基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51678435,52078367)
第一作者:李 越(1993—),男,博士生,主要研究方向为桥梁混凝土多尺度建模与耐久性模拟.E-mail:yueli@tongji.edu.cn 通信作者:阮 欣(1977—),男,教授,博导,工学博士,主要研究方向为桥梁设计理论与长期性能.E-mail:ruanxin@tongji.edu.cn
(1.同济大学 土木工程学院,上海 200092; 2.工程结构性能演化与控制教育部重点实验室(同济大学),上海 200092; 3.扬州大学 建筑科学与工程学院,江苏 扬州 225127)
(1.College of Civil Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China; 2.Key Laboratory of Performance Evolution and Control for Engineering Structures (Ministry of Education), Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China; 3.College of Architecture Science and Engineering, Yangzhou University, Jiangsu Yangzhou 225127, China)
concrete carbonization; mass concrete; mesoscopic simulation; subtropical humid climate
DOI: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2023.04.004
混凝土结构作为基础设施建设的重要部分,长期服役中也面临环境作用导致的耐久性退化问题,其中最为常见的是碳化作用[1-3].大气环境中的二氧化碳向混凝土内部渗透扩散并与矿物水化产物发生反应,降低混凝土内部碱性水平,导致内部钢筋锈蚀失效、保护层开裂损伤,最终结构性能受此影响[4-5].在我国钢筋混凝土结构设计规范中,碳化问题也是耐久性设计关注的重点,但现行规范中将一般环境划分为干燥和干湿循环等情况的处理策略仍较为粗放[6-7].碳化过程中的混凝土内部水分物质传输和反应速率,受到环境温湿度影响显著,因此不同环境条件下结构碳化问题也存在较大差异,尤其是我国南方亚热带湿热环境下服役的基础设施结构[8].因此,能够考虑真实服役环境的复杂影响,建立精准描述结构碳化规律的预测方法,并分析潜在病害问题的空间分布和涌现时机,对于结构服役性能的保障和提升十分关键.
目前,在研究层面,混凝土碳化试验研究中已经关注到环境温湿度影响并开展相关参数讨论,但对比实际环境中日周期、年周期环境波动相比试验参数仍过于简单.因此,由试验研究得到的物理化学机理开展数值模拟研究逐渐吸引了工程研究者的关注[9-10].另一方面本世纪初我国建设的大量桥梁基础设施,在经历十余年服役后,局部病害问题逐渐暴露.而基于试验回归的碳化影响参数模型在面对实际退化空间涌现问题略显乏力,难以描述退化问题的随机空间分布,且局部碳化开裂损伤远早于设计预期.除了前述的环境输入简化,主流材料模型与实际混凝土内部颗粒空间随机分布也差异较大[11].近年来,在模型变异性方面,大量前沿研究工作也在陆续开展,多尺度模型[12-13]、贝叶斯更新模型[14-15]、人工神经网络模型[16]等模型和方法也逐渐被引入混凝土碳化问题分析中.但精细化材料研究成果在应用于工程结构分析中,庞大的数据模型和计算成本激增难以避免.因此,联结材料与结构多尺度研究并推广于工程应用仍较为棘手,平衡分析效率和精度也是目前混凝土结构耐久性研究的共性难题.
综合亚热带湿热环境特点、碳化作用物理化学机理以及基础设施大体积混凝土分析中多尺度计算瓶颈,本研究将架构材料碳化机理与结构局部退化之间的高效传递模型.模拟方法基于扩散路径映射(Diffusion Path Dependent Mapping)方法进行改进适用于大体积混凝土结构考虑精细环境参数的时程变化,实现工程结构细观碳化过程的精准高效仿真分析.研究依托我国东南省份某桥梁工程大体积混凝土锚碇结构开展模拟,基于气象数据细节,对长期服役过程中的碳化深度和钢筋锈蚀概率空间分布进行预测,且求解效率也大幅提升至工程应用可以接受的程度.最终结合具体工程养护策略,研究对工程案例防护措施的耐久性能提升影响进行评估,并为相关混凝土结构服役管养提供建议.
