量的50%以上,是建筑能耗重要构成部分.因此,降低建筑供热能耗总量、提升能耗强度是实现建筑节能的重要途径.
对建筑供热能耗进行空间分析是了解其空间分布的重要手段.Grossi等[1]利用Zenga不平等指数揭示建筑能耗强度影响因素对能耗强度分布不均的影响.周洁[2]采用空间自相关分析方法阐明了建筑业能耗强度空间基本特征,发现了中国建筑业能耗强度仍存在明显的区域差异,空间分布不均衡等现象.现有文献的研究方法中多采用单一指标或方法直接评判地区差异,而采用多指标评价空间分布的规律会更加全面客观.
除了建筑能耗空间分析,建筑能耗的影响因素及其权重研究也是至关重要的.孙海玲[3]在对驱动建筑能耗增长的影响因素进行分析的基础上,首次采用岭回归进行影响程度的测算,并得到较为合理的结果.刘晓君[4]对建筑能耗进行了GIS时空对比,并以STIRPAT模型为基础建立了建筑能耗数学模型,分析出主要驱动影响因素.现有文献多基于STIRPAT模型建立数学模型并利用岭回归分析对建筑能耗的影响因素进行研究,缺乏针对建筑供热能耗影响因素的研究.
综上所述,本研究选取2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗总量和强度作为基础数据,通过空间相关分析获取建筑供热能耗总量和强度的空间分布规律,采用标准差椭圆分析方法描述空间分布的时间演变格局.在此基础上,以STIRPAT空间数据模型为基础进一步探究建筑供热能耗强度和总量的影响因素权重,从而为政策的制定提供一定的参考,本文研究框架参见图1.
采用空间分析可揭示建筑供热能耗空间分布格局和不同地区之间影响因素的差异性[1].本文选用全局空间自相关分析和局部空间自相关分析的方法对建筑供热能耗进行空间相关性分析.
通过建立空间权重对建筑供热能耗进行全局空间自相关分析,以清晰地描述出变量在空间区域的分布特征.现多采用全局Moran's I指数,Moran's I指数可以度量整个空间序列的集聚情况,反映整个地区中相邻区域之间的空间自相关情况.其表达式为
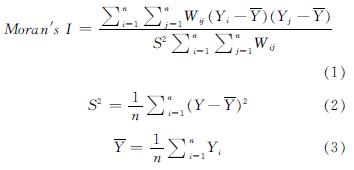
式中:n为研究范围内的样本总数; Yi和Yj分别为第i个和第j个地区的观测值; Wij为空间权重矩阵; S2表示为不同区域的方差; Y^-为不同区域观测值的均值.
局部空间自相关分析现常用莫兰散点图来表征,可弥补全局空间自相关分析的不足.莫兰散点图横轴表示研究区变量的观测值,纵轴表示空间滞后水平,散点图回归线的斜率即为莫兰指数.散点图共有四个象限,第一象限与第三象限分别表示空间正相关,即建筑供热能耗存在空间集聚效应,其中第一象限为空间变量高高相邻,第三象限为空间变量低低相邻; 第二象限与第四象限,表现为空间负相关性,即建筑供热能耗存在空间分散效应,其中第二象限为空间变量低高相邻,第四象限为空间变量高低相邻[1].
标准差椭圆分析是一种能从整体上、空间上对各要素空间分布的中心性和方向性进行定量描述的分析方法[5].采用标准差椭圆分析可以描述各采样点在不同空间上的分布范围与扩散程度,其平均中心点的移动可以反映出整体的偏移方向.
为了更好地评估不断变化中的决定性因素以及各部分的权重,美国学者Ehrlich和Holdren提出IPAT模型,表达式为I=PAT[6],创造性地将环境影响视为人口、技术与富裕程度的函数.其中:I为环境影响; P为人口; A为富裕程度,一般以GDP表示; T代表科技进步.Schulze提出人类活动也会对环境造成影响,并将这种活动定义为B,将表达式改为I=PBAT.Rose等修正了该框架同比例线性变化的局限性,得到STIRPAT模型表达式:I=aPbiAciTdiei(其中,a为常数项,b、c、d分别为各变量的估计指数,e为模型误差).当a、b、c、d、e均为1时,即I=PAT,为模型的特殊形式,这时对I=aPbiAciTdiei取对数,可得
lnI=lna+blnP+clnA+dlnT+lne (4)
采用数值计算的方法获取2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑能耗和建筑供热能耗总量及强度数据,针对两组数据进行了对比分析.
