基金项目:国家自然科学基金(H872287); 中国博士后科学基金(2022M712495); 陕西省自然科学基础研究计划资助项目(2023-JC-QN-0451)
第一作者:邵珠山(1986—),男,博士,教授,主要从事微波辅助固体材料破碎方面研究.E-mail:shaozhushan@xauat.edu.cn
(School of Science, Xi'an Univ. of Arch. & Tech., Xi'an 710055, China)
microwave irradiation; granite; mineral composition; fracture toughness; thermal stress
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2023.03.001
硬岩破碎是建筑行业及地下工程开挖等项目中的重要环节,机械磨削是硬岩破碎过程中采用的主要技术,但机械磨削对机械结构损耗较大,不经济且耗时较长.因此劣化岩石性能,提高破岩效率,减小破岩过程中时间及能源的消耗成为硬岩破碎面临的热点问题[1-2].
岩石为典型的多项矿物材料,同时含有微波敏感矿物和非敏感矿物[3].在微波照射下,矿物微波敏感性的差异会使岩石内部产生不均匀温度场,诱发热应力,引起岩石内部裂纹的萌生及扩展[4],进而导致岩石性能的劣化.因此,微波辅助机械破岩技术成为近年来国内外广泛关注的新型破岩方法.
微波辅助破岩的热效率远远高于传统加热破岩的热效率.在微波辐射下,岩石的力学性能可显著降低.国内外的学者针对微波辐射下岩石物理及力学性能进行了大量的实验研究,包括微波照射下岩石强度[5]、断裂韧性[6,7]的变化规律,岩石的开裂行为[8]等等,也探究了岩石的含水量[9]在微波辐射下升温的差异,以及岩石对不同微波辐射频率响应的差异[10]等等.这些研究表明微波辐射热诱导岩石的裂解,降低岩石力学性能的机制依赖于矿物对微波热响应的差异[11].
对多种矿物在微波辐射下热现象的研究[12]表明:不同矿物对微波的响应存在差异,即矿物介电特性的差异导致岩石在微波辐射下不能实现均匀加热,进而造成岩石损伤[13-14].已有研究通过分析多种矿物在微波辐射下的升温速率,揭示了微波辐射下矿物的损伤机理[15].但目前多数研究是通过建立两相模型分析强微波响应矿物与弱微波响应矿物间的热应力[16],进一步分析该热应力诱发裂纹的能力; 或者根据各矿物的百分占比,生成随机矿物分布模型,对微波辐射下矿物的热响应进行分析[17].很少有文献根据岩石内部真实的矿物结构进行热应力场研究,并且针对热应力导致的裂纹扩展及性能劣化并未进一步分析.
本文以典型硬岩——花岗岩为研究对象,根据真实的矿物结构显微图像,建立多项矿物的二维模型,模拟微波辐射下的微波敏感矿物与非敏感矿物间的不均匀温度场及应力场,分析损伤演化规律,并结合裂纹扩展实验研究分析裂纹扩展行为.用断裂韧性描述花岗岩力学性能的劣化,解释断裂韧性劣化机理,并根据断裂韧性劣化规律的实验结果完善理论分析.
使用COMSOL软件,通过电磁加热、固体传热及固体力学三个模块的耦合,研究微波加热过程中矿物间的温度场、应力场以及损伤演化.
该模型对电磁-热-应力方程进行联合求解.麦克斯韦方程用于描述电磁传播,见式(1):
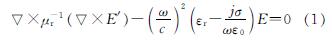
式中:μr为相对磁导率; E'为电场强度; εr为相对介电常数; j为虚单位; σ为导电性; ω为角频率; ε0为自由空间介电常数; c为真空中的光速.
微波加热产生的热量作为热源,如式(2):

式中:Pd为矿物的体积能量吸收密度; f是微波能量的频率; ε″是为矿物的介电损耗因子.其与矿物间的传热方程相耦合,不考虑传热过程中的流体对流项,传热的能量平衡方程,如式(3):
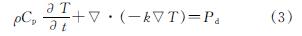
式中:ρ是样本密度; Cp为比热容; T为温度; Q为热源; k为导热系数.
矿物受热膨胀,诱发热应力,其热膨胀方程见式(4):
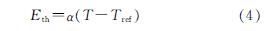
式中:Eth为弹性应变张量; α为热膨胀系数; Tref为应变参考温度(零应变温度).