混凝土碳化模拟的策略与实际碳化反应过程是一致的,通过材料配比中矿物成分含量和可供反应消耗的水分分布计算构件内部水化产物的空间分布,再通过考虑大气环境的二氧化碳向内传输过程中接触的水化产物含量计算碳化反应影响.传统宏观模拟建立材料均匀化假定,考虑混凝土等效的均质材料内部水化和碳化效应,从而提供碳化作用的均值结论.细观模拟在宏观模拟的基础上引入夹杂颗粒的空间随机分布,采取更为复杂的网格划分,赋予骨料、水泥浆体和界面层不同的单元属性,最终得到带有概率信息的碳化作用预测结果.混凝土碳化作用在宏观和细观不同尺度上的机理和模拟策略在本质上没有区别,而细观求解效率方面的困境在于精细化网格划分后,大量用于描述模型几何特征的单元重复参与水化和碳化过程的迭代求解.
机理层面,混凝土水化与碳化作用机理如式(1)和式(2)所示,水化过程中矿物成分硅酸二钙、硅酸三钙、铝酸二钙以及铁铝酸四钙消耗孔隙水分形成水合硅酸钙、凝胶以及氢氧化钙晶体,碳化过程中大气环境中的二氧化碳扩散溶解于孔隙溶液,水化产物与孔隙溶液中的二氧化碳发生反应,生成碳化产物碳酸钙.其中反应原料中化学物质、水分和二氧化碳的空间浓度分布决定化学反应能否顺利进行,而具体水化和碳化反应速率也受到环境因素中温度和湿度的影响,根据Papadakis的水化动力学模型以及Henry定律中二氧化碳溶解平衡关系可以得到相关反应的消耗和产物的生成[17-18].
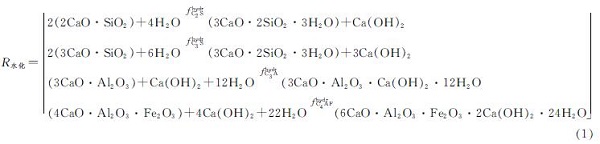
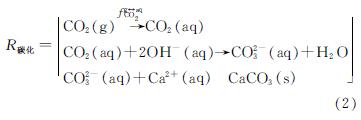
考虑到矿物成分、水化产物在混凝土内部不可移动,因此水化碳化过程的数值模拟主要考虑水分和二氧化碳的传输效应以及时变消耗关系.基于Fick扩散定律以及上述化学反应机理[12,19],可以建立数值求解方程(3)和方程(4).

式中:H和C分别为混凝土内部含水量和二氧化碳浓度; gH,水化和gH,碳化分别为水化过程水分消耗和碳化过程水分产生的时变函数; gC,碳化则为混凝土内部碳化反应的二氧化碳消耗函数.在细观数值模拟中,首先需要对模型单元按照骨料和水泥浆体位置进行区分,求解过程仅在水泥浆体域内进行求解.因此如图1所示,将细观几何特征影响与复杂化学机理求解过程进行分离,这也是本研究中扩散路径算法的核心逻辑.计算过程中单独提取由于颗粒阻碍效应在水泥浆体内部形成的扩散路径网络,再通过纯砂浆介质属性的代理模型计算复杂环境下碳化作用过程,最终将包括水化产物和二氧化碳浓度结果沿着扩散路径映射到细观模型中得到场域碳化结果.
扩散路径映射方法中的细观路径特征提取主要包含两个部分:细观几何建模和扩散路径计算.