建筑能耗的测算方法主要有三种:基于能耗强度的计算方法、基于终端能耗模型的计算方法和基于统计年鉴的计算方法,前两种方法需要大规模的数据统计,而基于统计年鉴的计算方法计算简单,数据来源可靠且易获取,因此选取该方法来对建筑能耗进行进一步的统计与分析,计算公式为
BE=BEb-TE+EH+BEo (5)
式中:BE为建筑能耗; BEb为建筑能耗基础量; TE为交通能耗扣除量; EH为供热能耗修正量; BEo为其他部分.获取建筑能耗总量后,通过将其除以该年的建筑面积总量以求得该年的建筑能耗强度.
本文通过《中国能源统计年鉴》获取西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区2010—2020年的能源数据,再通过式(5)计算得到了建筑能耗总量和强度,结果如图2所示.
图2 2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑能耗
Fig.2 Building energy consumption of provinces and autonomous regions along “the Belt and Road” in Western China from 2010 to 2020
图2中西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑能耗总量一直保持着增长态势,其建筑能耗总量可以分为三个梯队.陕西和新疆的建筑能耗总量为第一个梯队,其建筑能耗总量在2010—2020年之间都大于1000万tce,且总体增长都较多,陕西建筑能耗总量从2010—2020年增长率为42.41%; 新疆建筑能耗总量从2010—2020年增长率为85.24%.甘肃建筑能耗总量为第二梯队,其建筑能耗总量略低于陕西和新疆但大于青海和宁夏,总体增长趋势与陕西和新疆也大致相同,建筑能耗总量从2010—2020年增长率为37.30%.青海和宁夏的建筑能耗总量为第三梯队,其建筑能耗总量均较低,总体增长趋势也与其它省份及自治区不同,青海建筑能耗总量从2010—2020年一直保持着增长趋势,增长率为88.67%; 宁夏建筑能耗总量从2010—2020年整体保持波动的趋势,增长率为8.97%.就建筑能耗强度而言,陕西2010—2020年的建筑能耗强度最低,在2011年达到最低,为9.02 kgce/m2; 其余省份及自治区的建筑能耗强度升序排列依次为甘肃、新疆、宁夏和青海.
本文通过对《中国城市建设年鉴》2010—2020年的建筑供热能耗数据进行筛选和计算获得了西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗总量和强度,具体数据见图3.
图3 2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗
Fig.3 Building heating energy consumption of provinces and autonomous regions along “the Belt and Road” in Western China from 2010 to 2020
图3中西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区建筑供热能耗总量的变化表现出不同的趋势.陕西和甘肃除个别年份整体呈现出上升的趋势,陕西在2010—2020年增长率达到了242.08%; 甘肃在2011—2020年增长率最大,为110.85%.青海、宁夏和新疆都呈现出波动的趋势,由于青海前几年的数据统计工作缺失导致其在2010—2016年的建筑供热能耗数据偏小,所以主要根据其后面几年的建筑供热能耗总量来对其进行趋势判断.青海和宁夏的建筑供热能耗总量相差不大且都较小,而新疆建筑供热能耗总量最大.2017—2020年青海的建筑供热能耗数据在169.17~184.62万tce之间; 宁夏在2011—2018年增长率最大,为49.79%; 新疆在2013—2018年增长率最大,为23.75%.就建筑供热能耗强度而言,沿线省份及自治区都呈现出减小趋势,其中甘肃、青海和宁夏在2011年都呈现出较大的变化,陕西变化较为缓和,新疆整体下降速率较快.陕西、甘肃、青海、宁夏和新疆2010—2020年的建筑供热强度的变化率依次为4.04%、23.60%、22.71%、17.00%和16.35%.