破坏准则使用莫尔-库仑准则[17],当作用在材料中任何单元上的剪应力和正应力满足该式(5),就发生破坏.
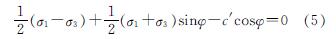
式中:σ1、σ3是矿物间第一和第三主应力; c'为黏聚力; φ为内摩擦角.
真实的矿物结构显微图像见图1,由石英、长石及黑云母构成.以此为基础,建立石英-长石-黑云母的多项矿物二维模型.黑云母为微波敏感矿物,石英为微波非敏感矿物,长石的微波敏感性略强于石英.矿物结构模型的生成过程见图1,具体流程如下:
(1)使用Image J开源软件结合真实的花岗岩矿物结构显微图像,获取矿物的不规则边界.
(2)使用MATLAB对上述矿物边界进行二值化处理,忽略矿物内部的细小裂纹,得到清晰的矿物轮廓,并将其置于AutoCAD中进行坐标重构.
(3)根据实验采用的花岗岩试件的真实尺寸,建立花岗岩二维模型,将AutoCAD重构后的矿物轮廓导入上述花岗岩试件的中,得到多项矿物二维模型.
使用矩形波导施加微波能量,建立微波加热的二维模型.矿物的热力学等参数见表1,其中Em为杨氏模量,v为泊松比,其余参数表示量同1.1小节.
表1 数值模型的热力学参数[18]
Table 1 Thermodynamic parameters of the numerical model[18]
微波辐射下,矿物温度梯度的演化过程见图3.在微波加热初期,各矿物间无明显的温度梯度,随着加热时间的延长,不同矿物间的温度梯度逐渐增大.
温度梯度的分布与矿物的种类及体积含量有关,温度梯度较大值点均位于矿物边界处,这是不同矿物的介电特性以及传热系数的差异造成的.在加热时间达到30 s时,温度梯度的最大值点出现在石英和狭窄长石接触的边界上.持续加热,黑云母周边的温度梯度开始变大,最大值点出现在黑云母的边界上.这是由于长石的介电损耗因子比石英高一个数量级,短暂加热后,长石在电场的影响下升温虽低于黑云母,但高于石英,而长石的传热系数小于黑云母,所以短时间内温度在小面积的长石内部积累,还没通过热传导传递给石英.故加热初期,石英和小面积长石接触的边界上温度梯度较高.随着加热时间的延长,矿物间的传导热通量稳定时,黑云母依靠较大的介电损耗因子,获得最大的温度,与石英和长石形成温差,进而黑云母周边的温度梯度开始变大.
为量化微波场下各矿物及其边界处的热响应,在矿物模型上选取一条同时涵盖长石-石英、石英-黑云母和黑云母-长石边界的测线(图4(a)),在测线上各矿物内部选取一个矿物点(图4(b)),绘制测线及矿物点的温度梯度随时间的变化曲线.
从图4(a)可以看出,微波辐射下,矿物各点的温度梯度不同且矿物边界处存在较大的温度梯度值.在721 s后,各点的温度梯度值基本稳定.这是因为随着微波辐射时间的延长,各矿物间的热传导更加充分,矿物间的温度梯度不再受微波辐射时间的影响.微波辐射下,矿物点的温梯度的先急速上升后趋于稳定(图4(b)),且长石和黑云母的温度梯度值相近,约为石英矿物的两倍.这是由于石英矿物对微波的敏感性最差,在微波辐射下响应较差.
图5为微波辐射20 s后的冯米塞斯应力图.可以发现,石英边界周边的等效应力较大.狭长分布的石英晶体边界处的等效应力最大值达到了11.43 MPa,而此时黑云母和长石边界附近的等效应力仅在3 MPa以下,约为石英边界处等效应力最大值的1/4.可见不同矿物边界处等效应力存在显著差异.此外,在大面积石英分布区域处,应力极小,可见损伤的发生不仅与矿物的性质有关,还与矿物分布的面积密切相关.同种矿物,狭窄面积处更易发生损伤.
从图5中高应力处的放大图可以看出,高应力区主要分布在石英和长石内部.黑云母内部的应力值较低,这是由于黑云母的弹性模量比石英和长石小很多,在相同的应变下,弹性模量越小,产生的应力越小.因此,即使黑云母的温度较高,产生的热膨胀略大,但内部的应力却比长石和石英小.可见矿物间的应力的发生不仅取决于温度梯度,也与矿物的弹性模量也有关.