基于Wang等[20-21]提出的随机骨料结构(Random Aggregate Structure, RAS)框架上,细观建模方法快速发展,不同模型的建模效率存在差异,适用的分析场景也存在不同.针对精细化骨料颗粒粒径、形状以及棱角细节的模拟场景,本研究采用多重抽样细观建模,其参数形式如式(5)所示[22].骨料几何特征由粒径D,长宽比β以及棱角细节T三个参数进行描述,各参数通过真实材料试块切割图像识别的方法得到概率分布函数.在考虑各粒径颗粒不同数量的情况下,不同粒径骨料的形状参数概率分布也有所区分,其中小颗粒骨料更易形成针片状细长碎石,而大颗粒骨料则容易形成卵圆形状骨料颗粒.实际建模中将骨料建模为多边形形状,通过形状缩放和轴向拉伸,达到所需的颗粒尺寸和长宽比.骨料空间分布参数由空间坐标X和主轴方位角θ进行表示,建模过程中骨料颗粒按照粒径从大到小的顺序逐个随机投放入模型空间,判断颗粒与模型边界以及已投放骨料是否冲突,直至所有颗粒投放进入模型空间,最终形成所需的混凝土细观模型[22].
SAgg={PAgg(D,β,T,X,θ)} (5)
式中:SAgg为骨料几何参数的集合; PAgg为单个骨料的特征参数集合包含的几何和位置信息.
在骨料几何特征明确后,模型内部物质最短路径扩散的过程则通过Dijkstra算法进行求解.混凝土细观扩散路径是指材料水泥浆体内部各节点到环境暴露表面的所需距离,受到不可渗透骨料介质空间随机分布的影响,实际物质传输扩散长度要略长于各点到暴露表面的直线距离.因此,该路径分布主要受到骨料颗粒的随机分布影响,是与时间无关的标量.Dijkstra算法是通过不断更新网络中两两节点之间的最短距离,以得到遍历全图的最短路径网络,较为常用的变体是设置部分“源”节点来计算网络所有其他节点到源头的最短路径树,这也是本研究中采用的计算方式[23].通过网格划分,将模型划分为适应于描述骨料几何棱角细节的单元尺寸,并基于节点和单元所处位置区分骨料节点、水泥浆体节点以及界面层节点; 扩散路径长度的计算更新主要基于Dijkstra最短路径算法,基于介质内物质主要沿最短路径向低浓度区域传输扩散的假定,将模型与外部环境直接接触的暴露边界设定为扩散起点,由表面向内遍历所有水泥浆体节点并对扩散路径长度进行更新,直至得到所有节点的最短路径长度场域分布.不同的骨料几何模型下,物质传输穿过水泥浆体的所需长度也存在较大差异,通过不同模型的路径计算则可以在物理层面考虑对应混凝土结构的局部抗侵蚀能力.由于界面层区域的孔隙率差异,其局部扩散属性容易形成物质扩散的快速通道,因此在路径计算过程中需要对界面层局部路径长度按照Dcm/DITZ进行修正,其中Dcm和DITZ分别为水泥浆体和界面层内的物质扩散系数.
代理模型的求解主要关注水泥浆体内部水化和碳化过程的物质传输迁移和化学反应变化,对水分和主要矿物成分、水化产物、碳化产物的空间分布进行建模,通过偏微分方程的逐时间步求解来考虑传输、产生和消耗.真实结构服役退化难以精准预测的关键在于边界环境的时变波动,诸如昼夜温差、潮汐干湿循环等,因此求解过程需要能够考虑并反映出环境参数波动的影响.传统模拟方法在面临结构尺度分析需求,或者精细化细观骨料描述的需要,大模型小网格带来计算效率的急剧下降.而本方法中代理模型则可以采用能够反映碳化深度方向影响的狭长模型,不必考虑细观特征的影响,也能够调大网格划分尺寸,带来计算成本的下降.模拟能力的提升则可以用于关注环境参数的时变波动变化,基于气象统计数据采用3小时一步的计算步骤,能够通过精细化的8个计算步来考虑服役过程中每一天的温湿度波动细节.面向结构百年服役过程的代理模型通过292 000步求解,能够精细考虑昼夜温差、季节温差以及湿度变化的复杂影响.
随着长期服役过程中碳化作用的影响加深,大体积混凝土结构表面和内部的碱性环境被逐渐削弱,进而造成钢筋表面中性化脱钝锈蚀,其对应的关键指标是氢氧化钙浓度的下降.因此,对代理模型各时间步中氢氧化钙浓度随深度变化进行统计,并将结果按照对应的扩散路径长度映射到混凝土细观路径网络中,则可以得到混凝土内部关键物质的细观浓度分布.其中,由于骨料颗粒随机分布和棱角细节影响,同样服役条件下碳化作用的影响范围也存在较大差异,结合具体工程需求则可以得到结构耐久性退化整体水平和随机特性.