建筑供热能耗总量与建筑能耗总量对比关系随时间变化关系可参见图4.图4中通过对比建筑供热能耗总量占建筑能耗总量的比重来表明两者的关系,可见陕西的占比情况随着时间推移呈现出整体上升的趋势,这可能是由于城镇化的进程加快,导致供热面积和供热总量增加,从而使其占比逐年上升; 甘肃、青海、宁夏占比呈现出波动趋势,这或许是由许多因素共同变化导致的结果; 新疆呈现出逐年减小的趋势,从2010年占比55.02%降低到2020年的占比为29.49%,这是由于建筑节能的效果逐渐得到提升导致的,在2010—2020年建筑能耗总量在逐年上升,但是建筑供热能耗总量并没有呈现出逐年上升的趋势.西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区在2020年除宁夏外其他省份及自治区占比都维持在30%左右,而宁夏则一直保持在50%左右,并未发生太大的变化,表明宁夏的居住建筑节能是建筑能耗节能中重中之重.
建筑供热能耗强度与建筑能耗强度对比关系随时间变化关系可参见图4.图4中对比建筑供热能耗强度与建筑能耗强度的变化值来表明两者的关系,如果建筑能耗强度与建筑供热能耗强度变化值为正值,则表明城镇居住建筑的供热能耗强度较小,若为负值则表明城镇居住建筑的供热能耗强度较大.图4中陕西、甘肃和宁夏的强度变化值一直为负值,且变化量的绝对值一直在减小,表明其城镇居住建筑随着时间的推移逐渐节能,但是仍然大于建筑能耗强度; 青海和新疆的强度变化值由负值变为正值,表明其城镇居住建筑供热能耗的强度正在逐渐降低,建筑节能的主体和重点则变为农村居住建筑和公共建筑.
图4 2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗与建筑能耗对比
Fig.4 Comparison of building heating energy consumption and building energy consumption of provinces and autonomous regions along “the Belt and Road” in Western China from 2010 to 2020
通过建筑能耗与建筑供热能耗的强度与总量对比分析可知,对于北方城市,供热能耗是建筑能耗中的重要组成部分,分析建筑供热能耗的时空分布和影响因素将是实现建筑节能过程中不可或缺的一步,而建筑能耗的市级数据由于缺失不能获取,因此,本文通过选取建筑供热能耗作为研究对象,为建筑节能提供新思路.
通过空间分析软件对西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗进行空间分析,获取建筑供热能耗的分布规律和特征,从而判断该地区的建筑供热能耗发展特征.
通过Arcgis10.5对西部“一带一路”沿线城市的2010—2020年建筑供热能耗数据进行可视化处理,获取其建筑供热能耗总量和强度的空间分布特征.本文通过对比逐年的建筑能耗特征选取出典型年份2010年、2014年、2017年和2020年进行分析,见图5和图6.
从图5中可见西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗总量随着时间的推移,建筑供热能耗总量的变化情况.其中,乌鲁木齐市在2014年建筑供热能耗总量达到了西部“一带一路”沿线城市的最高值; 陕西在2010年只有北侧城市的建筑供热总量处于中游水平,但随着年份的推移,陕西省城市的建筑能耗总量表现出整体的上升趋势,这与其城镇化进程的速度和经济发展存在着很大的关系[7].图中有一条明显的斜竖线贯穿中心,这主要是由于青海省城市存在较大的数据缺失,而周围已有的城市的数据又处于一个较高的水平,在采用克里金插值法进行空间分析时会利用算法将其进行数据补充,从而形成完整的空间分析,但这样分析也会导致一定的误差.
图5 2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗总量空间分布
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of total heating energy consumption of urban buildings along “the Belt and Road” in Western China from 2010 to 2020
图6 2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗强度空间分布
Fig.6 Spatial distribution of heating energy consumption intensity of urban buildings along “the Belt and Road” in Western China from 2010 to 2020
图6中可见随着时间的推移西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗强度的空间变化关系.新疆西部、青海、甘肃、宁夏在2010年为强度较高的主要区域,但随着时间的推移,强度较高的主要区域逐渐向着西部“一带一路”沿线城市的中心靠拢; 2014年强度较高区域主要集中在新疆的中部和东部、青海、甘肃、宁夏; 到2017年则主要集中在新疆北部、青海全域和宁夏的部分区域; 到2020年则变化更大,强度较大区域主要集中在新疆中部和小范围的青海和宁夏,其他区域城市的建筑供热能耗强度逐渐趋于持平.陕西省城市的建筑供热能耗总量在2010—2020年间虽有较大的增长,但是其供热能耗强度在西部“一带一路”沿线城市中一直处于较低的水平.