为量化微波场下各矿物及边界处的应力变化,在矿物模型上选取一条测线及三个测点,见图6.可见微波加热时间越长,热应力越大,对岩石造成的损伤也就越大.从图6(a)可以看出,随着加热时间的延长,矿物边界处的应力差值会增大,将更有利于矿物的分离.石英与黑云母边界处的应力增长最快,石英与长石的边界处的应力增长次之.这与矿物的吸波性能及膨胀系数有关.从图6(b)可以看出,石英矿物中应力的生长速度远高于长石和黑云母,根据第四强度理论,当某一矿物的冯米塞斯应力大于其屈服应力时,认为该矿物进入塑性状态,有裂纹的萌生和扩展.由此可以判断石英矿物优先进入塑性阶段,石英与长石边界处优先发生损伤.
使用摩尔库伦准则判断矿物的损伤破坏,当作用在矿物中任何位置处的剪应力和正应力满足式(5),就认为其发生破坏.在此准则下绘制了图7所示微波辐射下矿物模型的损伤演变规律图,其中红色代表已经损伤区域.可见矿物破坏优先发生在矿物的边界处.在微波加热90 s时,石英的边界附近优先发生损伤,随后损伤开始在石英矿物的狭长区域及边界处发育.随着微波加热时间的不断延长,矿物的损伤面积逐渐扩大.
对照图8中不同微波辐射时间(0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30 min)下岩石的SEM图像,可以发现,随着微波辐射时间的延长,矿物的损伤破碎程度在不断增加,与图7中的矿物随时间的演化规律一致.
对比图8中的图片,可以看出矿物裂纹的密度和宽度都会随着加热时长的延长而增多.
图8(b)中的裂纹相对图8(a)有一定的闭合.短时间加热后,试件的强度可能有小幅上升.短期荷载可使得微观结构(裂缝和孔隙)改变.
图8(a)中没有大面积的条纹花样(图中单向箭头所指区域),随着微波辐射时间的延长,条纹花样的面积明显扩大,试件发生塑性形变,也表明矿物发生损伤.微波辐射时间为30 min时,条纹花样面积减少是由于试件内部微裂纹增多,导致条纹花样不再清晰.
断裂行为对脆性材料性能劣化评价具有重要意义[19-20],反映了材料容纳应力场的能力.采用公式(6)计算微波辐射后花岗岩的断裂韧度[20]:
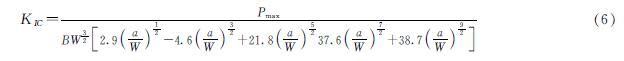
式中:Pmax为试件峰值载荷,W、B分别为试件的宽度和厚度,a为预制切口长度.图9为试件断裂韧度的折线图.
可见,在微波辐射下,试件的断裂韧性小幅度增加后持续下降.这是由于经过6 min微波辐射后,各矿物间热膨胀变形导致部分初始裂纹发生闭合,由图8(b)也可以看出6 min时岩石结构相对初始状态更加致密.当微波辐射时间达到24 min时,试件断裂韧性趋于稳定.在微波加热时间为24 min时,试件断裂韧度最小为23.31 MPa×mm1/2,低于未经过微波辐射试件断裂韧度均值的27.96%.可见,此时试件虽然未发生明显的宏观破坏,但是试件内部已产生较大程度的损伤.
基于岩石真实矿物结构建立数值模型,分析了在微波辐射下岩石内温度场和应力场的演化规律,并结合岩石断裂韧性劣化实验,分析了微波辐射时间对岩石断裂韧性的影响.得出以下结论:
(1)微波辐射下,在花岗岩试件发生宏观破坏前,断裂韧性下降将近28%.当照射时间较少时(≤6 min),矿物热膨胀会使部分初始裂纹闭合,导致岩石结构更加致密,使其断裂韧性小幅上升.随后持续增加照射时间,岩石断裂韧性则持续下降;
(2)微波辐射下,同一矿物不同边界的应力有很大差别,在狭长边界上易出现应力集中.石英(微波非敏感矿物)的边界处的应力大于黑云母-长石(微波较敏感矿物)边界处的应力.受弹性模量的影响,黑云母内部的应力最小,长石和石英会优先发生损伤;
(3)微波辐射下,花岗岩的升温速率随着照射时间的增加而减小.各矿物间的温度梯度在照射初期随时间增大而增大,到达一定程度后则进入相对稳定状态.