本文选取了广州地区某大跨径斜拉桥锚碇结构开展碳化作用分析,锚碇结构平面尺寸73 m×73 m,地面以上部分高度47 m,地下埋置深度36 m以上,整体布置如图2所示.
锚碇结构包含锚固系统和混凝土锚体两部分,其中锚固系统包括核心区域拉杆、连接器、预应力钢束和管道、预应力锚具以及锚头防护等组件; 而锚体结构则包括锚块、散索鞍支墩及底板、前锚室、后浇段.锚体结构地上部分在长期服役过程中暴露于桥址大气环境,在混凝土浇筑施工完成后,大气二氧化碳侵入造成表面碳化作用影响.考虑到锚碇结构表面积大,碳化作用病害的空间分布随机性强,造成病害问题较为隐蔽且爆发时机难以预测,因此有必要针对锚碇结构各关键局部开展相关碳化作用模拟和服役性能分析.
桥址地区属亚热带季风气候,年平均气温22 ℃,夏季最热月份为七月份,平均28.5 ℃,日最高气温≥35 ℃的天数为10 d,极端最高气温38.7 ℃; 冬季1月份最冷,平均气温13.6 ℃,极端最低气温在0 ℃.多年平均降雨量1 694~1 726 mm,最大降雨量2 517 mm; 最少降雨量1 243 mm.雨日在150 d以上,日降雨量≥80 mm的天数为3 d.暴雨较集中的月份为5~9月份.连续降雨天数为20 d,一般出现在6~7月份.基于桥址周边气象站实测数据,可以得到环境温度和湿度时变结果如图3所示,数据频率为3小时1次,温度数据精度0.1 ℃,湿度数据精度1%.从图中数据可以看出桥址亚热带湿热环境的特点显著,环境温度季节温差明显,夏季温度主要波动于25~35 ℃,冬季温度波动于5~25 ℃温差波动更为显著,季节之间过渡过程中短周期的升温和降温剧烈波动也较为显著且复杂; 环境湿度则一直保持相对较高的水平,全年大部分时间湿度维持于60%以上,冬夏季节湿度较高且稳定,而在春秋季节中温度剧烈变化过程也常伴随着湿度的短期下降,最低湿度约为35%.由此可见亚热带地区气候条件特殊,对于混凝土碳化作用等耐久性温度发展的影响较为复杂,有必要采用合适的模拟分析方法,用以预测环境波动下结构服役退化过程规律.
基于前述扩散路径映射方法求解策略,针对锚碇结构开展关键截面细观建模与碳化作用代理模型求解.选择锚碇表面与角隅区域共计6处关键局部,分别建立平均宽度600 mm、深度200 mm的混凝土细观模型,如图4左侧所示.针对锚碇结构混凝土材料配合比设计,考虑到骨料含量46.9%,模拟骨料级配为经典Fuller级配中1.0~25.0 mm粒径范围,骨料具体形状建模方面采用多边形碎石骨料模型,单个局部细观模型中投放骨料5 000颗左右.为了能够较为精准地描述各粒径尺寸下骨料颗粒形状与棱角细节,扩散路径计算精度达到0.1 mm,网格单元数量达到107量级.针对结构细观模型的深度,代理模型建模尺寸为20.0 mm×200.0 mm,模型单元的化学属性设置为考虑界面层效应的水泥浆体材料.考虑到结构服役的亚热带湿热气候的复杂影响,本研究代理模型求解中采用3 h的标准计算步时长,环境边界的温度、湿度和大气二氧化碳浓度也采用气象站实测数据进行输入.通过细观路径计算考虑骨料颗粒对于迂曲扩散路径的影响,由于材料内部非均匀性与时间无关所以扩散路径仅需单次求解,而真实服役的碳化过程则通过代理模型的传统偏微分方程进行求解.代理模型尺寸20.0mm×200.0mm,网格尺寸5.0mm,得益于小模型和大网格,对百年服役按照3小时一步进行求解分析,292 000步骤,计算耗时约15分钟,对氢氧化钙的时变浓度-深度数据进行存储,数据体积100KB以内,可见该方法在求解效率和存储空间方面优势显著.代理模型求解结果如图4右侧所示.选取氢氧化钙浓度作为材料局部碱性的判断依据,其中较浅的黄色区域为碳化作用影响范围,而较深的蓝色区域为未受碳化影响的区域范围.随着结构百年服役过程中碳化作用在水泥浆体中逐步侵入,碳化早期侵入速率较快,深度达到20 mm左右,服役百年后水泥浆体内碳化深度约为60 mm.