通过Geoda软件对西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗总量和强度是否存在空间效应进行验证,选取以Queen相邻原则建立不同城市之间的空间权重矩阵,测算了西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗的总量和强度的全局Moran's I指数,结果见表1.
表1 2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗Moran's I指数
Tab.1 Moran's I index of building heating energy consumption in cities along “the Belt and Road” in Western China from 2010 to 2020
由表1可知,2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗总量的全局Moran's I指数均为负值; 2010年、2013—2017年的P值大于0.1; Z值均大于-1.65,说明其不存在统计学意义.西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗总量的分布是分散的、随机的、独立的.究其原因是大城市存在辐射和吸收周边城市资源的现象,从而出现点状随机分布的大城市格局,不会出现明显的聚集现象,而且西北地区的经济发展较沿海地区较为落后,发展动力不足、起步晚等条件共同影响下导致其城市发展落后,大中型城市数量较少[8].2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗强度的全局Moran's I指数大多为正值; 2013年、2015—2019年的P值小于0.1; 2013年、2015年、2018—2020年的Z值大于1.65,具有统计学意义,说明其在90%的置信度下研究区域存在空间正自相关性.建筑供热能耗强度在空间分布上呈现出集聚现象.导致这样的结果是因为相互临近的城市其区域环境和资源条件相似,相同省份城市的建筑节能政策相差不大[2].观察建筑供热能耗强度的全局Moran's I指数变化可以发现,随着时间的推移,供热能耗强度的空间分布关系逐渐由分散转变为集聚.
由2.2.2中的全局空间自相关分析可知,西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗总量的分析结果不具有统计学意义,因此本文在局部空间自相关分析的过程中主要针对建筑供热能耗强度展开.在进行局部空间自相关性分析中选取Moran's I指数为正值的2013年、2016年、2018年、2020年来展开介绍.
图7为2013年、2016年、2018年和2020年这四个典型年份西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗强度的莫兰散点图以及其强度演化过程.莫兰散点图中位于不同象限的数据点代表不同含义,从图7中可以观测到,随着时间的推移,西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗强度虽然均为正相关,却由建筑供热能耗强度高的城市之间相邻逐渐向建筑供热能耗强度低的城市之间相邻演化,这是由于技术的进步和节能意识的增强,导致城市逐渐降低建筑供热能耗强度,出现较低供热能耗的城市之间相互毗邻的空间效应[2].对每个象限的城市进行了梳理,发现青海的城市一直存在建筑供热能耗强度高高相邻的现象,而陕西的大部分城市都存在建筑供热能耗强度低低相邻的现象,并且逐渐影响到周围城市,而其余省份城市在不同象限之间跳跃,表现出明显的空间差异化.从总体上而言,西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗强度表现出明显的空间效应,并且随着时间的推移空间效应逐渐增强,空间分布格局逐渐趋于稳定.
对西部“一带一路”沿线城市2010—2020年的建筑供热能耗进行重心演化足迹分析和标准差椭圆分析.
地理空间系统分析中的平均中心可以计算出研究区域中的密度中心,本研究通过将西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗强度和总量分别作为各市中心的权重,并通过此来求解2010—2020年建筑供热能耗强度和总量的平均中心,具体信息见图8.
由图8可知2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗总量重心一直都在甘肃省内,随着时间的推移其整体趋近于甘肃和青海的交界处,建筑供热能耗总量的重心整体向东南方向移动,且一直都位于西部“一带一路”沿线城市几何中心的东北侧.这是由于建筑供热能耗总量的统计中青海和新疆存在较多市级建筑供热能耗缺失,并且市域面积较大,而陕西省城市由于其经济发展水平较高,城市发展水平较新疆和青海的城市更高,并且建筑供热能耗的缺失也很少,进而导致建筑供热能耗的重心出现偏向陕西省.
