2.1 模型结构
地震动衰减模型一般选用由震源项、几何扩散项和非弹性衰减项表示的数学模型.随着强震动数据的积累和对地震动认识的不断加深,衰减关系形式得到不断改进以反映更多的地震特性.本文参考美国NGA项目建立的地震动衰减关系模型,并结合本地区构造特征及场地条件特性对其进行适当修正,最终确定的地震动衰减关系表达式如下.
lnY=fmag+fdis+fsite+fhng+fflt (1)
式中:Y为地震动参数(PGA、PGV及加速度反应谱); fmag震级项; fdis表示距离项; fsite表示场地反应项,场地特征由地表30 m平均剪切波速VS30来表征; fflt表示断层类型项; fhng表示上盘效应项,上盘效应函数使用了NGA-West2项目中CB14模型的函数形式,但使用国内数据重新拟合了函数系数.
(1)震级项fmag
fmag=C1+C2M+C3(8.5-M)2 (2)
(2)距离项fdis
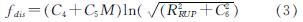
(3)场地反应项fsite
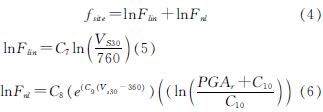

式中:RS和S为哑变量,分别表示逆断层(RS=1,S=0)和其它类型断层(RS=0,S=1); f1和f2为回归系数.
2.2 模型结果与对比分析
本文运用随机效应回归算法[21]计算模型系数,随机效应回归方法最大优点是根据产生的原因将残差分为了两部分,可以消除同一地震的各记录之间的相关性,避免记录数量相对较多的地震对衰减起控制作用.模型系数回归结果如表2所示.
将本文地震动衰减模型与NGA-West2项目中CB14模型[22]和BSSA14[23]模型进行对比,结果如图3所示.从图中可以看出,本文模型在T=0.05~1 s周期段显著高于NGA模型,在T<0.05 s和T>1 s周期段与NGA模型较为一致; 随着震级减小本文模型和NGA模型的预测偏差逐渐减小,当震级到6时,本文模型预测反应谱与NGA模型接近.
表2 地震动模型系数
Tab.2 Coefficient of ground motion model
图3 不同震级、场地条件下模型对比图
Fig.3 Comparison of models at different magnitudes and site
为了进一步验证本文模型的合理性,选取汶川Mw7.9、芦山Mw6.7、九寨沟Mw6.5、岷漳Mw6.0四个地震的强震动数据(123组断层距150 km以内强震记录)对本文模型进行验证,并与两种NGA模型预测结果进行对比.我们定义了一个能够反应多个衰减模型预测结果相对优劣的“地震动衰减模型与强震记录的匹配级数Ri”,以此来评估地震动衰减模型预测结果与台站记录的吻合度,方法如下.

式中,Dij是表示模型i与模型j评估结果相对优劣的指示变量,对于某个强震动台站.模型i预测结果与台站记录值的吻合度比模型j高(即模型i偏离度<模型j偏离度)时Dij为1,反之则为0,二者相等时为0,理论上二者相等的概率极低.Ri表示模型i依次与其他模型经过对比后得到的累计值,值越高,表示模型评估结果与台站记录越接近.
图4为三种模型与国内强震动记录的匹配度级数Ri随距离的分布.从图中可以看出,当周期T小于3 s时,本文模型在断层距大于100 km时预测效果要好于两种NGA模型,在断层距小于100 km时预测效果不如BSSA14模型,但好于CB14模型; 当周期T大于3 s时,本文模型预测效果整体好于两种NGA模型.整体来看,本文模型反应谱预测值与青藏高原东北缘地区强震记录的吻合度要好于NGA模型.
图4 模型匹配级数Ri随距离分布
Fig.4 Model ranks Ri versus distance bins