将长期服役下水泥浆体内部碳化作用模拟结果,映射于锚碇截面关键局部细观扩散路径网络,可以得到不同位置、角隅区域的碳化作用分布情况,如图5所示.模拟结果表明锚碇结构长期服役过程中,环境二氧化碳侵入与材料内部水化产物发生化学反应,造成由暴露表面向内的碱性下降.碳化作用影响范围随服役时间增长而不断扩大,在服役百年后锚碇结构一般区域平均碳化深度达到50 mm左右,而在角隅区域由于两段暴露边界的向内传输共同作用,碳化深度略有增大,总体差异并不显著.但基于本方法中细观扩散路径场的计算,骨料颗粒随机分布对于碳化作用空间分布的复杂影响也得到充分考虑,不同骨料颗粒粒径、形状、棱角分布对碳化作用的扩散影响形成阻碍,这也是结构与纯水泥浆体代理模型差异的关键所在.综上,基于扩散路径映射方法,能够得到锚碇结构在亚热带湿热环境服役的碳化作用细观尺度分布,也可以为后续保护层厚度下钢筋局部锈蚀概率以及结构耐久性能演化分析提供量化依据.
图4 锚碇结构关键截面建模与代理模型求解
Fig.4 Modeling of key section of anchorage structure and solving of surrogate model
图5 锚碇结构长期服役碳化作用映射结果
Fig.5 Mapping results of carbonation effect of anchorage structure in long-term service
为了对比分析亚热带湿热环境对于结构碳化的具体影响,以及材料精细化模拟的差异,研究针对锚碇截面关键局部开展简化模拟分析,材料属性采用均质化混凝土物理化学属性,环境边界温湿度按照实测数据年平均数值进行取值,其中温度19.89 ℃湿度81.80%,得到对应的局部碳化模拟结果如图6所示.对比结果表明,采用均质化材料模型中碳化作用从暴露表面均匀向内侵入,各局部位置碳化深度一致与细观模拟结果差异显著; 采用年平均温湿度环境条件输入后,碳化作用在高温干湿交替影响下的加速侵入难以考虑,整体碳化深度略小于复杂环境工况.从右侧模拟结果局部对比可以发现,考虑材料和环境复杂影响下的截面碳化分布复杂,更加接近真实混凝土碳化作用情况,采取扩散路径映射方法在碳化模拟效果方面优势显著.
基于图6中锚碇结构在亚热带湿热环境下碳化作用随服役时间变化规律,为比较分析精细化气候环境模拟对于结构碳化的具体影响,因此,本研究将背景工程服役碳化过程与忽略气候特征的简化模型进行对比.对比研究中针对百年服役采用的292 000计算步骤(8步/d×365 d/a×100 a服役)中每步温湿度更新输入,简化模型中采用年平均温度和年平均湿度进行输入,而模型其余方面设定均与前述模型保持一致,求解得到对应碳化作用影响.对平均碳化深度、95%分位深度以及深度标准差进行统计分析如表1所示,结果表明考虑湿热环境影响下的锚碇结构碳化深度的平均值、极值以及变异性均略高于简化模型计算结果,偏差水平约为3.7%左右.通过量化统计结果可以发现,采用考虑日周期、年周期的环境时变输入能够较好地反映结构真实退化过程,而采用简化模拟的环境年平均水平输入策略则会忽视温差和湿度波动对于碳化作用的加速和减缓效果,最终结果中对于碳化深度的预测结果略低也会导致低估碳化对结构性能影响的风险,因此有必要在结构碳化仿真分析中考虑具体服役环境气候和时变特征.