由图8可知2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗强度重心一直都在甘肃省和青海省的交界处,相较于建筑供热能耗总量的变化规律,建筑供热能耗强度随着时间的推移,重心演化轨迹并没有明显的变化规律.导致这样的结果一方面是由于每年的建筑供热能耗统计的城市不尽相同,会存在个别的增加和减少,若这个值变化较大则会对强度的重心变化影响较大,另外一方面则是各城市的建筑供热能耗强度本身就存在较大的波动.建筑供热能耗强度的重心一直位于几何中心的东侧的原因与建筑供热能耗总量是一致的.
本文从空间形状、覆盖范围与方向趋势等角度定量描述西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗的总量和强度空间分布特征,并使得空间发展的演变过程可视化,为了方便表示,本研究选取了部分年份进行了绘制,如图8.
图8 2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗重心和标准差椭圆轨迹变化
Fig.8 Changes in the center of gravity and standard deviation ellipse of heating energy consumption of urban buildings along “the Belt and Road” in Western China from 2010 to 2020
图8(a)为西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗总量的标准差椭圆移动轨迹,可见其整体成西北—东南方向的空间分布,并且随着时间的推移逐渐向东南方向移动,运动轨迹相对规律,空间分布格局逐渐趋于稳定变化.从图中可以观察到其面积变化并未出现较大的波动,这说明西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗总量空间集聚效应正在逐渐加强.标准差椭圆随着时间推移的移动轨迹是由于在西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建设过程中,陕西省城市较其他地区城市城镇化进程和经济发展速度更快,从而使得轨迹逐渐向东南方向发生偏移,而青海省城市的发展相较于甘肃省落后,从而导致标准差椭圆的移动轨迹并不位于西部“一带一路”沿线城市的中心地带,而是几乎都集中在甘肃省.
图8(b)为西部“一带一路”沿线城市建筑供热能耗强度的标准差椭圆移动轨迹,可见其标准差椭圆也是呈现出西北—东南方向发展,但是相较于建筑供热能耗总量的轨迹偏斜角度更小一点.从2010—2020年中挑选了2010年、2013年、2018年、2020年作为典型年来分析其变化规律,可知其相较于建筑供热能耗总量而言变化规律并不明显,面积变化较大,同时沿x轴、y轴的标准差变化也较大.这说明就西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗强度仍处于发展变化的时期,空间分布较为分散,还未形成较为明显的变化规律.究其原因是因为相较于陕西省城市,其他地区城市建筑供热能耗强度都在变化的重要时期,虽然各省和自治区的城市建筑供热能耗强度都在降低,但是降低的幅度还是存在较大变化,这也是现阶段建筑供热能耗强度整体偏向陕西省的重要原因.
建筑供热能耗的总量和强度会受到政策引导、经济发展状况、产业结构、居民人口基数等诸多因素的共同干扰,这些因素之间存在着交互关系,并非相互独立.因此,本文选取2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗总量和强度作为被解释变量,以人口总数、城镇化率、人均供热面积、第三产业增长指数和技术创新水平作为解释变量纳入空间面板数据分析,来进一步量化这些因素对建筑供热能耗强度和总量的影响程度.本文所选取的变量及具体的说明见表2.
根据以上信息选取的建筑供热能耗强度和总量的解释变量,对STIRPAT模型进行改动,得到了建筑供热能耗总量和强度最终的分析模型分别为:
lnTE=alnP+blnU+clnS+dlnD+elnT+f (6)
lnEI=alnP+blnU+clnS+dlnD+elnT+f (7)
在对变量进行数据分析过程中,首先应选取线性回归的方式来验证各影响因素之间的共线性,从而选取计算分析的模型.本文选取SPSS软件对西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗及其影响因素进行分析.
本文选取了陕西建筑供热能耗强度和总量进行了线性回归的分析.人口总数、城镇化率、人均供热面积、第三产业增长指数、技术创新水平作为解释变量,而将建筑供热能耗强度作为被解释变量,R2为0.967,p为0.001(小于0.05),说明以上影响因素至少一项与建筑供热能耗强度产生了影响,但是由于模型中的方差膨胀因子(VIF)均大于10,说明存在着明显的共线性,因此线性回归分析方法并不适合作为分析模型.同样陕西建筑供热能耗总量受其影响因素的线性回归分析模型中也存在着同样的问题,由此以最小二乘法进行参数的无偏估计不适用于本研究中所考察的数据.