图6 亚热带湿热环境碳化作用细观模拟与简化模拟结果差异
Fig.6 Differences in results of mesoscopic simulation and simplified simulation of carbonization in subtropical humid environment
表1 考虑亚热带气候影响与简化环境输入的碳化深度差异
Tab.1 Difference of carbonization depth considering influence of subtropical environment and simplified environment state
得益于扩散路径映射方法在复杂服役环境方面的模拟精度,在大体积锚碇结构关键局部碳化作用模拟的基础上,可以针对耐久性能防护措施效果开展精细化研究分析.考虑到锚碇结构耐久性能保障和提升的主要策略是通过防护涂层、添加剂等形式封闭阻断环境物质侵入和改良材料自身抗渗透能力,其中涂层防护方法成熟高效,且在长期服役管养维护方面相对便捷经济.混凝土结构涂层防护是通过隔绝混凝土暴露表面的环境物质侵入实现耐久性能提升,考虑到桥梁建成开通于2008年12月,距今服役已有14 a,因此本研究也考虑了无防护碳化、建成10 a后防护和建成后立即防护三种工况进行对比,也能够为类似工程的新建桥梁防护方案制定和在役桥梁耐久性能提升提供支撑.
图8 桥梁锚碇结构涂层防护过程(摄于2020年10月)
Fig.8 Coating protection process of bridge anchorage structure(taken in October 2020)
不同防护方案下锚碇结构长期服役碳化作用如图9所示,模拟结果表明考虑涂层防护后锚碇结构百年服役碳化作用影响深度大幅减少,碳化深度缩短一半以上.
对比无防护方案下碳化深度50 mm以上,服役10 a后采取涂层防护的方案,尽管在服役早期10 a内碳化深度达到22 mm左右,但得益于涂层隔绝二氧化碳输入,后续服役的90 a内碳化深度仅仅向内侵入2 mm,可以结构服役早期的耐久性能防护措施能够及时杜绝继续退化问题.而对比服役后立即采用涂层隔绝的防护方案效果,后者防护效果更为显著,新建结构早期快速退化过程被及时避免,结构百年服役内总体碳化深度不足20 mm.结合本方法细观模拟结果,骨料颗粒随机分布影响也十分显著,临近结构表面的大颗粒骨料对于碳化过程的阻碍效应显著,大颗粒骨料和狭窄间隙下方能够看到碳化影响区域的缺口; 而大颗粒缺失小颗粒聚集的局部,水分和环境物质的传输扩散通道畅通,该局部碳化影响的范围也更深,容易形成钢筋锈蚀和耐久性退化的薄弱位置.
基于锚碇截面细观模拟能够获得碳化作用影响区域的空间分布,以及随时间变化的结构服役不同阶段碳化区域发展规律,但与结构整体耐久性能演化和对应的不确定性概率仍有差距.因此可以将氢氧化钙浓度骤降的临界区域作为碳化锋面位置,提取考虑细观材料特性的碳化深度概率分布情况,并深入对比不同防护措施对于碳化深度的量化影响.因此得到具体各个防护方案下锚碇截面百年服役后碳化深度概率密度分布如图 10所示,其对应的相关统计量化指标数值如表2所示.图中黄色分布为无防护方案,绿色分布为服役10后采取涂层防护方案,蓝色分布为服役初始即采用涂层防护方案.结果表明自然服役无防护方案下碳化平均深度最深达53.43 mm,变异性更大,考虑到常规锚碇结构50 mm左右的净保护层厚度,钢筋表面受碳化区域达到90%左右,存在表层钢筋大面积脱钝锈蚀风险,有必要采取合适的耐久性能保障措施进行防护; 而在服役10 a相对较短的时间内进行涂层防护,虽然错过了早期快速碳化防护的关键阶段,但后续阻断环境物质侵入,碳化深度也得以控制,平均深度24.45 mm最大深度也不超过26.90 mm,在保障涂层防护完好的前提下能够有效降低百年服役期间耐久性能退化病害风险; 显然在新建结构服役初始阶段采取必要的防护措施能够达到较好的防护效果,百年服役碳化深度极值降低至20 mm左右.
图 10 不同防护方案下锚碇碳化深度概率密度分布
Fig.10 Probability density distribution of anchorage carbonization depth under different protection schemes
表2 不同防护方案下锚碇碳化深度统计
Tab.2 Statistics of carbonation depth of anchorage under different protection schemes
从碳化深度变异性的角度,细观方法通过考虑材料内部组分的不均匀性来反映出耐久性退化的不确定性,这也揭示出以碳化作用为代表的耐久性退化存在显著的空间变异性,传统数值模拟均质化假定得到的平均退化程度与实际局部极值仍存在差异,如分析结果中碳化深度平均值与5%分位数差值接近5 mm.实际退化过程不同于结构整体的均匀退化,往往会表现出早期局部退化随机涌现和后期病害大规模爆发的情况,且退化时机早于传统预测结果中的均值失效.由此可见,结合细观尺度模型的扩散路径映射方法能够揭示大体积混凝土结构复杂服役环境下退化的空间随机分布,也具备支撑工程耐久性能演化概率分析的潜力.
碳化作用是大体积混凝土基础设施在长期服役过程中最为常见的耐久性退化问题,亚热带湿热环境中碳化问题更为显著,有必要开展模拟预测和量化分析.本研究提出适用于复杂服役环境下大体积混凝土结构碳化分析的扩散路径映射方法,研究依托我国东南沿海地区某桥梁锚碇结构开展细观碳化分析,对长期服役过程碳化深度和钢筋锈蚀概率特征进行预测,求解效率和精度均实现大幅提升,可以总结为以下结论:
(1)在亚热带湿热环境大体积混凝土构件碳化作用模拟中,材料内部组分不均匀分布和环境温湿度时变波动,与结构退化空间分布以及时间随机涌现紧密关联.通过采用基于扩散路径映射的细观碳化模拟方法,能够保持100 μm网格划分和3 h时间步的精度下,完成构件百年服役求解.其中精细化模型路径求解可以充分考虑1~25 mm粒径范围内骨料级配、形状、棱角细节对于局部碳化的复杂效应,百年服役中每天8计算步的环境边界时变输入也能够较为精准反映湿热环境下温湿度昼夜波动、季节波动等对于碳化进程的影响;
(2)选取锚碇截面6个关键局部开展细观建模,单个模型内部骨料颗粒数量约5 000颗粒,网格单元数量达到107量级; 代理模型基于桥址周边气象站实测数据进行环境边界建模.模拟结果表明锚碇结构百年服役中一般区域碳化深度达到50 mm左右.通过将亚热带湿热环境碳化细观模拟结果与材料环境简化模型进行对比,模拟结果在碳化深度整体水平和变异性存在差异,精细化材料建模和环境边界模拟十分必要;
(3)针对耐久性能防护措施效果开展精细化研究分析,模拟结果表明,服役10 a后采取涂层防护的方案,可以将无防护状态下百年服役50 mm以上的碳化深度降低至24 mm左右,而服役后立即采用涂层隔绝的防护方案效果更为显著,平均碳化深度18.05 mm变异性也更小.基于对比分析,对于现役时间不长的大型混凝土基础设施采取必要的防护方案十分必要;
(4)研究通过桥梁锚碇结构案例论证了该方法在求解效率和模拟效果方面的优势,研究结论为结构早期退化随机涌现和后期病害整体爆发的性能突变提供量化支撑.在后续研究中,将该方法迁移至相关耐久性问题数值模拟,能够为大型混凝土结构服役灾变演化预测提供依据,也能够为基础设施耐久性与韧性提升提供支撑.