现有的研究中消除多重共线性的方法主要为岭回归分析法.岭回归分析法是一种专门用于共线性数据分析的有偏估计的改良最小二乘法,它可以使得接近真实值的可能性更大.因此,本文采用这种方法来分析解释变量和被解释变量之间的关系.
本文通过SPSS软件的语法进行岭回归分析,从而得到了西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗强度和总量的岭迹图,分析各省份及自治区的岭迹图的稳定区间,将k值设定为0.5,从而计算出了西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的岭回归计算结果,如表3所示.由表3可知西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗强度岭回归结果中陕西和新疆的R2都较大,p值小于0.05,因此可认为其具有统计学意义,被解释变量与解释变量在陕西和新疆存在着明显的影响关系.依此类推,被解释变量和解释变量在甘肃、宁夏和青海并不存在明显的影响关系.西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗总量岭回归分析结果中陕西和青海的被解释变量与解释变量存在着明显的影响关系; 甘肃、宁夏和新疆被解释变量和解释变量并不存在明显的影响关系.
在采用岭回归分析法对西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区建筑供热能耗强度和总量的分析中存在许多解释因素并没有很强的相关性,针对此问题,本研究通过采用逐步回归分析法来求取解释变量中与被解释变量之间存在更加密切的关联的变量.分析结果见表4.
由表4可见,西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗强度和总量的逐步回归分析结果中除甘肃建筑供热能耗总量无显著解释变量外p均小于0.05,说明具有统计学意义,所选取出来的解释变量对西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗强度和总量产生了影响.
表3 岭回归分析下西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区建筑供热能耗影响因素的权重分布
Tab.3 Weight distribution of factors influencing building heating energy consumption of provinces and autonomous regions along “the Belt and Road” in Western China under ridge regression analysis
通过SPSS软件对西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗进行了线性回归、岭回归和逐步回归分析,获取了其各因素的影响程度,具体的分析结果如下:
(1)从岭回归分析结果可知,陕西和青海的建筑供热能耗总量的主要影响因素均为人均供热面积,分别达到了22.4%和40.2%; 陕西建筑供热能耗强度的主要影响因素为人均供热面积,达到了-27.8%,新疆建筑供热能耗强度的主要影响因素为第三产业增长指数;
(2)通过逐步回归分析,获得了甘肃、青海和宁夏中对建筑供热能耗强度影响最大的因素为技术创新水平,均呈现负相关的关系,其中宁夏的影响程度最大,达到了91.1%.宁夏和新疆建筑供热能耗总量的影响因素中最大的为人均建筑供热面积,且宁夏较新疆的影响程度更大.
本文对2010—2020年西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗强度和总量进行统计与核算,通过空间相关性分析和空间计量分析,得到以下主要结论:
(1)从空间相关性特征来看,西部“一带一路”沿线城市的建筑供热能耗总量和强度都呈现出非均衡的空间分布特征,建筑供热能耗总量的空间分布呈现出大城市带动小城市发展的格局,建筑供热能耗强度呈现出空间正相关关系,其中陕西省城市表现较为明显,呈现出低低相邻格局,随着时间的推移相关性逐渐减弱,趋于平衡发展;
(2)从影响因素来看,西部“一带一路”沿线省份及自治区的建筑供热能耗总量的影响因素中,宁夏和新疆的主要驱动力为人均供热面积,其他因素影响并不大; 而陕西和青海的主要驱动力为人口总量、城镇化率、人均供热面积、第三产业增长指数以及技术创新水平,其中人均供热面积的影响权重最大.建筑供热能耗强度的影响因素中,甘肃、青海和宁夏的主要驱动力为技术创新水平,陕西和新疆的主要驱动力为人口总量、城镇化率、人均供热面积、第三产业增长指数以及技术创新水平,其中陕西和新疆的影响权重最大的因素为人均供热面积和第三产业增长指数.